Mystery Number!
... Third round: I’m thinking of an odd number between 7 and 19. The number has 2 digits. It can be divided into three equal groups. What’s the number? ...
... Third round: I’m thinking of an odd number between 7 and 19. The number has 2 digits. It can be divided into three equal groups. What’s the number? ...
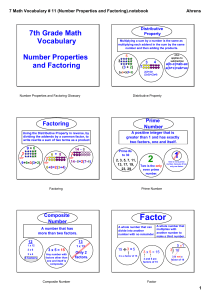
numbers and the number system
... • Which numbers less than 100 have exactly three factors? • What number up to 100 has the most factors? • Find some prime numbers which, when their digits are reversed, are also prime. • There are 10 two-digit prime numbers that can be written as the sum of two square numbers. What are they? • Write ...
... • Which numbers less than 100 have exactly three factors? • What number up to 100 has the most factors? • Find some prime numbers which, when their digits are reversed, are also prime. • There are 10 two-digit prime numbers that can be written as the sum of two square numbers. What are they? • Write ...
Discovering Composite and Prime Numbers Fourth Grade/60
... 5. Which numbers have more than one color circled around them? 6. Are there some numbers that have many colors around them? 7. What do you notice about any patters with these circled numbers? 8. Are these circled numbers odd or even? 9. Are there any numbers that have no circles around them? 10. Wha ...
... 5. Which numbers have more than one color circled around them? 6. Are there some numbers that have many colors around them? 7. What do you notice about any patters with these circled numbers? 8. Are these circled numbers odd or even? 9. Are there any numbers that have no circles around them? 10. Wha ...
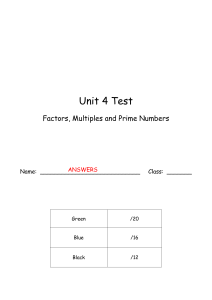
Unit 4 Test Factors, Multiples and Prime Numbers Name: Class
... swims every 4th day. If they all swam after school on Monday, after how many days will they all swim at the same time? What day of the week will that be? (3 marks) LCM of 2, 3 and 4 = 12 (1 mark) 12 Days later (1 mark) Wednesday (1 mark) 6) An odd number between 90 and 110 has exactly three differen ...
... swims every 4th day. If they all swam after school on Monday, after how many days will they all swim at the same time? What day of the week will that be? (3 marks) LCM of 2, 3 and 4 = 12 (1 mark) 12 Days later (1 mark) Wednesday (1 mark) 6) An odd number between 90 and 110 has exactly three differen ...
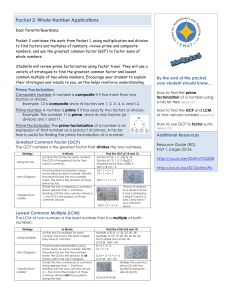
Least Common Multiple
... In the Real World Ferry Boats Two ferry boats leave a loading platform at the same time. One of the ferry boats returns to the loading platform every 25 minutes. The other returns every 30 minutes. In the next 300 minutes, when will they return at the same time? You can use multiples to answer the q ...
... In the Real World Ferry Boats Two ferry boats leave a loading platform at the same time. One of the ferry boats returns to the loading platform every 25 minutes. The other returns every 30 minutes. In the next 300 minutes, when will they return at the same time? You can use multiples to answer the q ...
Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
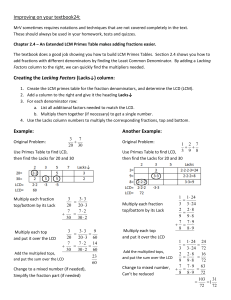
... are smaller it is easiest to list out the factors of each number and look for the biggest one that they have in common. 1. List the factors of each number. 2. Find the greatest factor that they have in common. EXAMPLE: Find the GCF of 24 and 30. 24: The factors are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24 30: The f ...
... are smaller it is easiest to list out the factors of each number and look for the biggest one that they have in common. 1. List the factors of each number. 2. Find the greatest factor that they have in common. EXAMPLE: Find the GCF of 24 and 30. 24: The factors are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24 30: The f ...
Sieve of Eratosthenes

In mathematics, the sieve of Eratosthenes (Ancient Greek: κόσκινον Ἐρατοσθένους, kóskinon Eratosthénous), one of a number of prime number sieves, is a simple, ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to any given limit. It does so by iteratively marking as composite (i.e., not prime) the multiples of each prime, starting with the multiples of 2.The multiples of a given prime are generated as a sequence of numbers starting from that prime, with constant difference between them that is equal to that prime. This is the sieve's key distinction from using trial division to sequentially test each candidate number for divisibility by each prime.The sieve of Eratosthenes is one of the most efficient ways to find all of the smaller primes. It is named after Eratosthenes of Cyrene, a Greek mathematician; although none of his works have survived, the sieve was described and attributed to Eratosthenes in the Introduction to Arithmetic by Nicomachus.The sieve may be used to find primes in arithmetic progressions.