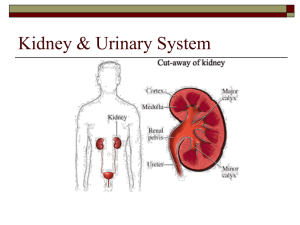
Kidney
... Renal artery : Two renal arteries come from the aorta, each connecting to a kidney. The artery divides into five branches, each of which leads to a ball of capillaries. The arteries supply (unfiltered) blood to the kidneys. The left kidney receives about 60% of the renal blood flow. Renal vein : The ...
... Renal artery : Two renal arteries come from the aorta, each connecting to a kidney. The artery divides into five branches, each of which leads to a ball of capillaries. The arteries supply (unfiltered) blood to the kidneys. The left kidney receives about 60% of the renal blood flow. Renal vein : The ...
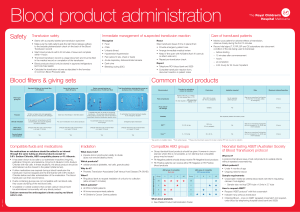
Blood product administration - The Royal Children`s Hospital
... No medications or solutions should be added to or infused through the same tubing as blood products except for 0.9% Sodium Chloride, ABO compatible plasma or 4% Albumin. ...
... No medications or solutions should be added to or infused through the same tubing as blood products except for 0.9% Sodium Chloride, ABO compatible plasma or 4% Albumin. ...
Document
... ● Thrombocytopenia ● The number of leukemic cells in the peripheral blood is highly variable, sometimes being more 100•109/L, but being under 10•109/L in about 50% of the patients ● Occasionally the peripheral blood smear may not contain ...
... ● Thrombocytopenia ● The number of leukemic cells in the peripheral blood is highly variable, sometimes being more 100•109/L, but being under 10•109/L in about 50% of the patients ● Occasionally the peripheral blood smear may not contain ...
Sickle Cell Anemia
... Sickle red blood cells become hard, sticky and shaped like sickles used to cut wheat. When these hard and pointed red cells go through the small blood tube, they clog the flow and break apart. This can cause pain, damage and a low blood count, or anemia. ...
... Sickle red blood cells become hard, sticky and shaped like sickles used to cut wheat. When these hard and pointed red cells go through the small blood tube, they clog the flow and break apart. This can cause pain, damage and a low blood count, or anemia. ...
Blood Web Quest
... 22. What type of patients might use the plasma? ___________________________________________ Phase 5: The Transfusion 23. Which blood type can receive blood from all groups? ___________________________ 24. What are the two most common blood types in the U.S.? ____________________________ Test Your Bl ...
... 22. What type of patients might use the plasma? ___________________________________________ Phase 5: The Transfusion 23. Which blood type can receive blood from all groups? ___________________________ 24. What are the two most common blood types in the U.S.? ____________________________ Test Your Bl ...
File
... 26. Which circulatory disorder is known as the “silent killer”? 27. What can cause varicose veins? 28. “Low iron”, fatigue, dyspnea and paleness are symptoms of ______________________. 29. Define transient ischemic attack. 30. Which blood type has NO antibodies? 31. Define hematology. 32. Which bloo ...
... 26. Which circulatory disorder is known as the “silent killer”? 27. What can cause varicose veins? 28. “Low iron”, fatigue, dyspnea and paleness are symptoms of ______________________. 29. Define transient ischemic attack. 30. Which blood type has NO antibodies? 31. Define hematology. 32. Which bloo ...
BLOOD - Doctor Jade Main
... • Pulmonary emboluslung • Conditions that roughen endothelium encourage clot formation– Arteriosclerosis ...
... • Pulmonary emboluslung • Conditions that roughen endothelium encourage clot formation– Arteriosclerosis ...
Cell Salvage n=20 - Serious Hazards of Transfusion
... of free cytokines have led to profound vasodilation, which is treatable and the effect is only transient due to the short half-life of the vasoactive cytokines. In all cases a LDF has been used and where the red cells were urgently needed the LDF was removed and the remaining cell salvaged red cells ...
... of free cytokines have led to profound vasodilation, which is treatable and the effect is only transient due to the short half-life of the vasoactive cytokines. In all cases a LDF has been used and where the red cells were urgently needed the LDF was removed and the remaining cell salvaged red cells ...
