Delayed hemolytic reaction due to anti Jka alloimmunization
... refers to the fact that antibodies of certain blood group systems react more strongly with homozygous (double dose antigen) red cells and may not react when both antithetical antigens are present on red cells (heterozygous red cells). Moreover these antibodies often occur in combination with other a ...
... refers to the fact that antibodies of certain blood group systems react more strongly with homozygous (double dose antigen) red cells and may not react when both antithetical antigens are present on red cells (heterozygous red cells). Moreover these antibodies often occur in combination with other a ...
Morphometric Characteristics of Central Retinal Artery and
... cause-and-consequence relationship and interpret how the pathologies found in experimental and clinical studies relate to one another and how they contribute to disease progression.3,4 There is abundant evidence suggesting early changes in retinal perfusion before the onset of diabetic retinopathy t ...
... cause-and-consequence relationship and interpret how the pathologies found in experimental and clinical studies relate to one another and how they contribute to disease progression.3,4 There is abundant evidence suggesting early changes in retinal perfusion before the onset of diabetic retinopathy t ...
Characterisation of Rh and Other Blood Group Systems Amongst the
... will produce IgM alloanti-P antibodies and is active at body temperature against P1 and P2 phenotype cells. Most P2 phenotype individuals have naturally occurring IgM anti-P1 which is a weak cold agglutinin and does not cause HDN. However, unusual association with clinically significant transfusion ...
... will produce IgM alloanti-P antibodies and is active at body temperature against P1 and P2 phenotype cells. Most P2 phenotype individuals have naturally occurring IgM anti-P1 which is a weak cold agglutinin and does not cause HDN. However, unusual association with clinically significant transfusion ...
Acute Ischemic Infarction Defined by a Region of Multiple
... within 6 hours after symptom onset. The following data were recorded: patient age, sex, location of infarction, and time of onset of clinical symptoms at admission to the hospital. Stroke severity was assessed according to the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score. The following c ...
... within 6 hours after symptom onset. The following data were recorded: patient age, sex, location of infarction, and time of onset of clinical symptoms at admission to the hospital. Stroke severity was assessed according to the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score. The following c ...
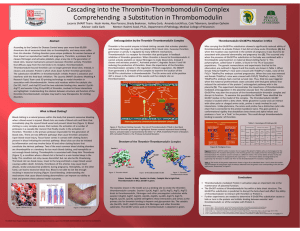
Poster
... when the mutation was examined in the context of pregnancy it was found to be associated with placental abnormality and pregnancy loss (5). This occurred only when the presence of Gln387Pro substitution in the baby was combined with a thrombophilic polymorphism in maternal blood clotting factor V. T ...
... when the mutation was examined in the context of pregnancy it was found to be associated with placental abnormality and pregnancy loss (5). This occurred only when the presence of Gln387Pro substitution in the baby was combined with a thrombophilic polymorphism in maternal blood clotting factor V. T ...
Hemorheology and Hemodynamics
... of blood depends on the acting shear forces and is determined by hematocrit value, plasma viscosity and the mechanical properties of red blood cells (RBC) under given shear conditions. RBC are highly deformable bodies and this property significantly contributes to blood flow both under bulk flow con ...
... of blood depends on the acting shear forces and is determined by hematocrit value, plasma viscosity and the mechanical properties of red blood cells (RBC) under given shear conditions. RBC are highly deformable bodies and this property significantly contributes to blood flow both under bulk flow con ...
013513739x_tb_ch1 - Test Bank|testbank.is
... calculated by taking the mean and 2 standard deviations above and below the mean value. (Objective 1, Level II) 2. Name three blood analytes that show significantly different results in adults, children, and infants. ...
... calculated by taking the mean and 2 standard deviations above and below the mean value. (Objective 1, Level II) 2. Name three blood analytes that show significantly different results in adults, children, and infants. ...
Blood Typing Lab
... Blood typing (determining blood type) One test used to determine blood is to mix a blood sample with “anti” serums. These serums contain antibodies that are against the blood type being tested for. So, anti-A serum will bond with antigen A and coagulate (clump together) and anti-B se ...
... Blood typing (determining blood type) One test used to determine blood is to mix a blood sample with “anti” serums. These serums contain antibodies that are against the blood type being tested for. So, anti-A serum will bond with antigen A and coagulate (clump together) and anti-B se ...
Acute Traumatic Coagulopathy in Severe Injury
... Society (Traumaregister der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Unfallchirurgie, TRDGU) relating to the incidence, causes, and outcome of ATC. We provide an overview of current treatment recommendations, supplemented by our own findings regarding the ratio of packed red blood cell concentrate (pRBC) to fresh ...
