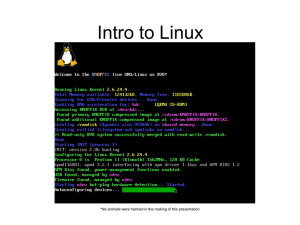
Lecture 22 File-System Interface
... collection of similar records treated as a single entity have unique file names may restrict access ...
... collection of similar records treated as a single entity have unique file names may restrict access ...
CS 620 Comparative Operating Systems Interfaces
... Network Operating Systems A situation like this, where each machine has a high degree of autonomy and there are few system-wide requirements is known as a network operating system. It is apparent to the users such a system consists of numerous computers. • There is no coordination among the com ...
... Network Operating Systems A situation like this, where each machine has a high degree of autonomy and there are few system-wide requirements is known as a network operating system. It is apparent to the users such a system consists of numerous computers. • There is no coordination among the com ...
CS 620 Comparative Operating Systems Interfaces
... Network Operating Systems A situation like this, where each machine has a high degree of autonomy and there are few system-wide requirements is known as a network operating system. It is apparent to the users such a system consists of numerous computers. • There is no coordination among the com ...
... Network Operating Systems A situation like this, where each machine has a high degree of autonomy and there are few system-wide requirements is known as a network operating system. It is apparent to the users such a system consists of numerous computers. • There is no coordination among the com ...
Introduction
... Personal computer operating systems Real-time operating systems Embedded operating systems Smart card operating systems ...
... Personal computer operating systems Real-time operating systems Embedded operating systems Smart card operating systems ...
Architectural support for OS
... Switches the sp to the kernel stack Saves the old (user) SP value Saves the old (user) PC value Saves the old privilege mode Saves cause of the interrupt/exception Sets the new privilege mode to 1 Sets the new PC to the kernel interrupt/exception handler ...
... Switches the sp to the kernel stack Saves the old (user) SP value Saves the old (user) PC value Saves the old privilege mode Saves cause of the interrupt/exception Sets the new privilege mode to 1 Sets the new PC to the kernel interrupt/exception handler ...
Architectural Support for Operating Systems
... Switches the sp to the kernel stack Saves the old (user) SP value Saves the old (user) PC value Saves the old privilege mode Saves cause of the interrupt/exception Sets the new privilege mode to 1 Sets the new PC to the kernel interrupt/exception handler ...
... Switches the sp to the kernel stack Saves the old (user) SP value Saves the old (user) PC value Saves the old privilege mode Saves cause of the interrupt/exception Sets the new privilege mode to 1 Sets the new PC to the kernel interrupt/exception handler ...
Multiuser Systems
... that can progress. Some operating systems allow only non preemptable processes, which means that the scheduler is invoked only when a process voluntarily relinquishes the CPU. But processes of a multiuser system must be preemptable; the operating system tracks how long each process holds the CPU and ...
... that can progress. Some operating systems allow only non preemptable processes, which means that the scheduler is invoked only when a process voluntarily relinquishes the CPU. But processes of a multiuser system must be preemptable; the operating system tracks how long each process holds the CPU and ...
Section for Related Work % \section{Related Work} Rootkit detection
... (DMA). It is known that a kernel function, \_\_generic\_copy\_from\_user actually copies data from user space to a location in the kernel on Linux. Rhee et al. propose monitoring kernel functions to ensure that DMA is not performed on protected kernel structures \cite{rhee2009defeating}. The problem ...
... (DMA). It is known that a kernel function, \_\_generic\_copy\_from\_user actually copies data from user space to a location in the kernel on Linux. Rhee et al. propose monitoring kernel functions to ensure that DMA is not performed on protected kernel structures \cite{rhee2009defeating}. The problem ...
Basic Operating System Concepts
... and starts executing it. When that job needs to wait for some event the CPU is switched to another job. Primary objective: eliminate CPU idle time Time sharing: An extension of multiprogramming. After a certain amount of time the CPU is switched to another job regardless of whether the process/threa ...
... and starts executing it. When that job needs to wait for some event the CPU is switched to another job. Primary objective: eliminate CPU idle time Time sharing: An extension of multiprogramming. After a certain amount of time the CPU is switched to another job regardless of whether the process/threa ...
process
... • Process management is the task of shepherding programs through the OS gauntlet. • In process management there are several issues we need to deal with: – What is the basic entity involved (i.e., the units of execution) – How are those entities represented in the OS – How is work scheduled in the CP ...
... • Process management is the task of shepherding programs through the OS gauntlet. • In process management there are several issues we need to deal with: – What is the basic entity involved (i.e., the units of execution) – How are those entities represented in the OS – How is work scheduled in the CP ...
