Stress Definition for a Layman
... Stress Definition for a Layman Stress is defined as the force over the area of an object. Force is related to the amount of pressure applied to an object (The American Heritage, 2006). The word stress comes from the shortening of the middle French word “destresse” to mean hardship, adversity, force, ...
... Stress Definition for a Layman Stress is defined as the force over the area of an object. Force is related to the amount of pressure applied to an object (The American Heritage, 2006). The word stress comes from the shortening of the middle French word “destresse” to mean hardship, adversity, force, ...
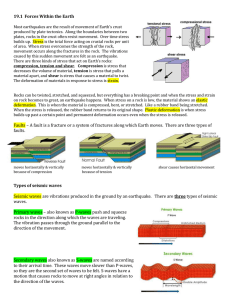
19.1-forces-within-Earth
... plates, rocks in the crust often resist movement. Over time stress builds up. Stress is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area. When stress overcomes the strength of the rock, movement occurs along the fractures in the rock. The vibrations caused by this sudden movement are felt as ...
... plates, rocks in the crust often resist movement. Over time stress builds up. Stress is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area. When stress overcomes the strength of the rock, movement occurs along the fractures in the rock. The vibrations caused by this sudden movement are felt as ...
At what grain diameter will the lower yield point be 310 Mpa?
... Slip and Deformation: Conclusion • Dislocations are the elementary carriers of plastic flow thus they define material mechanical properties • Dislocations allow deformation at much lower stress than in a perfect crystal because slip does not require all bonds across the slip line to break simultane ...
... Slip and Deformation: Conclusion • Dislocations are the elementary carriers of plastic flow thus they define material mechanical properties • Dislocations allow deformation at much lower stress than in a perfect crystal because slip does not require all bonds across the slip line to break simultane ...
Tensile Testing
... DUCTILITY - a material property that allows it to undergo considerable plastic deformation under a load before failure. ELASTICITY - a material property that allows it to retain its original dimensions after removal of a deforming load. STIFFNESS - a material property that allows a material to withs ...
... DUCTILITY - a material property that allows it to undergo considerable plastic deformation under a load before failure. ELASTICITY - a material property that allows it to retain its original dimensions after removal of a deforming load. STIFFNESS - a material property that allows a material to withs ...
CHE 333 Class 19
... In some materials, mainly steels, ductility can decrease very sharply with temperature, so a ductile materials becomes brittle – know as the ductile brittle transition. The standard test is to use an impact tester – a pendulum type hammer and the energy absorbed in failure is measured by how far the ...
... In some materials, mainly steels, ductility can decrease very sharply with temperature, so a ductile materials becomes brittle – know as the ductile brittle transition. The standard test is to use an impact tester – a pendulum type hammer and the energy absorbed in failure is measured by how far the ...
1 2 General Properties of Fatigue the Mechanic of Muscle Fatigue
... connection with strenuous athletic events, this relationship is not usually present in prolonged light or moderate work. Subjective feelings of fatigue usually occur at the end of an 8-h workday when the average work exceeds 30%-40%of the individual maximal aerobic power, and certainly when the load ...
... connection with strenuous athletic events, this relationship is not usually present in prolonged light or moderate work. Subjective feelings of fatigue usually occur at the end of an 8-h workday when the average work exceeds 30%-40%of the individual maximal aerobic power, and certainly when the load ...
Mechanical Principles
... at outcome level in order to provide maximum flexibility of delivery. Evidence may be accumulated by learners building a portfolio of activities or by a tutor-led combination of tests and assignments. In either case, the evidence must be authentic, relevant and sufficient to justify the grade awarde ...
... at outcome level in order to provide maximum flexibility of delivery. Evidence may be accumulated by learners building a portfolio of activities or by a tutor-led combination of tests and assignments. In either case, the evidence must be authentic, relevant and sufficient to justify the grade awarde ...
Laboratory experiments, high angular
... of differential stresses applied during deformation. Stresses averaged over each map are in reasonable agreement with the outcome of stress-dip tests. Third, we implement an elasto-visco-plastic spectral micromechanical model to predict the full stress field in a deforming olivine aggregate. An EBSD ...
... of differential stresses applied during deformation. Stresses averaged over each map are in reasonable agreement with the outcome of stress-dip tests. Third, we implement an elasto-visco-plastic spectral micromechanical model to predict the full stress field in a deforming olivine aggregate. An EBSD ...
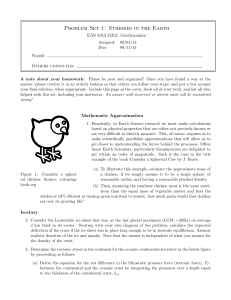
Problem Set 1: Stresses in the Earth
... Stress and Friction 4. Consider a block of vesicular basalt that is 3 m long in each x, y, and z directions. The block is sitting on a rough horizontal surface (on the z-plane) with a coefficient of friction, f =0.4. Assuming 10% porosity, use an appropriate density, ρ, to answer the following: (a) ...
