Chapter 2 – Operating System Overview
... 10. The paging system in a memory management system provides for dynamic mapping between a virtual address used in a program and: a. ...
... 10. The paging system in a memory management system provides for dynamic mapping between a virtual address used in a program and: a. ...
Operating System Overview
... Virtual Memory • Allows programmers to address memory from a logical point of view • No hiatus between the execution of successive processes while one process was written out to secondary store and the successor proceess was read in ...
... Virtual Memory • Allows programmers to address memory from a logical point of view • No hiatus between the execution of successive processes while one process was written out to secondary store and the successor proceess was read in ...
What is an Operating System? - Oman College of Management
... Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) Each processor runs an identical copy of the operating system (same instruction vector processing) . Many processes can run at once without performance deterioration. Most modern operating systems support SMP Asymmetric multiprocessing Sharing the job exec ...
... Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) Each processor runs an identical copy of the operating system (same instruction vector processing) . Many processes can run at once without performance deterioration. Most modern operating systems support SMP Asymmetric multiprocessing Sharing the job exec ...
operating-systems-7th-edition-william-stallings
... 2.7 A virtual address refers to a memory location in virtual memory. That location is on disk and at some times in main memory. A real address is an address in main memory. 2.8 Round robin is a scheduling algorithm in which processes are activated in a fixed cyclic order; that is, all processes are ...
... 2.7 A virtual address refers to a memory location in virtual memory. That location is on disk and at some times in main memory. A real address is an address in main memory. 2.8 Round robin is a scheduling algorithm in which processes are activated in a fixed cyclic order; that is, all processes are ...
1. Pradeep K Sinha - Distributed Operating System: Concepts and
... Outcomes Students who have successfully completed this course will have full understanding of the following concepts Course outcome The Concepts of operating system The Concepts of distributed system Synchronization memory Case Study: Amoeba Program outcome The concepts of Distributed System can be ...
... Outcomes Students who have successfully completed this course will have full understanding of the following concepts Course outcome The Concepts of operating system The Concepts of distributed system Synchronization memory Case Study: Amoeba Program outcome The concepts of Distributed System can be ...
Operating systems
... The objective of the course The acquisition of basic knowledge of operating systems and work in them. Knowledge of modern operating systems. Understanding the key differences between objectoriented, modular, layered or systems based on a microkernel. Knowledge of the mechanisms of competitive execut ...
... The objective of the course The acquisition of basic knowledge of operating systems and work in them. Knowledge of modern operating systems. Understanding the key differences between objectoriented, modular, layered or systems based on a microkernel. Knowledge of the mechanisms of competitive execut ...
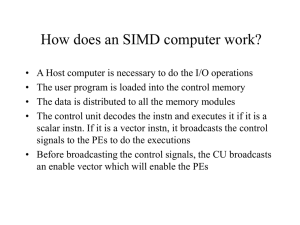
How does an SIMD computer work?
... • A,B,C – working registers • Si = status (1 active, 0 inactive) • Ri – Data routing register • Di – holds address • Ii – Index register ...
... • A,B,C – working registers • Si = status (1 active, 0 inactive) • Ri – Data routing register • Di – holds address • Ii – Index register ...
Ch 5 Quick Quiz
... T F 2. With sequential processing techniques, multiple tasks are performed at the exact same time. ...
... T F 2. With sequential processing techniques, multiple tasks are performed at the exact same time. ...
Course Overview, History
... Issues in OS Design • Communication: how can we exchange information ? • Concurrency: how are parallel activities created and controlled ? • Scale, growth: what happens as demands or resources increase ? • Persistence: how can data outlast processes that created them • Compatibility: can we ever do ...
... Issues in OS Design • Communication: how can we exchange information ? • Concurrency: how are parallel activities created and controlled ? • Scale, growth: what happens as demands or resources increase ? • Persistence: how can data outlast processes that created them • Compatibility: can we ever do ...
Operating-System Structures
... Due to the complex nature of the modern operating systems, it is partitioned into smaller component. Each component performs a well-defined function with well-defined inputs and outputs. Many modern operating systems have the following ...
... Due to the complex nature of the modern operating systems, it is partitioned into smaller component. Each component performs a well-defined function with well-defined inputs and outputs. Many modern operating systems have the following ...
