JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
... To make the students understand the basic operating system concepts such as processes, threads, scheduling, synchronization, deadlocks, memory management, file and I/O subsystems and protection. To get acquaintance with the class of abstractions afford by general purpose operating systems that a ...
... To make the students understand the basic operating system concepts such as processes, threads, scheduling, synchronization, deadlocks, memory management, file and I/O subsystems and protection. To get acquaintance with the class of abstractions afford by general purpose operating systems that a ...
Figure 15.1 A distributed multimedia system
... Access transparency: enables local and remote resources to be accessed using identical operations. Location transparency: enables resources to be accessed without knowledge of their physical or network location (for example, which building or IP address). Concurrency transparency: enables several ...
... Access transparency: enables local and remote resources to be accessed using identical operations. Location transparency: enables resources to be accessed without knowledge of their physical or network location (for example, which building or IP address). Concurrency transparency: enables several ...
02_OperatingSystemOverview
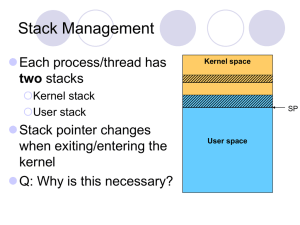
... • Multiple jobs in memory must be protected from each other’s data • File system must be protected so that only authorised users can access • Contention for resources must be handled – Printers, storage etc ...
... • Multiple jobs in memory must be protected from each other’s data • File system must be protected so that only authorised users can access • Contention for resources must be handled – Printers, storage etc ...
Operating System: A Software Engineering Perspective
... Find a way to organize the OS in order to simplify its design and implementation ...
... Find a way to organize the OS in order to simplify its design and implementation ...
Principles of Operating System
... • The kernel itself is an executable; on Linux, this executable is located at /boot/vmlinuz ...
... • The kernel itself is an executable; on Linux, this executable is located at /boot/vmlinuz ...
MS Powerpoint Format
... – networking (Internet) – enhanced file system (over Minix) – many devices, dynamic kernel modules ...
... – networking (Internet) – enhanced file system (over Minix) – many devices, dynamic kernel modules ...
CS 4410/4411 Systems Programming and Operating Systems
... • Structure: how is an operating system organized ? • Sharing: how are resources shared among users ? • Naming: how are resources named by users or programs ? • Protection: how is one user/program protected from another ? • Security: how to authenticate, control access, secure privacy ? • Perf ...
... • Structure: how is an operating system organized ? • Sharing: how are resources shared among users ? • Naming: how are resources named by users or programs ? • Protection: how is one user/program protected from another ? • Security: how to authenticate, control access, secure privacy ? • Perf ...
ppt
... • Bday 1991, Linus Torvalds, 80386 processor – v.01, limited devices, no networking, – with proper Unix process support! ...
... • Bday 1991, Linus Torvalds, 80386 processor – v.01, limited devices, no networking, – with proper Unix process support! ...
Parallel, Distributed, and Multithreaded Computing
... Why Parallel Processing ? Parallel Hardwares Parallel Operating Systems Parallel Programming Paradigms ...
... Why Parallel Processing ? Parallel Hardwares Parallel Operating Systems Parallel Programming Paradigms ...
Cooperation in Intrusion Detection Networks
... • A p2p system is used for the scalability of the system • Emails are divided into feature trunks and digested into feature finger prints ...
... • A p2p system is used for the scalability of the system • Emails are divided into feature trunks and digested into feature finger prints ...
This course is an introduction to computer operating systems
... 3 Credits; 4 Hours (3 lecture, 1 lab) ...
... 3 Credits; 4 Hours (3 lecture, 1 lab) ...
Ch_01
... d. Real time. Often used in a dedicated application, this system reads information from sensors and must respond within a fixed amount of time to ensure correct performance. e. Network. Provides operating system features across a network such as file sharing. f. SMP. Used in systems where there are ...
... d. Real time. Often used in a dedicated application, this system reads information from sensors and must respond within a fixed amount of time to ensure correct performance. e. Network. Provides operating system features across a network such as file sharing. f. SMP. Used in systems where there are ...
Consensus Inside - LPD
... So far – shared memory view • set of registers that any process can read or write to; • communication – implicit through these registers; • problems: Scalabil Mops/s ...
... So far – shared memory view • set of registers that any process can read or write to; • communication – implicit through these registers; • problems: Scalabil Mops/s ...
Communication
... Update operations are initially performed at one node Node passes its updated state to a limited number of ‘peers’ (often chosen randomly) … … which, in-turn, pass the update to other peers Eventually, each update will reach every node ...
... Update operations are initially performed at one node Node passes its updated state to a limited number of ‘peers’ (often chosen randomly) … … which, in-turn, pass the update to other peers Eventually, each update will reach every node ...
