Al- Balqa Applied University Al-huson University College Dept. of
... 17- To access the services of operating system, the interface is provided by the A) system calls B) API C) library D) assembly instructions 18- Which one of the following is not true? A) kernel is the program that constitutes the central core of the operating system B) kernel is the first part of op ...
... 17- To access the services of operating system, the interface is provided by the A) system calls B) API C) library D) assembly instructions 18- Which one of the following is not true? A) kernel is the program that constitutes the central core of the operating system B) kernel is the first part of op ...
Lecture7
... been assigned a direct byte-for-byte correlation with some portion of a file or file-like resource. This resource could be a file physically present on-disk, or a device, shared memory object, or other resource that the OS can reference through a file descriptor. Memory-mapped I/O uses the same addr ...
... been assigned a direct byte-for-byte correlation with some portion of a file or file-like resource. This resource could be a file physically present on-disk, or a device, shared memory object, or other resource that the OS can reference through a file descriptor. Memory-mapped I/O uses the same addr ...
Operating System Functions
... •You computer only has a limited amount of Memory (for example 4gb) •The operating system has something built in known as a memory manager. •When you open, and are working on an application it is stored in the RAM (memory) ...
... •You computer only has a limited amount of Memory (for example 4gb) •The operating system has something built in known as a memory manager. •When you open, and are working on an application it is stored in the RAM (memory) ...
ppt
... Exports small no of abstractions including threads, address space and communication channels Application specific extensions occur at or above the kernel level interface Needs large modifications even for small extensibility ...
... Exports small no of abstractions including threads, address space and communication channels Application specific extensions occur at or above the kernel level interface Needs large modifications even for small extensibility ...
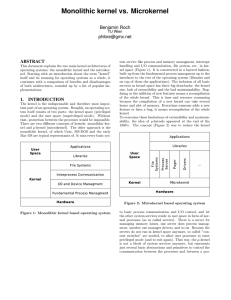
Monolithic kernel vs. Microkernel
... sent to the hardware. Monolithic kernels (and most of the first generation µ-kernels) run device drivers inside the kernel space. Hardware interrupts are directly handled by kernel processes. To add or change features provided by the hardware, all layers above the changed layer in the monolithic ker ...
... sent to the hardware. Monolithic kernels (and most of the first generation µ-kernels) run device drivers inside the kernel space. Hardware interrupts are directly handled by kernel processes. To add or change features provided by the hardware, all layers above the changed layer in the monolithic ker ...
Microkernel Operating Systems
... Fault injection: simulate faults representative to common programming errors in operating system code Goal: Show that common OS errors in a properly isolated extension cannot propagate and damage the system. Method: Inject faults into an extension in order to induce a failure, and observe how th ...
... Fault injection: simulate faults representative to common programming errors in operating system code Goal: Show that common OS errors in a properly isolated extension cannot propagate and damage the system. Method: Inject faults into an extension in order to induce a failure, and observe how th ...
Working with Images - Faculty of Computer Science and
... – Lacks support for older Windows and MS-DOS software and hardware – Complex to learn and use – Requires more memory and processing power ...
... – Lacks support for older Windows and MS-DOS software and hardware – Complex to learn and use – Requires more memory and processing power ...
CIS 170 – Understanding Operating Systems
... List the responsibilities of the file manager Describe the differences in sequential versus direct access file organization methods Evaluate and compare features of operating systems for the purpose of selecting an appropriate operating system for given tasks Describe differences in operating system ...
... List the responsibilities of the file manager Describe the differences in sequential versus direct access file organization methods Evaluate and compare features of operating systems for the purpose of selecting an appropriate operating system for given tasks Describe differences in operating system ...
pdf
... – The Septium has no interrupts, traps or exceptions, supports only physical addressing and uses only programmed I/O. – The technical writers are really happy as well, because the desi gn specification fits on a single page. ...
... – The Septium has no interrupts, traps or exceptions, supports only physical addressing and uses only programmed I/O. – The technical writers are really happy as well, because the desi gn specification fits on a single page. ...
Operating systems
... application programs. They perform basic tasks, such as recognizing input from the keyboard, sending output to the display screen, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers. For large systems, the operating system has even ...
... application programs. They perform basic tasks, such as recognizing input from the keyboard, sending output to the display screen, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers. For large systems, the operating system has even ...
