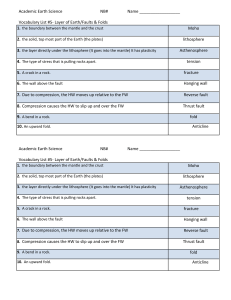
Types of Faults and Plate Tectonics
... • Occurs when two tectonic plates slide past each other • Fault that occurs at this boundary is called a strike-slip fault KNOW THIS IMAGE! ...
... • Occurs when two tectonic plates slide past each other • Fault that occurs at this boundary is called a strike-slip fault KNOW THIS IMAGE! ...
Joints and veins
... • 3 principal vectors: σ1, σ2, and σ3 at right angles to each other • σ 1 ≥ σ2 ≥ σ3 • σ1 is the maximum principal stress direction, σ2 is the intermediate principal stress direction, and σ3 is the minimum principal stress direction ...
... • 3 principal vectors: σ1, σ2, and σ3 at right angles to each other • σ 1 ≥ σ2 ≥ σ3 • σ1 is the maximum principal stress direction, σ2 is the intermediate principal stress direction, and σ3 is the minimum principal stress direction ...
Forces in Earth`s Crust
... rock of the crust is pushed together, compression causes reverse faults to form. It has the same structure as a normal fault, but the blocks move in the opposite directions. ...
... rock of the crust is pushed together, compression causes reverse faults to form. It has the same structure as a normal fault, but the blocks move in the opposite directions. ...
Earthquakes T. Perron – 12.001 – March 17, 2010 In our lab on
... In our lab on plate tectonics, one of the main datasets we drew on was earthquake epicenter locations and depths. We saw that both correlate strongly (though not exclusively) with plate boundary locations, and inferred that most seismicity is associated somehow with plate motions. Today we’ll examin ...
... In our lab on plate tectonics, one of the main datasets we drew on was earthquake epicenter locations and depths. We saw that both correlate strongly (though not exclusively) with plate boundary locations, and inferred that most seismicity is associated somehow with plate motions. Today we’ll examin ...
strike and dip
... • Because of their large size and linear nature, many strike-slip faults produce a trace that is visible over a great distance • Crushed and broken rocks produced during faulting are more easily eroded, often producing linear valleys or troughs ...
... • Because of their large size and linear nature, many strike-slip faults produce a trace that is visible over a great distance • Crushed and broken rocks produced during faulting are more easily eroded, often producing linear valleys or troughs ...
Unit 2 Chapter 5 Study Guide Answers
... existed as one supercontinent. 2. Why was Wegener’s theory of continental drift rejected? He could not give a cause as to what force could move the continents. 3. Why is old oceanic crust denser than new oceanic crust? It is saturated with water and is cooler 4. What is a rift valley and where does ...
... existed as one supercontinent. 2. Why was Wegener’s theory of continental drift rejected? He could not give a cause as to what force could move the continents. 3. Why is old oceanic crust denser than new oceanic crust? It is saturated with water and is cooler 4. What is a rift valley and where does ...
Z SR Midterm Test Review
... Draw and label an example of sea floor spreading in the box below. Be sure to include and label: molten material (magma) convection current motion and direction mid-ocean ridge crust direction direction of rock/crust movement crust, lithosphere, asthenosphere, lower mantle location of ...
... Draw and label an example of sea floor spreading in the box below. Be sure to include and label: molten material (magma) convection current motion and direction mid-ocean ridge crust direction direction of rock/crust movement crust, lithosphere, asthenosphere, lower mantle location of ...
Lecture 6 Structural Geology, Gettysburg NMP, Chickamauga and Chattanooga NMP
... the collision of African and North American plates and the closing of the Iapetus ...
... the collision of African and North American plates and the closing of the Iapetus ...
Forces in the Crust Day1
... AIM: Describe the types of stress and the land features (faults,uplift,folds) that result from forces (stress) in the Earth’s crust? OBJ: Given notes and activity sheet SWBAT describe the types of stress and the land features (faults, uplift, folds) that result from forces (stress) in the Earth’s cr ...
... AIM: Describe the types of stress and the land features (faults,uplift,folds) that result from forces (stress) in the Earth’s crust? OBJ: Given notes and activity sheet SWBAT describe the types of stress and the land features (faults, uplift, folds) that result from forces (stress) in the Earth’s cr ...
Synthetic Seismicity of Multiple Interacting Faults and its use for
... • What is the probability of two (or more ) large earthquakes in the Wellington region within a few years of one another? • What sort of shaking should we expect from a large earthquake on the Wellington Fault? ...
... • What is the probability of two (or more ) large earthquakes in the Wellington region within a few years of one another? • What sort of shaking should we expect from a large earthquake on the Wellington Fault? ...
Normal Fault
... it may cause a lot of damage because of the short distance that it has to travel to reach the surface. There isn’t a lot of crust above it to vibrate, so they are still strong. • The deeper the hypocenter is, the more material on top needs to be vibrated by the energy from the earthquake, so it redu ...
... it may cause a lot of damage because of the short distance that it has to travel to reach the surface. There isn’t a lot of crust above it to vibrate, so they are still strong. • The deeper the hypocenter is, the more material on top needs to be vibrated by the energy from the earthquake, so it redu ...
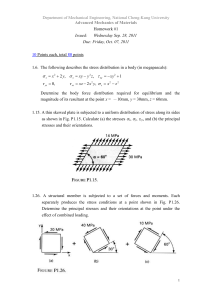
HW1
... Determine the principal stresses and their orientations at the point under the effect of combined loading. ...
... Determine the principal stresses and their orientations at the point under the effect of combined loading. ...
File
... 7.5 – Recognize that lithospheric plates on the scale of continents and oceans continually move at rates of centimeters per year 7.6 – Describe the relationship between plate movements and earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading ...
... 7.5 – Recognize that lithospheric plates on the scale of continents and oceans continually move at rates of centimeters per year 7.6 – Describe the relationship between plate movements and earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading ...
IE 2.1 Earth`s Crust in Motion
... • Friction: a force that opposes the motion of one surface as it moves across another What about the surfaces causes friction? – It exist because surfaces are not perfectly smooth. ...
... • Friction: a force that opposes the motion of one surface as it moves across another What about the surfaces causes friction? – It exist because surfaces are not perfectly smooth. ...
Faults brochure Een revised 9
... • Form when the hanging wall moves up. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional, pushing the sides together. ...
... • Form when the hanging wall moves up. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional, pushing the sides together. ...
Earthquakes
... 1. Earthquakes are vibrations of the earth’s crust. a. Earthquakes occur when rocks under stress suddenly shift along a fault. b. The area along a fault where motion first occurs is called the focus of an earthquake. i. When an earthquake occurs seismic waves radiate outward in all directions from t ...
... 1. Earthquakes are vibrations of the earth’s crust. a. Earthquakes occur when rocks under stress suddenly shift along a fault. b. The area along a fault where motion first occurs is called the focus of an earthquake. i. When an earthquake occurs seismic waves radiate outward in all directions from t ...
Elastic Rebound Theory The Earthquake Cycle
... the relative plate motion rate is 25 mm per year but there is no sudden jump in velocity across the plateboundary fault ...
... the relative plate motion rate is 25 mm per year but there is no sudden jump in velocity across the plateboundary fault ...