Introduction to CS-4513
... • If (my distance to network > neighbor’s distance to network + my distance to neighbor), then … • … update my table entry for that network so that neighbor is ...
... • If (my distance to network > neighbor’s distance to network + my distance to neighbor), then … • … update my table entry for that network so that neighbor is ...
Unit OS1: The Evolution of Operating Systems
... Multiuser/Timesharing Systems Management of multiple simultaneous users interconnected via terminals Fair resource management: CPU scheduling, spooling, mutual exclusion Real-Time Systems (process control systems) Management of time-critical processes High requirements with respect to reliability an ...
... Multiuser/Timesharing Systems Management of multiple simultaneous users interconnected via terminals Fair resource management: CPU scheduling, spooling, mutual exclusion Real-Time Systems (process control systems) Management of time-critical processes High requirements with respect to reliability an ...
Slides. - Department of Computer Science and Information Systems
... Mainframe operating systems Server operating systems Multiprocessor operating systems Personal computer operating systems Real-time operating systems Embedded operating systems Smart card operating systems ...
... Mainframe operating systems Server operating systems Multiprocessor operating systems Personal computer operating systems Real-time operating systems Embedded operating systems Smart card operating systems ...
CDF
... Catalog Description: The main aim of this course is to acquire a systematic knowledge of operating systems and to develop a critical understanding of their purpose, the main concepts, techniques and methods. Topics covered include processes and threads, scheduling, memory management, file systems, a ...
... Catalog Description: The main aim of this course is to acquire a systematic knowledge of operating systems and to develop a critical understanding of their purpose, the main concepts, techniques and methods. Topics covered include processes and threads, scheduling, memory management, file systems, a ...
Operating Systems
... • Multiple jobs in memory must be protected from each other’s data • File system must be protected so that only authorised users can access • Contention for resources must be handled – Printers, storage etc ...
... • Multiple jobs in memory must be protected from each other’s data • File system must be protected so that only authorised users can access • Contention for resources must be handled – Printers, storage etc ...
Selling an Idea or a Product
... – Each built on top of lower layers – Bottom layer (layer 0) is hardware – Highest layer (layer N) is the user interface ...
... – Each built on top of lower layers – Bottom layer (layer 0) is hardware – Highest layer (layer N) is the user interface ...
Operating System Architecture and Distributed
... application to application and service to service. – For example, an ideal scheduling system would provide mechanisms that enable a multimedia application such as videoconferencing to meet its real-time demands while coexisting with a non-real-time application such as web browsing. – That is kernel ...
... application to application and service to service. – For example, an ideal scheduling system would provide mechanisms that enable a multimedia application such as videoconferencing to meet its real-time demands while coexisting with a non-real-time application such as web browsing. – That is kernel ...
Solution
... d. Real time. Often used in a dedicated application, this system reads information from sensors and must respond within a fixed amount of time to ensure correct performance. ...
... d. Real time. Often used in a dedicated application, this system reads information from sensors and must respond within a fixed amount of time to ensure correct performance. ...
introduction - Eastern Mediterranean University
... Each processor runs an identical copy of the operating system which communicates with each other as needed. Many processes can run at once without performance deterioration. Most modern operating systems support SMP Asymmetric multiprocessing Each processor is assigned a specific task; mas ...
... Each processor runs an identical copy of the operating system which communicates with each other as needed. Many processes can run at once without performance deterioration. Most modern operating systems support SMP Asymmetric multiprocessing Each processor is assigned a specific task; mas ...
OPERATING SYSTEM CONCEPTS
... saving the state of the old process and loading the saved state for the new process. This task is known as a context switch. Context-switch time is pure overhead, because the system does no useful work while switching. Its speed varies from machine to machine, depending on the memory speed, the numb ...
... saving the state of the old process and loading the saved state for the new process. This task is known as a context switch. Context-switch time is pure overhead, because the system does no useful work while switching. Its speed varies from machine to machine, depending on the memory speed, the numb ...
Distributed operating system
A distributed operating system is a software over a collection of independent, networked, communicating, and physically separate computational nodes. Each individual node holds a specific software subset of the global aggregate operating system. Each subset is a composite of two distinct service provisioners. The first is a ubiquitous minimal kernel, or microkernel, that directly controls that node’s hardware. Second is a higher-level collection of system management components that coordinate the node's individual and collaborative activities. These components abstract microkernel functions and support user applications.The microkernel and the management components collection work together. They support the system’s goal of integrating multiple resources and processing functionality into an efficient and stable system. This seamless integration of individual nodes into a global system is referred to as transparency, or single system image; describing the illusion provided to users of the global system’s appearance as a single computational entity.