Computational Thinking: A Necessary Subject in Education Walter
... wu=sqrt(n); % upper bound for k=p % for all primes in list if k>wu, break,end % which are < sqrt(n) prim=rem(n,k)~=0; % test remainder if ~prim, break, end % exit loop if not prime end if prim, p=[p,n]; end % store if prime end hm=length(p); % length of list ...
... wu=sqrt(n); % upper bound for k=p % for all primes in list if k>wu, break,end % which are < sqrt(n) prim=rem(n,k)~=0; % test remainder if ~prim, break, end % exit loop if not prime end if prim, p=[p,n]; end % store if prime end hm=length(p); % length of list ...
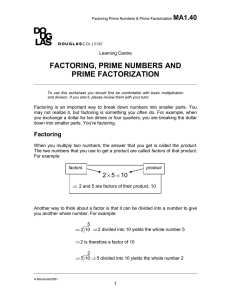
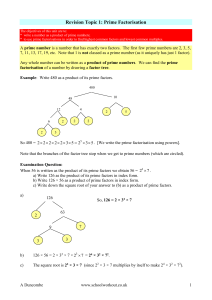
factoring, prime numbers and prime factorization
... To use this worksheet you should first be comfortable with basic multiplication and division. If you aren’t, please review them with your tutor. ...
... To use this worksheet you should first be comfortable with basic multiplication and division. If you aren’t, please review them with your tutor. ...
Partial-Quotient Division Algorithm
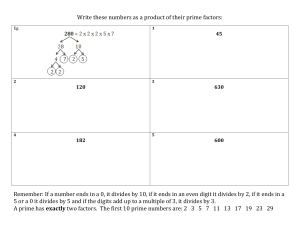
... -Are there at least 10 (7s) in 127? ______________________________________________ -Are there at least 20 (7s) in 127? ______________________________________________ -10 (7s) = 70 is the closest to 127 without going over 4) Find out how much is left to divide. Subtract 70 from 127. 5) Now find the n ...
... -Are there at least 10 (7s) in 127? ______________________________________________ -Are there at least 20 (7s) in 127? ______________________________________________ -10 (7s) = 70 is the closest to 127 without going over 4) Find out how much is left to divide. Subtract 70 from 127. 5) Now find the n ...
CS-4620 Functional Programming I 2012-2013
... The list of tuples of distinct items and their frequencies in list ‘xs’. frequencies "mississippi" ⇒ [ ( 'm', 1 ), ( 'i', 4 ), ( 's', 4 ), ( 'p', 2 ) ] ...
... The list of tuples of distinct items and their frequencies in list ‘xs’. frequencies "mississippi" ⇒ [ ( 'm', 1 ), ( 'i', 4 ), ( 's', 4 ), ( 'p', 2 ) ] ...
Exponents and Square Numbers
... would earn for washing 11 plates? How many pennies would he earn for washing 11 plates? ...
... would earn for washing 11 plates? How many pennies would he earn for washing 11 plates? ...
Parallel Programming in C with the Message Passing Interface
... Sequential algorithm Sources of parallelism Data decomposition options Parallel algorithm development, analysis MPI program Benchmarking Optimizations ...
... Sequential algorithm Sources of parallelism Data decomposition options Parallel algorithm development, analysis MPI program Benchmarking Optimizations ...
Sieve of Eratosthenes

In mathematics, the sieve of Eratosthenes (Ancient Greek: κόσκινον Ἐρατοσθένους, kóskinon Eratosthénous), one of a number of prime number sieves, is a simple, ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to any given limit. It does so by iteratively marking as composite (i.e., not prime) the multiples of each prime, starting with the multiples of 2.The multiples of a given prime are generated as a sequence of numbers starting from that prime, with constant difference between them that is equal to that prime. This is the sieve's key distinction from using trial division to sequentially test each candidate number for divisibility by each prime.The sieve of Eratosthenes is one of the most efficient ways to find all of the smaller primes. It is named after Eratosthenes of Cyrene, a Greek mathematician; although none of his works have survived, the sieve was described and attributed to Eratosthenes in the Introduction to Arithmetic by Nicomachus.The sieve may be used to find primes in arithmetic progressions.