* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanical Principles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
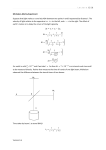
Unit 5: Learning hours: NQF level 4: Mechanical Principles 60 BTEC Higher National - H2 Description of unit This unit covers an extended range of mechanical principles which underpin the design and operation of mechanical engineering systems. It includes strengths of materials and mechanics of machines. The aim of the unit is to provide a firm foundation for work in engineering design and a basis for more advanced study. Summary of learning outcomes To achieve this unit a learner must: 1 Analyse complex loading systems 2 Investigate the behaviour of loaded beams and cylinders 3 Analyse power transmission system elements 4 Investigate the dynamics of rotating systems. 81950028 Created on 11/1/2004 10:53:00 AM 1 Content 1 Complex loading systems Relationship: definition of Poisson's Ratio; typical values of Poisson's Ratio for common engineering materials Two and three-dimensional loading: expressions for strain in the x, y and zdirections; calculation of changes in dimensions Volumetric strain: expression for volumetric strain; calculation of volume change Elastic constants: definition of Bulk Modulus; relationship between Modulus of Elasticity; Shear Modulus; Bulk Modulus and Poisson's Ratio for an elastic material 2 Loaded beams and cylinders Relationships: slope: i deflection y 1 Mdx E1 1 Mdxdx E1 Loaded beams: slope and deflection for loaded beams (eg cantilever beams carrying a concentrated load at the free end or a uniformly distributed load over the entire length, simply supported beams carrying a central concentrated load or a uniformly distributed load over the entire length) Stresses in thin-walled pressure vessels: circumferential hoop stress and longitudinal stress in cylindrical and spherical pressure vessels subjected to internal and external pressure (eg compressed-air receivers, boiler steam drums, submarine hulls, condenser casings); factor of safety; joint efficiency Stresses in thick-walled cylinders: circumferential hoop stress, longitudinal stress and radial stress in thick-walled cylinders subjected to pressure (eg hydraulic cylinders, extrusion dies, gun barrels); Lame's theory; use of boundary conditions and distribution of stress in the cylinder walls 81950028 Created on 11/1/2004 10:53:00 AM 2 3 Power transmission Belt drives: flat and v-section belts; limiting coefficient friction; limiting slack and tight side tensions; initial tension requirements; maximum power transmitted Friction clutches: flat single and multi-plate clutches; conical clutches; coefficient of friction; spring force requirements; maximum power transmitted by constant wear and constant pressure theories; validity of theories Gear trains: simple, compound and epicycle gear trains; velocity ratios; torque, speed and power relationships; efficiency; fixing torques 4 Dynamics of rotating systems Single and multi-link mechanisms: slider crank and three/four bar mechanisms; production of vector diagrams and determination of relationships between velocity, acceleration, power and efficiency Balancing: single plane and multi-plane rotating mass systems; Dalby's method for determination of out-of-balance forces and couples and the required balancing masses Flywheels: angular momentum; kinetic energy; coefficient of fluctuation of speed; coefficient of fluctuation of energy; calculation of flywheel mass/dimensions to give required operating conditions Effects of coupling: conservation of angular momentum; energy loss due to coupling; final common rotational speed 81950028 Created on 11/1/2004 10:53:00 AM 3 Outcomes and assessment criteria 81950028 Created on 11/1/2004 10:53:00 AM 4 Guidance Delivery This unit may be delivered as a stand-alone package or integrated into other programme units. If it is delivered in an integrated way, care must be taken in the tracking of evidence for the outcomes. Wherever possible, a practical approach should be adopted. Effort should be made to identify the relevance of the principles covered to engineering applications and system design. Assessment Evidence of outcomes may be in the form of assignments, laboratory notes, solutions to applied problems or the results of unseen, timed tests/examinations. Evidence is likely to be at outcome level in order to provide maximum flexibility of delivery. Evidence may be accumulated by learners building a portfolio of activities or by a tutor-led combination of tests and assignments. In either case, the evidence must be authentic, relevant and sufficient to justify the grade awarded. Links This unit can be linked with the mathematics and mechanical applications units in the programme. Entry requirements for this unit are at the discretion of the centre. However, it is advised that learners should have completed the BTEC National unit in Mechanical Principles or equivalent. Resources Sufficient laboratory/test equipment should be available to support a range of practical investigations. Appropriate software packages should also be used wherever possible to verify solutions to problems and system behaviour (for example, stress analysis). Support materials Textbooks Hannah J and Hillier M J -Applied Mechanics (Longman, 1995) ISBN 0582256321 Hannah J and Hillier M J - Mechanical Engineering Science (Pearson, 1999) ISBN 0582326753 Tooley M and Dingle L - Higher National Engineering (Butterworth-Heinemann, 1999) ISBN 0750646292 81950028 Created on 11/1/2004 10:53:00 AM 5