Handout 5 - Porterville College Home
... b. _________________________ Jaundice c. __________________ 4. Treatment a. ________________ therapy 1) ___________________ breaks down when exposed to _______ b. Blood ___________________ B. ABO Incompatibility 1. Etiology: a. Mom blood type: ____________________ b. Fetus blood type: ____________ ...
... b. _________________________ Jaundice c. __________________ 4. Treatment a. ________________ therapy 1) ___________________ breaks down when exposed to _______ b. Blood ___________________ B. ABO Incompatibility 1. Etiology: a. Mom blood type: ____________________ b. Fetus blood type: ____________ ...
all about anaemia - Kidney Health Australia
... example, when the numbers of red blood cells drop, your heart works harder to maintain the oxygen levels in the body. If the heart works too hard, the heart muscle can become weak, which can lead to heart failure. ...
... example, when the numbers of red blood cells drop, your heart works harder to maintain the oxygen levels in the body. If the heart works too hard, the heart muscle can become weak, which can lead to heart failure. ...
PPT - Larry Smarr - California Institute for Telecommunications and
... the future," I have been increasingly quantifying my own body over the last ten years. This involves not only non-invasive macro-variables such as weight, pulse, blood pressure, caloric intake and burn, but also invasive blood, saliva, and stool measurements. I currently track over 100 molecular and ...
... the future," I have been increasingly quantifying my own body over the last ten years. This involves not only non-invasive macro-variables such as weight, pulse, blood pressure, caloric intake and burn, but also invasive blood, saliva, and stool measurements. I currently track over 100 molecular and ...
Medical Grand Rounds Clinical Vignette October 3, 2007
... History of Present Illness • He was in his usual state of health until three months prior to admission when he began experiencing frequent early satiety and subjective weight loss. • One week prior to presentation patient noted bright red blood per rectum with clots which spontaneously resolved aft ...
... History of Present Illness • He was in his usual state of health until three months prior to admission when he began experiencing frequent early satiety and subjective weight loss. • One week prior to presentation patient noted bright red blood per rectum with clots which spontaneously resolved aft ...
Apheresis units - World Health Organization
... from the patient and moves it through centrifuges and/or filters to separate blood products. The blood is then returned to the patient via tubing or is collected in bags, often suspended from a pole, for donation or disposal. A display and control panel allow the operator to program the unit and vie ...
... from the patient and moves it through centrifuges and/or filters to separate blood products. The blood is then returned to the patient via tubing or is collected in bags, often suspended from a pole, for donation or disposal. A display and control panel allow the operator to program the unit and vie ...
Blood groups
... b- If agglutination occurs with anti-B serum only , the blood group is type B. c- If agglutination occurs with both anti-A and anti-B sera , the blood group is type AB. d- If no agglutination occurs with either anti-A or anti-B , the blood group is type O. ...
... b- If agglutination occurs with anti-B serum only , the blood group is type B. c- If agglutination occurs with both anti-A and anti-B sera , the blood group is type AB. d- If no agglutination occurs with either anti-A or anti-B , the blood group is type O. ...
Glossary and Resources
... Central Venous Catheter - a small hollow tube inserted into blood vessels and used to painlessly draw blood and give medicines and fluids Chest X-ray - examination of lungs using lowdose radiation to produce a picture CMV (cytomegalovirus) - a virus that can cause infection in immunosuppressed peopl ...
... Central Venous Catheter - a small hollow tube inserted into blood vessels and used to painlessly draw blood and give medicines and fluids Chest X-ray - examination of lungs using lowdose radiation to produce a picture CMV (cytomegalovirus) - a virus that can cause infection in immunosuppressed peopl ...
Powerpoint - Blood Journal
... Cellular IC50 (nM) of imatinib (IM), nilotinib (NI), and dasatinib (DA) and fold increase with respect to the IC50 for wild-type (WT) Bcr-Abl of the F311L, T315I, F317L, M351T, F359V, V379I, L384M, L387M, H396R, H396P, and F486S mutant forms. ...
... Cellular IC50 (nM) of imatinib (IM), nilotinib (NI), and dasatinib (DA) and fold increase with respect to the IC50 for wild-type (WT) Bcr-Abl of the F311L, T315I, F317L, M351T, F359V, V379I, L384M, L387M, H396R, H396P, and F486S mutant forms. ...
Lecture 1 - gserianne.com
... • thin rims of cytoplasm • T cells • B cells • important in immunity • produce antibodies • 25% - 33% of leukocytes • decreased T Cells in AIDS ...
