follow up solids
... 1. What atoms are involved and their electronic configuration? 2. What types of chemical bonds are formed? 3. How are the atoms arranged in the crystal structure? 4. What is the symmetry of the crystal? 5. Do these arrangements promote certain mechanisms for electronic or atomic motions? 6. How do ...
... 1. What atoms are involved and their electronic configuration? 2. What types of chemical bonds are formed? 3. How are the atoms arranged in the crystal structure? 4. What is the symmetry of the crystal? 5. Do these arrangements promote certain mechanisms for electronic or atomic motions? 6. How do ...
10 - PSU MNE
... Once specimen necking starts, the material fails, because the cross-sectional area in the necked region becomes progressively smaller, and thus no additional load is needed to cause further deformation. The stress at which necking occurs is called the ultimate tensile strength of the material or U ...
... Once specimen necking starts, the material fails, because the cross-sectional area in the necked region becomes progressively smaller, and thus no additional load is needed to cause further deformation. The stress at which necking occurs is called the ultimate tensile strength of the material or U ...
Metal
... Crystal systems; BCC, FCC, HCP atomic packing crystallographic directions, planes ● QUIZ (will start at 14:50 p.m. !) ...
... Crystal systems; BCC, FCC, HCP atomic packing crystallographic directions, planes ● QUIZ (will start at 14:50 p.m. !) ...
Concepts of stress and strain
... Modulus of elasticity E is proportional to (dF/dr)r Slope of stress strain plot (which is proportional to the elastic modulus) depends on bond strength of metal ...
... Modulus of elasticity E is proportional to (dF/dr)r Slope of stress strain plot (which is proportional to the elastic modulus) depends on bond strength of metal ...
Thermally activated processes in materials probed by nanoindentation
... Nanoindentation experiments are widely used for assessing the local mechanical properties of materials. In recent years some new exciting developments were established for also analyzing thermally activated processes during deformation using indentation based techniques, namely nanoindentation strai ...
... Nanoindentation experiments are widely used for assessing the local mechanical properties of materials. In recent years some new exciting developments were established for also analyzing thermally activated processes during deformation using indentation based techniques, namely nanoindentation strai ...
Downloadable - University of New Hampshire
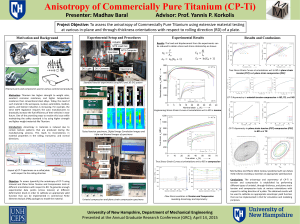
... Motivation: Titanium has higher strength to weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and higher temperature resistance than conventional steel alloys. Today, the need of such material in the aerospace, nuclear, automobile, medical, sports, and fashion industries is increasing. For example, the ...
... Motivation: Titanium has higher strength to weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and higher temperature resistance than conventional steel alloys. Today, the need of such material in the aerospace, nuclear, automobile, medical, sports, and fashion industries is increasing. For example, the ...
Radioactive isotopes in solid state physics
... Doping of semiconductors Progress in semiconductor technology is driven by two requirements: Developing new materials with unique optical or electrical features and reducing the size of the individual constituents of an integrated device. These requirements demand a thorough understanding and contro ...
... Doping of semiconductors Progress in semiconductor technology is driven by two requirements: Developing new materials with unique optical or electrical features and reducing the size of the individual constituents of an integrated device. These requirements demand a thorough understanding and contro ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids
... are the same for both FCC and HCP crystal structures. • We can predict the density of a material, provided we know the atomic weight, atomic radius, and crystal geometry (e.g., FCC, BCC, HCP). • Crystallographic points, directions and planes are specified in terms of indexing schemes. Crystallograph ...
... are the same for both FCC and HCP crystal structures. • We can predict the density of a material, provided we know the atomic weight, atomic radius, and crystal geometry (e.g., FCC, BCC, HCP). • Crystallographic points, directions and planes are specified in terms of indexing schemes. Crystallograph ...
Bragg`s second law.
... • Threading dislocations may be shown (e.g. by CL) to act as non-radiative recombination centres. • For efficient light emission, dislocation densities should be less than ~103 cm-2 in GaAs and other III-V semiconductors. • Some microstructural feature of the InGaN QW appears to prevent the carriers ...