... Stress and Friction 4. Consider a block of vesicular basalt that is 3 m long in each x, y, and z directions. The block is sitting on a rough horizontal surface (on the z-plane) with a coefficient of friction, f =0.4. Assuming 10% porosity, use an appropriate density, ρ, to answer the following: (a) ...
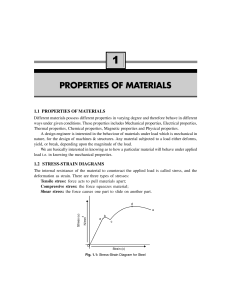
properties of materials
... below elastic limit is called creep. At high temperatures, stresses even below the elastic limit can cause some permanent deformation on stress-strain diagram. There are three stages of creep. In the first stage the material elongates rapidly but at a decreasing rate. In the second stage, the rate o ...
... below elastic limit is called creep. At high temperatures, stresses even below the elastic limit can cause some permanent deformation on stress-strain diagram. There are three stages of creep. In the first stage the material elongates rapidly but at a decreasing rate. In the second stage, the rate o ...
Polymers composed of a large number of repeating units. Isomers
... An edge dislocation is a defect where an extra half-plane of atoms is introduced mid way through the crystal, distorting nearby planes of atoms. A screw dislocation is much harder to visualize. Imagine cutting a crystal along a plane and slipping one half across the other by a lattice vector, the h ...
... An edge dislocation is a defect where an extra half-plane of atoms is introduced mid way through the crystal, distorting nearby planes of atoms. A screw dislocation is much harder to visualize. Imagine cutting a crystal along a plane and slipping one half across the other by a lattice vector, the h ...
Simplified Thermal Stress Analysis
... this. However, note that there are other causes of stress, too, such as vibrations or material faults. *Note again that this is simplified, so other sources may have a somewhat different version of this equation. ...
... this. However, note that there are other causes of stress, too, such as vibrations or material faults. *Note again that this is simplified, so other sources may have a somewhat different version of this equation. ...
Fluids - Northern Illinois University
... A change in a property like pressure depends on the view. In a Lagrangian view the total time derivative depends on position and time. An Eulerian view is just the partial derivative with time. • Points are fixed ...
... A change in a property like pressure depends on the view. In a Lagrangian view the total time derivative depends on position and time. An Eulerian view is just the partial derivative with time. • Points are fixed ...
recent developments in the design and manufacture of plastic pipes
... between stress cycle amplitude, defined here as the difference between the maximum and minimum stress (see Fig 4), and the number of cycles to failure. From these relationships it is possible to derive load factors that can be applied to the operating pressures to enable selection of an appropriate ...
... between stress cycle amplitude, defined here as the difference between the maximum and minimum stress (see Fig 4), and the number of cycles to failure. From these relationships it is possible to derive load factors that can be applied to the operating pressures to enable selection of an appropriate ...
Determining the fatigue properties of dielectric elastomers (DEs)
... switching/actuation devices, then establishing that they can accumulate a large number of cycles and exhibit resilience is essential. CER has recently developed a new DE for such applications. The material is a promising candidate for adoption in machines and instruments across a range of industry s ...
... switching/actuation devices, then establishing that they can accumulate a large number of cycles and exhibit resilience is essential. CER has recently developed a new DE for such applications. The material is a promising candidate for adoption in machines and instruments across a range of industry s ...
web 9-14
... a crack - resistance to crack propagation under load Common specimen configurations ...
... a crack - resistance to crack propagation under load Common specimen configurations ...
Classes of materials
... is an indication of a material’s ability to resist wear or scratching. This will be an important property if the equipment is being designed to handle abrasive solids, or liquids containing suspended solids which are likely to cause erosion. ...
... is an indication of a material’s ability to resist wear or scratching. This will be an important property if the equipment is being designed to handle abrasive solids, or liquids containing suspended solids which are likely to cause erosion. ...
Department of Civil Engineering
... 15 cycles @ 38 ksi, 20 cycles @ 42 ksi, 25 cycles @ 50 ksi, 20 cycles @ 60 ksi, 15 cycles @ 65 ksi, 18 cycles @ 55 ksi, 10 cycles @ 50 ksi, 20 cycles @ 40 ksi, 10 cycles @ 35 ksi Using the following S-N relationship for the steel making up the strut, determine how many days of service the strut can ...