... Society (Traumaregister der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Unfallchirurgie, TRDGU) relating to the incidence, causes, and outcome of ATC. We provide an overview of current treatment recommendations, supplemented by our own findings regarding the ratio of packed red blood cell concentrate (pRBC) to fresh ...
Effect of Zinc Supplementation on Red Blood Cell Osmotic Fragility
... trace element required for the action of more than 200 metallo enzymes and plays an important role in polymeric organization of macromolecules (like DNA and RNA), protein synthesis and cell division. Zinc plays many significant roles in metabolism ...
... trace element required for the action of more than 200 metallo enzymes and plays an important role in polymeric organization of macromolecules (like DNA and RNA), protein synthesis and cell division. Zinc plays many significant roles in metabolism ...
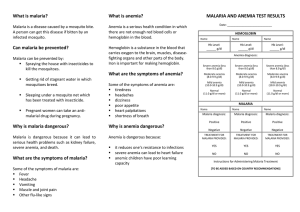
doc - Malaria Indicator Surveys
... [IMPLEMENTING AGENCY] is conducting a study on anemia and malaria. The study will help us identify whether there are problems with anemia and malaria among young children in [COUNTRY]. We appreciate that we have had the opportunity to interview members of your household and to test children 6 months ...
... [IMPLEMENTING AGENCY] is conducting a study on anemia and malaria. The study will help us identify whether there are problems with anemia and malaria among young children in [COUNTRY]. We appreciate that we have had the opportunity to interview members of your household and to test children 6 months ...
Distribution and frequency of ABO blood groups and Rhesus (RH
... in Europeans (group A was in higher frequency), while it was dissimilar to Africans in which B group was much commoner.6 The results of our study were similar to many other studies likes in the United States of America, 46% constitute group O, 41% A, 9% B and 4% AB, also a study in IRAN show O group ...
... in Europeans (group A was in higher frequency), while it was dissimilar to Africans in which B group was much commoner.6 The results of our study were similar to many other studies likes in the United States of America, 46% constitute group O, 41% A, 9% B and 4% AB, also a study in IRAN show O group ...
The kidney trade: or, the customer is always wrong
... heavier burden on replaceability than it can bear. If I can live perfectly well with just one kidney, why not sell the other, at least provided the risk I take is amply rewarded? After all, I can (temporarily) live with less blood in my body than the standard eight pints. So far, then, it would appe ...
... heavier burden on replaceability than it can bear. If I can live perfectly well with just one kidney, why not sell the other, at least provided the risk I take is amply rewarded? After all, I can (temporarily) live with less blood in my body than the standard eight pints. So far, then, it would appe ...
“responders,” defined as a reduction in ambulatory systolic
... patients. This is even more important in view of recent findings demonstrating that baroreflex func- ...
... patients. This is even more important in view of recent findings demonstrating that baroreflex func- ...
compartment syndrome of the buttock following a total
... injury of the forearm: Presenting as acute compartment syndrome. NZ ...
... injury of the forearm: Presenting as acute compartment syndrome. NZ ...
16-Hypertension Lecture of Prof. Jamal Al Wakeel 24 Ocotber 2015
... but the rest of the heart is not greatly enlarged. This is typical for hypertensive heart disease. The hypertension creates a greater pressure load on the heart to induce the hypertrophy. ...
... but the rest of the heart is not greatly enlarged. This is typical for hypertensive heart disease. The hypertension creates a greater pressure load on the heart to induce the hypertrophy. ...
JAK2V617F mutation and endogenous erythroid colony formation in
... The mutant has enhanced kinase activity, and when overexpressed together with the EPOR in cells, it causes hyperactivation of EPO-induced cell signaling. This gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 may explain the hypersensitivity of PV progenitor cells to growth factors and cytokines [41]. A point mutat ...
... The mutant has enhanced kinase activity, and when overexpressed together with the EPOR in cells, it causes hyperactivation of EPO-induced cell signaling. This gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 may explain the hypersensitivity of PV progenitor cells to growth factors and cytokines [41]. A point mutat ...
Recent Approach in Conversion of Universal Blood Group by
... Blood group A Blood group A specificity is a terminal α-1,3-linked-Nacetylgalactosamine (GalNAc). Blood group A plasma contains naturally occurring antibodies to the B antigen. The genetic basis of ABO antigens has been clarified; genes defining A and B blood types translate glycosyltransferases in ...
... Blood group A Blood group A specificity is a terminal α-1,3-linked-Nacetylgalactosamine (GalNAc). Blood group A plasma contains naturally occurring antibodies to the B antigen. The genetic basis of ABO antigens has been clarified; genes defining A and B blood types translate glycosyltransferases in ...