... • Threading dislocations may be shown (e.g. by CL) to act as non-radiative recombination centres. • For efficient light emission, dislocation densities should be less than ~103 cm-2 in GaAs and other III-V semiconductors. • Some microstructural feature of the InGaN QW appears to prevent the carriers ...
Heat Treating of Non Ferous Alloys
... deformation. Traditional Brasses and Bronzes fall into this category. It is to be noted that these alloys are not heat treatable. ...
... deformation. Traditional Brasses and Bronzes fall into this category. It is to be noted that these alloys are not heat treatable. ...
Structural Geology Stress and Strain
... • Time – Great amount of time allows plastic deformation to occur if force is applied continually. Little time doesn’t allow atoms to adjust so brittle failure is the result ...
... • Time – Great amount of time allows plastic deformation to occur if force is applied continually. Little time doesn’t allow atoms to adjust so brittle failure is the result ...
Study The Effect Of Sulfur Atoms On The Electronic Structure For
... where in the present work it equal to -447595.715 eV and the best lattice constant is 5.18A° while its experimental value is 5.65A° in the bulk model [Madelong, 1982]. Figure (3) shows that the total energy with the surface has the same behavior for the core with decreasing the values of total ener ...
... where in the present work it equal to -447595.715 eV and the best lattice constant is 5.18A° while its experimental value is 5.65A° in the bulk model [Madelong, 1982]. Figure (3) shows that the total energy with the surface has the same behavior for the core with decreasing the values of total ener ...
Study The Effect Of Sulfur Atoms On The Electronic Structure
... cause the increase of the total energy. The stability of the GaAs nanocrystal at the equilibrium lattice is due to the equality of attraction and repulsion forces at this point where in the present work it equal to -447595.715 eV and the best lattice constant is 5.18A° while its experimental value ...
... cause the increase of the total energy. The stability of the GaAs nanocrystal at the equilibrium lattice is due to the equality of attraction and repulsion forces at this point where in the present work it equal to -447595.715 eV and the best lattice constant is 5.18A° while its experimental value ...
Crystal structure
... at one of the unit cell corners; each of the x, y, and z axes coincides with one of the three parallelepiped edges that extend from this corner, as illustrated in Figure 1.2. The unit cell geometry is completely defined in terms of six parameters: the three edge lengths a, b, and c, and the three in ...
... at one of the unit cell corners; each of the x, y, and z axes coincides with one of the three parallelepiped edges that extend from this corner, as illustrated in Figure 1.2. The unit cell geometry is completely defined in terms of six parameters: the three edge lengths a, b, and c, and the three in ...
Final program with abstracts - Laboratoire de Glaciologie et
... very interesting geological and analog material, like metals it is cubic with many potential slip systems. The strength of the slip systems in NaCl is very different so the material has high plastic anisotropy, similar to most minerals and ice. NaCl is also a type material for “subgrain rotation” “g ...
... very interesting geological and analog material, like metals it is cubic with many potential slip systems. The strength of the slip systems in NaCl is very different so the material has high plastic anisotropy, similar to most minerals and ice. NaCl is also a type material for “subgrain rotation” “g ...
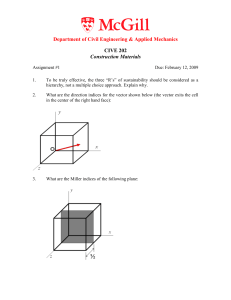
Department of Civil Engineering
... If the atoms in a material exhibiting a BCC configuration in a cubic unit cell have an atomic radius of 0.143 mm, calculate the volume of its unit cell in cubic meters. ...
... If the atoms in a material exhibiting a BCC configuration in a cubic unit cell have an atomic radius of 0.143 mm, calculate the volume of its unit cell in cubic meters. ...
Lecture 11 DFT for periodic crystalline solids CHEM6085: Density
... • Bloch’s theorem states that ...
... • Bloch’s theorem states that ...
Atomic arrangment
... Zinc Blende structure (ZnS) (covalent, or ionic when r/R<0.414) Exactly like diamond structure but with two elements Instead of one. This structure is typical for covalent materials and ionic materials with very small cations. The Sulfur atoms enters to tetrahedral sites in the FCC Zink lattice. Su ...
... Zinc Blende structure (ZnS) (covalent, or ionic when r/R<0.414) Exactly like diamond structure but with two elements Instead of one. This structure is typical for covalent materials and ionic materials with very small cations. The Sulfur atoms enters to tetrahedral sites in the FCC Zink lattice. Su ...
Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids
... Si-O bonds are very strong. Silicate structures vary in different arrangements as each oxygen atom requires an extra electron to achieve a stable electronic structure. The arrangements could be [1] or [2] or [3] dimensional structures. ...
... Si-O bonds are very strong. Silicate structures vary in different arrangements as each oxygen atom requires an extra electron to achieve a stable electronic structure. The arrangements could be [1] or [2] or [3] dimensional structures. ...
Defect accumulation behaviour in hcp metals and alloys - PolyU
... microstructure, and their dual function as both sources and sinks of point defects have to be taken into account. At low temperatures they are predominantly sinks which mainly acts as recombination centers, and at high temperatures they are predominantly sources, particularly the PVCs. The dierence ...
... microstructure, and their dual function as both sources and sinks of point defects have to be taken into account. At low temperatures they are predominantly sinks which mainly acts as recombination centers, and at high temperatures they are predominantly sources, particularly the PVCs. The dierence ...
Crystal Structures
... • Waves REFLECTED from the crystal planes INTERFERE with each other * In a manner that depends on the SPACING (d) of the crystal planes * The interference also depends on the WAVELENGTH () of the waves And the ANGLE () at which they are incident on the crystal * Consider the case of waves reflec ...
... • Waves REFLECTED from the crystal planes INTERFERE with each other * In a manner that depends on the SPACING (d) of the crystal planes * The interference also depends on the WAVELENGTH () of the waves And the ANGLE () at which they are incident on the crystal * Consider the case of waves reflec ...
GEOLOGY PPT
... ◦ Minerals are crystalline structures made from a mixture of different elemental compounds. ◦ The shape of a crystal is based on the atomic structure of these elemental building blocks. ◦ Atoms within a mineral are arranged in an ordered geometric pattern called a "motif" which determines its "cryst ...
... ◦ Minerals are crystalline structures made from a mixture of different elemental compounds. ◦ The shape of a crystal is based on the atomic structure of these elemental building blocks. ◦ Atoms within a mineral are arranged in an ordered geometric pattern called a "motif" which determines its "cryst ...
Lecture 7 Mechanical Properties of Rocks
... on any given plane besides the principal stresses. In general, this is a three dimensional problem and can be done using mathematical tensors and vectors. In a special case where we can assume that the intermediate and minimum stresses are equal (for example below the ground surface), we can work ...
... on any given plane besides the principal stresses. In general, this is a three dimensional problem and can be done using mathematical tensors and vectors. In a special case where we can assume that the intermediate and minimum stresses are equal (for example below the ground surface), we can work ...
X-ray Diffraction
... Solid matter can be described as: Amorphous: The atoms are arranged in a random way similar to the disorder we find in a liquid. Glasses are amorphous materials. Crystalline: The atoms are arranged in a regular pattern, and there is as smallest volume element that by repetition in three dimensions d ...
... Solid matter can be described as: Amorphous: The atoms are arranged in a random way similar to the disorder we find in a liquid. Glasses are amorphous materials. Crystalline: The atoms are arranged in a regular pattern, and there is as smallest volume element that by repetition in three dimensions d ...
Dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation is a crystallographic defect, or irregularity, within a crystal structure. The presence of dislocations strongly influences many of the properties of materials. The theory describing the elastic fields of the defects was originally developed by Vito Volterra in 1907, but the term 'dislocation' to refer to a defect on the atomic scale was coined by G. I. Taylor in 1934. Some types of dislocations can be visualized as being caused by the termination of a plane of atoms in the middle of a crystal. In such a case, the surrounding planes are not straight, but instead they bend around the edge of the terminating plane so that the crystal structure is perfectly ordered on either side. The analogy with a stack of paper is apt: if half a piece of paper is inserted in a stack of paper, the defect in the stack is only noticeable at the edge of the half sheet.There are two primary types: edge dislocations and screw dislocations. Mixed dislocations are intermediate between these.Mathematically, dislocations are a type of topological defect, sometimes called a soliton. The mathematical theory explains why dislocations behave as stable particles: they can be moved around, but they maintain their identity as they move. Two dislocations of opposite orientation, when brought together, can cancel each other, but a single dislocation typically cannot ""disappear"" on its own.