... • thin rims of cytoplasm • T cells • B cells • important in immunity • produce antibodies • 25% - 33% of leukocytes • decreased T Cells in AIDS ...
Bio102__Sp14_Lab1
... Be able to read and interpret a blood typing agglutination reaction and determine blood type from what you see Understand what determines blood type and under what circumstances a transfusion reaction may occur, i.e., what serum antibodies must be present for a reaction to take place Be able to dist ...
... Be able to read and interpret a blood typing agglutination reaction and determine blood type from what you see Understand what determines blood type and under what circumstances a transfusion reaction may occur, i.e., what serum antibodies must be present for a reaction to take place Be able to dist ...
Powerpoint - Blood Journal
... Structural basis for quinine-dependent antibody binding to platelet integrin αIIbβ3 by Jianghai Zhu, Jieqing Zhu, Daniel W. Bougie, Richard H. Aster, and Timothy A. Springer ...
... Structural basis for quinine-dependent antibody binding to platelet integrin αIIbβ3 by Jianghai Zhu, Jieqing Zhu, Daniel W. Bougie, Richard H. Aster, and Timothy A. Springer ...
TRYPTONE-SOY AGAR (blood agar base)
... triangle of total hemolysis in the zone of incomplete hemolysis of the staphylococcus, at the junction of the two cultures. This procedure should be done with known collection strains in parallel with the unknown strains to be identified. Group B streptococci generally present smaller hemolytic zone ...
... triangle of total hemolysis in the zone of incomplete hemolysis of the staphylococcus, at the junction of the two cultures. This procedure should be done with known collection strains in parallel with the unknown strains to be identified. Group B streptococci generally present smaller hemolytic zone ...
understanding blood work: the complete blood count (cbc)
... · WBC is an abbreviation for white blood cell count. These cells help fight infection and respond when an area of the body becomes inflamed. Elevated white blood cell counts indicate infection, inflammation and some forms of cancer or leukemia. Low white blood cells counts can indicate viral infecti ...
... · WBC is an abbreviation for white blood cell count. These cells help fight infection and respond when an area of the body becomes inflamed. Elevated white blood cell counts indicate infection, inflammation and some forms of cancer or leukemia. Low white blood cells counts can indicate viral infecti ...
Document
... spinal cord 40. After complete severing of which place in the central nervous system, the spontaneous respiration does not disappear but becomes less smooth? A. between cerebral cortex and thalamus B. between thalamus and cerebellum C. between pons and medulla oblongata D. between medullar oblongata ...
... spinal cord 40. After complete severing of which place in the central nervous system, the spontaneous respiration does not disappear but becomes less smooth? A. between cerebral cortex and thalamus B. between thalamus and cerebellum C. between pons and medulla oblongata D. between medullar oblongata ...
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (or haemolytic-uraemic syndrome), abbreviated HUS, is a disease characterized by hemolytic anemia (anemia caused by destruction of red blood cells), acute kidney failure (uremia), and a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia). It predominantly, but not exclusively, affects children. Most cases are preceded by an episode of infectious, sometimes bloody, diarrhea acquired as a foodborne illness or from a contaminated water supply and caused by E. coli O157:H7, although Shigella, Campylobacter and a variety of viruses have also been implicated. It is now the most common cause of acquired acute renal failure in childhood. It is a medical emergency and carries a 5–10% mortality; of the remainder, the majority recover without major consequences but a small proportion develop chronic kidney disease and become reliant on renal replacement therapy.The primary target appears to be the vascular endothelial cell. This may explain the pathogenesis of HUS, in which a characteristic renal lesion is capillary microangiopathy.HUS was first defined as a syndrome in 1955. The more common form of the disease, Shiga-like toxin-producing E. coli HUS (STEC-HUS), is triggered by the infectious agent E. coli O157:H7. Certain Shiga toxin secreting strains of Shigella dysenteriae can also cause HUS. Approximately 5% of cases are classified as pneumococcal HUS, which results from infection by Streptococcus pneumoniae, the agent that causes traditional lobar pneumonia. There is also a rare, chronic, and severe form known as atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), which is caused by genetic defects resulting in chronic, uncontrolled complement activation. Both STEC-HUS and aHUS cause endothelial damage, leukocyte activation, platelet activation, and widespread inflammation and multiple thromboses in the small blood vessels, a condition known as systemic thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), which leads to thrombotic events as well as organ damage/failure and death.