Concepts and Structures
... It allows programs to address memory from a logical point of view without regard to the amount that is physically available While a program is running only a portion of the program and data is kept in (real) memory Other portions are kept in blocks on disk The user has access to a memory space that ...
... It allows programs to address memory from a logical point of view without regard to the amount that is physically available While a program is running only a portion of the program and data is kept in (real) memory Other portions are kept in blocks on disk The user has access to a memory space that ...
Lecture 1: Overview - City University of New York
... An operating system is a program that controls the execution of application programs and acts as an interface between applications and the computer hardware. Three objectives of operating systems: ...
... An operating system is a program that controls the execution of application programs and acts as an interface between applications and the computer hardware. Three objectives of operating systems: ...
CSE451 Introduction to Operating Systems
... Embedded/mobile/pervasive computing • Pervasive computing – cheap processors embedded everywhere – how many are on your body now? in your car? – cell phones, PDAs, network computers, … ...
... Embedded/mobile/pervasive computing • Pervasive computing – cheap processors embedded everywhere – how many are on your body now? in your car? – cell phones, PDAs, network computers, … ...
CCN3133 Computer System Principles
... Segmentation; Dynamic Link Library (DLL); System programming for memory management. Processor Scheduling Types of processor scheduling; Scheduling algorithms; Multiprocessor scheduling; Case Study. ...
... Segmentation; Dynamic Link Library (DLL); System programming for memory management. Processor Scheduling Types of processor scheduling; Scheduling algorithms; Multiprocessor scheduling; Case Study. ...
COS 318: Operating Systems Introduction Kai Li Computer Science Department
... Hosting data in the cloud Software as services Examples: ...
... Hosting data in the cloud Software as services Examples: ...
The UNIX Operating System - Niagara College Technology
... Each UNIX command can get its input from any data source and send its output to any data destination. ...
... Each UNIX command can get its input from any data source and send its output to any data destination. ...
Answers
... 3. Find a creative/funny analogy to distinguish between a process and a program. Program: a recipe Process: everything needed to cook (e.g., kitchen) Two chefs can cook the same recipe in different kitchens One complex recipe can involve several chefs 4. Give an example where a uniprogramming enviro ...
... 3. Find a creative/funny analogy to distinguish between a process and a program. Program: a recipe Process: everything needed to cook (e.g., kitchen) Two chefs can cook the same recipe in different kitchens One complex recipe can involve several chefs 4. Give an example where a uniprogramming enviro ...
Ceng 334 - Operating Systems
... An interface between the user and the hardware (provides a virtual machine) ...
... An interface between the user and the hardware (provides a virtual machine) ...
What is an Operating System
... Definition: Is a collection of software enhancements, executed on the bare hardware, culminating in a high-level virtual machine that serves as an advanced programming environment ...
... Definition: Is a collection of software enhancements, executed on the bare hardware, culminating in a high-level virtual machine that serves as an advanced programming environment ...
CS 414/415 Systems Programming and
... Issues in OS Design • Communication: how can we exchange information ? • Concurrency: how are parallel activities created and controlled ? • Scale, growth: what happens as demands or resources increase ? • Persistence: how can data outlast processes that created them • Compatibility: can we ever do ...
... Issues in OS Design • Communication: how can we exchange information ? • Concurrency: how are parallel activities created and controlled ? • Scale, growth: what happens as demands or resources increase ? • Persistence: how can data outlast processes that created them • Compatibility: can we ever do ...
Multiprogrammed Batch Systems
... advanced CPU utilization of protection features. Migration of Operating-System Concepts and Features ...
... advanced CPU utilization of protection features. Migration of Operating-System Concepts and Features ...
Distributed operating system
A distributed operating system is a software over a collection of independent, networked, communicating, and physically separate computational nodes. Each individual node holds a specific software subset of the global aggregate operating system. Each subset is a composite of two distinct service provisioners. The first is a ubiquitous minimal kernel, or microkernel, that directly controls that node’s hardware. Second is a higher-level collection of system management components that coordinate the node's individual and collaborative activities. These components abstract microkernel functions and support user applications.The microkernel and the management components collection work together. They support the system’s goal of integrating multiple resources and processing functionality into an efficient and stable system. This seamless integration of individual nodes into a global system is referred to as transparency, or single system image; describing the illusion provided to users of the global system’s appearance as a single computational entity.