... 15 cycles @ 38 ksi, 20 cycles @ 42 ksi, 25 cycles @ 50 ksi, 20 cycles @ 60 ksi, 15 cycles @ 65 ksi, 18 cycles @ 55 ksi, 10 cycles @ 50 ksi, 20 cycles @ 40 ksi, 10 cycles @ 35 ksi Using the following S-N relationship for the steel making up the strut, determine how many days of service the strut can ...
R-29_ChenYQ.pdf
... A general numerical approach is developed to simulate the failure process of structure or heterogeneous material, in which different local failure models are defined for different structures and materials to describe the failure of structure joint or material element. A two-parameter Weibull distrib ...
... A general numerical approach is developed to simulate the failure process of structure or heterogeneous material, in which different local failure models are defined for different structures and materials to describe the failure of structure joint or material element. A two-parameter Weibull distrib ...
estimation of subsurface residual stress depth profiles via wideband
... hence the correlation between MBN properties and surface residual stresses. By analyzing a wider range of frequencies the effective maximum depth of emission of a MBN signal can be estimated. As a result, an approximate MBN-Depth relationship can be drawn. Approximate MBN-Depth relationships are cal ...
... hence the correlation between MBN properties and surface residual stresses. By analyzing a wider range of frequencies the effective maximum depth of emission of a MBN signal can be estimated. As a result, an approximate MBN-Depth relationship can be drawn. Approximate MBN-Depth relationships are cal ...
History and Current Status of the Plastics Industry
... Introduction Normal and Shear Stresses Direct Normal Stresses Direct Shear Stresses Stresses on an Inclined Plane ...
... Introduction Normal and Shear Stresses Direct Normal Stresses Direct Shear Stresses Stresses on an Inclined Plane ...
Ch 1: Engineering materials
... relevant specific property (property/density) of the composite is better than conventional material E.g. specific strength (strength/density), specific elastic modulus ( elastic modulus/density) Efficient use of composite can be achieved by tailoring the material for the application E.g., to achieve ...
... relevant specific property (property/density) of the composite is better than conventional material E.g. specific strength (strength/density), specific elastic modulus ( elastic modulus/density) Efficient use of composite can be achieved by tailoring the material for the application E.g., to achieve ...
AE 1350
... divided by its original length/size. • Young’s Modulus, E: Stress/Strain • I : Moment of inertia of the cross section • A rod of length L will buckle if the critical load exceeds p2EI/L2 ...
... divided by its original length/size. • Young’s Modulus, E: Stress/Strain • I : Moment of inertia of the cross section • A rod of length L will buckle if the critical load exceeds p2EI/L2 ...
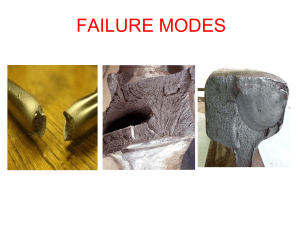
Failure Modes
... Fatigue: Cracks are initiated at little defects & propagate step wise through the component . Fatigue is a form of failure occurs in materials subjected to fluctuating stresses. • The term fatigue is used because this type of failure normally occurs after a lengthy period of repeated stress cycling ...
... Fatigue: Cracks are initiated at little defects & propagate step wise through the component . Fatigue is a form of failure occurs in materials subjected to fluctuating stresses. • The term fatigue is used because this type of failure normally occurs after a lengthy period of repeated stress cycling ...
Homework 37-40
... A metal has the yield strength Y under the uniaxial stress state. Load a sheet of this metal into a biaxial stress state, 1 in the x-direction and 2 in the y-direction. The two stress components can have different magnitudes, and can be either tensile or compressive. All the other stress compon ...
... A metal has the yield strength Y under the uniaxial stress state. Load a sheet of this metal into a biaxial stress state, 1 in the x-direction and 2 in the y-direction. The two stress components can have different magnitudes, and can be either tensile or compressive. All the other stress compon ...
Fatigue (material)

In materials science, fatigue is the weakening of a material caused by repeatedly applied loads. It is the progressive and localized structural damage that occurs when a material is subjected to cyclic loading. The nominal maximum stress values that cause such damage may be much less than the strength of the material typically quoted as the ultimate tensile stress limit, or the yield stress limit.Fatigue occurs when a material is subjected to repeated loading and unloading. If the loads are above a certain threshold, microscopic cracks will begin to form at the stress concentrators such as the surface, persistent slip bands (PSBs), and grain interfaces. Eventually a crack will reach a critical size, the crack will propagate suddenly, and the structure will fracture. The shape of the structure will significantly affect the fatigue life; square holes or sharp corners will lead to elevated local stresses where fatigue cracks can initiate. Round holes and smooth transitions or fillets will therefore increase the fatigue strength of the structure.