Chapter 6-OS - WordPress.com
... individual teachers. It may not be included in any product or employed in any service without the written permission of the authors. ...
... individual teachers. It may not be included in any product or employed in any service without the written permission of the authors. ...
Figure 15.1 A distributed multimedia system
... individual teachers. It may not be included in any product or employed in any service without the written permission of the authors. ...
... individual teachers. It may not be included in any product or employed in any service without the written permission of the authors. ...
Windows Kernel Internals Overview
... Overview, kernel extensions, I/O drivers, WDF Object manager, LPC, Processes & Threads ...
... Overview, kernel extensions, I/O drivers, WDF Object manager, LPC, Processes & Threads ...
Windows Kernel Internals Overview
... Overview, kernel extensions, I/O drivers, WDF Object manager, LPC, Processes & Threads ...
... Overview, kernel extensions, I/O drivers, WDF Object manager, LPC, Processes & Threads ...
MIPS Assembler Programming
... Switches the sp to the kernel stack Saves the old (user) SP value Saves the old (user) PC value Saves the old privilege mode Saves cause of the interrupt/exception Sets the new privilege mode to 1 Sets the new PC to the kernel interrupt/exception handler ...
... Switches the sp to the kernel stack Saves the old (user) SP value Saves the old (user) PC value Saves the old privilege mode Saves cause of the interrupt/exception Sets the new privilege mode to 1 Sets the new PC to the kernel interrupt/exception handler ...
Slides for week 2
... a single instance of an executable program User enters a command, invokes a program, while this program is executing it is called a process E.g, when a user types the command “ls” , the UNIX system creates a process for this command. ...
... a single instance of an executable program User enters a command, invokes a program, while this program is executing it is called a process E.g, when a user types the command “ls” , the UNIX system creates a process for this command. ...
**** 1 - Computer Engineering Research Laboratory
... other programs in a computer. Other examples of system software and what each does: The BIOS (basic input/output system) gets the computer system started after you turn it on and manages the data flow between the operating system and attached devices such as the hard disk, video adapter, keyboard, m ...
... other programs in a computer. Other examples of system software and what each does: The BIOS (basic input/output system) gets the computer system started after you turn it on and manages the data flow between the operating system and attached devices such as the hard disk, video adapter, keyboard, m ...
Threads
... a small disaster as only one message transfer can occur per time scheduling slot Co-scheduling (a.k.a. gang scheduling). Processes belonging to a job are scheduled ...
... a small disaster as only one message transfer can occur per time scheduling slot Co-scheduling (a.k.a. gang scheduling). Processes belonging to a job are scheduled ...
Slides - Winlab
... • GPL requires back attribution and redistribution of changes • BSD is Free for All (very few clauses). • There are others:Mozilla Public license, Creative ...
... • GPL requires back attribution and redistribution of changes • BSD is Free for All (very few clauses). • There are others:Mozilla Public license, Creative ...
1 - OoCities
... 9. [L1] Give an example of a critical region and how it is important to two competing processes. A critical region is a process or block of code which uses a resource, such that the process or code block must be completed as a unit before the resource is released for use by other processes. Race pro ...
... 9. [L1] Give an example of a critical region and how it is important to two competing processes. A critical region is a process or block of code which uses a resource, such that the process or code block must be completed as a unit before the resource is released for use by other processes. Race pro ...
Answers to Even-Numbered Exercises
... Linux is portable, is based on standards, is written in C, has a kernel programming interface, can support many users, and can run multiple tasks simultaneously. For more information refer to “What Is So Good About Linux?” on page 6. The source code for the operating system is readily available so s ...
... Linux is portable, is based on standards, is written in C, has a kernel programming interface, can support many users, and can run multiple tasks simultaneously. For more information refer to “What Is So Good About Linux?” on page 6. The source code for the operating system is readily available so s ...
Principles of Operating Systems
... • cards put on tape • tape processed by operator • output written to tape • tape printed on printer • Separate user from computer ...
... • cards put on tape • tape processed by operator • output written to tape • tape printed on printer • Separate user from computer ...
Module 3: Operating
... rather for ensuring efficient system operations. • Resource allocation – allocating resources, such as CPU cycles, main memory, file storage, I/O devices, to multiple users or multiple jobs running at the same time. • Accounting – keep track of and record which users use how much and what kinds of c ...
... rather for ensuring efficient system operations. • Resource allocation – allocating resources, such as CPU cycles, main memory, file storage, I/O devices, to multiple users or multiple jobs running at the same time. • Accounting – keep track of and record which users use how much and what kinds of c ...