Blood Transfusion - Patient Education Institute
... emergencies when there is no time to test a person’s Rh type. Types of Blood Transfusions The blood used in blood transfusions typically comes from a blood bank. Blood banks collect, test, and store blood. They carefully screen all donated blood for possible problems, such as viruses that could make ...
... emergencies when there is no time to test a person’s Rh type. Types of Blood Transfusions The blood used in blood transfusions typically comes from a blood bank. Blood banks collect, test, and store blood. They carefully screen all donated blood for possible problems, such as viruses that could make ...
HOW TO MANAGE... How to manage lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes
... patients, with responses of B40% in lower-risk patients using IWG (International Working Group) criteria for response.19–29 Given the deleterious effect of ESAs on progression-free and overall survival in solid tumors (in at least eight studies), should they be avoided in MDS patients? No MDS patien ...
... patients, with responses of B40% in lower-risk patients using IWG (International Working Group) criteria for response.19–29 Given the deleterious effect of ESAs on progression-free and overall survival in solid tumors (in at least eight studies), should they be avoided in MDS patients? No MDS patien ...
International society of blood transfusion working party on red cell
... Distinguishes this protein from other known GP(B-A-B) hybrids. Although PX2 is a product of b1,3GalNAc-T1 and therefore present on RBCs of common phenotype, it is absent from RBCs of Pk1 and Pk2 phenotypes whilst highly expressed on RBCs of the p phenotype. c Thus, all mutations causing the of Pk1 a ...
... Distinguishes this protein from other known GP(B-A-B) hybrids. Although PX2 is a product of b1,3GalNAc-T1 and therefore present on RBCs of common phenotype, it is absent from RBCs of Pk1 and Pk2 phenotypes whilst highly expressed on RBCs of the p phenotype. c Thus, all mutations causing the of Pk1 a ...
Transfusion of Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary
... renal dysfunction, prior myocardial infarction, or prior heart failure were more likely to receive transfusion. Receiving a transfusion was associated with myocardial infarction (42,803 events; 4.5 percent vs. 1.8 percent; odds ratio [OR], 2.60; 95 percent CI, 2.57-2.63), stroke (5,011 events; 2.0 p ...
... renal dysfunction, prior myocardial infarction, or prior heart failure were more likely to receive transfusion. Receiving a transfusion was associated with myocardial infarction (42,803 events; 4.5 percent vs. 1.8 percent; odds ratio [OR], 2.60; 95 percent CI, 2.57-2.63), stroke (5,011 events; 2.0 p ...
Administration of Fresh Frozen Plasma
... FFP must be administered through a filter. The standard blood filter is 170 to 260 microns. Multiple units given consecutively may be given through one administration set: A. up to two (2) units within a four (4) hour limit using straight and Y-type sets; or B. up to ten (10) units using a multiple ...
... FFP must be administered through a filter. The standard blood filter is 170 to 260 microns. Multiple units given consecutively may be given through one administration set: A. up to two (2) units within a four (4) hour limit using straight and Y-type sets; or B. up to ten (10) units using a multiple ...
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (or haemolytic-uraemic syndrome), abbreviated HUS, is a disease characterized by hemolytic anemia (anemia caused by destruction of red blood cells), acute kidney failure (uremia), and a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia). It predominantly, but not exclusively, affects children. Most cases are preceded by an episode of infectious, sometimes bloody, diarrhea acquired as a foodborne illness or from a contaminated water supply and caused by E. coli O157:H7, although Shigella, Campylobacter and a variety of viruses have also been implicated. It is now the most common cause of acquired acute renal failure in childhood. It is a medical emergency and carries a 5–10% mortality; of the remainder, the majority recover without major consequences but a small proportion develop chronic kidney disease and become reliant on renal replacement therapy.The primary target appears to be the vascular endothelial cell. This may explain the pathogenesis of HUS, in which a characteristic renal lesion is capillary microangiopathy.HUS was first defined as a syndrome in 1955. The more common form of the disease, Shiga-like toxin-producing E. coli HUS (STEC-HUS), is triggered by the infectious agent E. coli O157:H7. Certain Shiga toxin secreting strains of Shigella dysenteriae can also cause HUS. Approximately 5% of cases are classified as pneumococcal HUS, which results from infection by Streptococcus pneumoniae, the agent that causes traditional lobar pneumonia. There is also a rare, chronic, and severe form known as atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), which is caused by genetic defects resulting in chronic, uncontrolled complement activation. Both STEC-HUS and aHUS cause endothelial damage, leukocyte activation, platelet activation, and widespread inflammation and multiple thromboses in the small blood vessels, a condition known as systemic thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), which leads to thrombotic events as well as organ damage/failure and death.