I. Introduction, system calls, dual mode
... OS provides uniform, logical view of information storage – Abstracts physical properties to a logical storage unit - file – Each medium is controlled by a device (i.e., disk drive, tape drive) ...
... OS provides uniform, logical view of information storage – Abstracts physical properties to a logical storage unit - file – Each medium is controlled by a device (i.e., disk drive, tape drive) ...
CS 330 – Operating Systems
... 2. Describe classes of operating systems, roles of an operating system, and the services an operating system provides under each role to applications and users. 3. Understand process and thread concepts and how an operating system manages processes. 4. Explain issues in concurrency and mutual exc ...
... 2. Describe classes of operating systems, roles of an operating system, and the services an operating system provides under each role to applications and users. 3. Understand process and thread concepts and how an operating system manages processes. 4. Explain issues in concurrency and mutual exc ...
Chapter 1 Computer Basics
... • System software deals with the physical complexities of computer hardware. It consists of four kinds of programs: operating systems, utilities, device drivers, and language translators. • System software tells the computer – how to interpret data and instructions; – how to communicate with periphe ...
... • System software deals with the physical complexities of computer hardware. It consists of four kinds of programs: operating systems, utilities, device drivers, and language translators. • System software tells the computer – how to interpret data and instructions; – how to communicate with periphe ...
Appendix A-Linux_cs3
... "Runlevel" defines the state of the machine after boot. Different runlevels are typically assigned to: ...
... "Runlevel" defines the state of the machine after boot. Different runlevels are typically assigned to: ...
IES VILLABLANCA TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT Name
... multi-tasking Applications and programming languages 1.Which of the following is not an application? MP3 file web browser word processor 2.Which of the following controls the loading of programs and memory allocation? utilities operating system browser 3.A disk defragmenter is an example of which ty ...
... multi-tasking Applications and programming languages 1.Which of the following is not an application? MP3 file web browser word processor 2.Which of the following controls the loading of programs and memory allocation? utilities operating system browser 3.A disk defragmenter is an example of which ty ...
XOberon Operating System
... module loader, stacks pool, memory mapped input/output and DMA. Each of these blocks are managed differently based on its characteristics and is tuned for optimal performance. Many of the memory related problems are now solved by this memory management scheme, bringing reliability and more functiona ...
... module loader, stacks pool, memory mapped input/output and DMA. Each of these blocks are managed differently based on its characteristics and is tuned for optimal performance. Many of the memory related problems are now solved by this memory management scheme, bringing reliability and more functiona ...
Operating System Services
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface ...
... Programming interface to the services provided by the OS Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface ...
PDF
... (a) You have just installed a new webcam for your laptop. In order to use the webcam, you must install both a device driver and a chat application. Describe the purposes of and differences between these two pieces of software. (b) While installing the driver, the operating system asks you for admini ...
... (a) You have just installed a new webcam for your laptop. In order to use the webcam, you must install both a device driver and a chat application. Describe the purposes of and differences between these two pieces of software. (b) While installing the driver, the operating system asks you for admini ...
CSc 352: Systems Programming & Unix
... • Unix is an operating system – sits between the hardware and the user/applications – provides high-level abstractions (e.g., files) and services (e.g., multiprogramming) ...
... • Unix is an operating system – sits between the hardware and the user/applications – provides high-level abstractions (e.g., files) and services (e.g., multiprogramming) ...
hw1_wet
... file (syscall_tags.h). This file shouldn't be put inside the kernel but as a separate file. When you test your system calls you need to include this file in your user mode test program. ...
... file (syscall_tags.h). This file shouldn't be put inside the kernel but as a separate file. When you test your system calls you need to include this file in your user mode test program. ...
What is an Operating System?
... – Secondary storage limited or absent, data stored in shortterm memory, or read-only memory (ROM) – Conflicts with time-sharing systems, not supported by general-purpose operating systems. ...
... – Secondary storage limited or absent, data stored in shortterm memory, or read-only memory (ROM) – Conflicts with time-sharing systems, not supported by general-purpose operating systems. ...
Introduction to Object Technology
... – Only a few essential functions are assigned to the kernel (address space, inter-process communication, and basic scheduling) – Other OS services are provided by processes (servers) that run in user mode ...
... – Only a few essential functions are assigned to the kernel (address space, inter-process communication, and basic scheduling) – Other OS services are provided by processes (servers) that run in user mode ...