The Nature and Cause of Earthquakes
... An example of shaking in southern California due to the 1999 M7.4 Izmit earthquake in Turkey. [T. Tanimoto, UCSB] ...
... An example of shaking in southern California due to the 1999 M7.4 Izmit earthquake in Turkey. [T. Tanimoto, UCSB] ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... Types of Faults • Strike-slip faults have movement that is predominantly horizontal and parallel to the strike of the fault plane – A viewer looking across to the other side of a right-lateral strike-slip fault would observe it to be offset to their right – A viewer looking across to the other side ...
... Types of Faults • Strike-slip faults have movement that is predominantly horizontal and parallel to the strike of the fault plane – A viewer looking across to the other side of a right-lateral strike-slip fault would observe it to be offset to their right – A viewer looking across to the other side ...
Geology: Earthquake Concepts ANSWER KEY
... Instructions: The crust of the earth is constantly moving. This movement can create stress that can change the shape of a body of rock. Sometimes stress builds up between two bodies of rock and they can slide past, over, or under one another fairly quickly. This sudden release of stress can cause ea ...
... Instructions: The crust of the earth is constantly moving. This movement can create stress that can change the shape of a body of rock. Sometimes stress builds up between two bodies of rock and they can slide past, over, or under one another fairly quickly. This sudden release of stress can cause ea ...
Elastic rebound acti..
... Step 1. Build a fence across a fault. Step 2. The plates move past each other at a given rate. The fault is locked, so the crust deforms elsatically. The fence is bent in relation to the elastic deformation of the crust. Step 3. The strain from the fault exceeds the strength of the fault and the fau ...
... Step 1. Build a fence across a fault. Step 2. The plates move past each other at a given rate. The fault is locked, so the crust deforms elsatically. The fence is bent in relation to the elastic deformation of the crust. Step 3. The strain from the fault exceeds the strength of the fault and the fau ...
File
... A fault is a fracture along which rock on one side has moved relative to the rock on the other side Slip is the distance that rocks on opposite sides of a fault have moved A fault zone is an area of numerous closely spaced faults ...
... A fault is a fracture along which rock on one side has moved relative to the rock on the other side Slip is the distance that rocks on opposite sides of a fault have moved A fault zone is an area of numerous closely spaced faults ...
lec11_structures_folds_faults
... measurements of ground motions between May and September 1999. Large regions of metropolitan Los Angeles are rising and falling by up to 11 cm annually, and a large portion of the city of Santa Ana is sinking at a rate of 12 mm per year. ...
... measurements of ground motions between May and September 1999. Large regions of metropolitan Los Angeles are rising and falling by up to 11 cm annually, and a large portion of the city of Santa Ana is sinking at a rate of 12 mm per year. ...
Plate Movement and Geological Events
... tectonic plate that contains oceanic lithosphere sinks and pulls the rest of the tectonic plate with it in a process called slab pull. ...
... tectonic plate that contains oceanic lithosphere sinks and pulls the rest of the tectonic plate with it in a process called slab pull. ...
Deforming the Earth`s Crust
... • Two types of deformation can occur to rocks under stress –Layers can bend when stress is applied to them –When too much stress is applied, they can reach their elastic limit and break ...
... • Two types of deformation can occur to rocks under stress –Layers can bend when stress is applied to them –When too much stress is applied, they can reach their elastic limit and break ...
Whose fault is it? Name: Block: Background: The crust can move
... buoyant asthenosphere tries to push upon a plate. If a mountain erodes and the weight lessens on the asthenosphere the area can sometimes move upwards under the buoyant force of the asthenosphere in a process called uplift. If an area is weighted the rock can deform downwards into the asthenosphere. ...
... buoyant asthenosphere tries to push upon a plate. If a mountain erodes and the weight lessens on the asthenosphere the area can sometimes move upwards under the buoyant force of the asthenosphere in a process called uplift. If an area is weighted the rock can deform downwards into the asthenosphere. ...
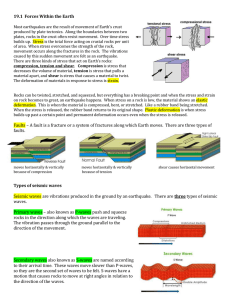
19.1-forces-within-Earth
... builds up past a certain point and permanent deformation occurs even when the stress is released. ...
... builds up past a certain point and permanent deformation occurs even when the stress is released. ...
STRESS – is the total amount of force that is placed upon crustal
... If the rocks actually break, or undergo failure, it can create fractures or faults in the rock layers. More on this in a moment. The type of rock, temperature, and pressure all influence deformation. Some rock types are more brittle or flexible and they will bend or break more easily. A rock layer ...
... If the rocks actually break, or undergo failure, it can create fractures or faults in the rock layers. More on this in a moment. The type of rock, temperature, and pressure all influence deformation. Some rock types are more brittle or flexible and they will bend or break more easily. A rock layer ...
Microfabrics of ultra-high pressure metamorphic rocks in the Dora
... In the pyrope quartzites, and locally in the Brossasco granite prominent microstructures (Chapter 3) are elongate quartz grains with sutured grain boundaries and no CPO in the matrix. These compare well to radially arranged small elongate quartz grains in inclusions in UHP minerals, and are therefor ...
... In the pyrope quartzites, and locally in the Brossasco granite prominent microstructures (Chapter 3) are elongate quartz grains with sutured grain boundaries and no CPO in the matrix. These compare well to radially arranged small elongate quartz grains in inclusions in UHP minerals, and are therefor ...
10) Folds and Faults Notes
... have two different points: a deformation zone in which they have been strained to the point where they will not return to their original shape, and a fracture point where the strain has reached a level that breaks the object in two. ...
... have two different points: a deformation zone in which they have been strained to the point where they will not return to their original shape, and a fracture point where the strain has reached a level that breaks the object in two. ...
Earth`s Stresses Convection currents fuel continental
... pulling are greatest. There are four main types of faults, normal faults, reverse faults, thrust faults, and lateral or strike slip faults, Normal Faults- occurs at an angle, where the crust is being pulled apart, one block lies above the fault (hanging wall), while the other lies below the fault (f ...
... pulling are greatest. There are four main types of faults, normal faults, reverse faults, thrust faults, and lateral or strike slip faults, Normal Faults- occurs at an angle, where the crust is being pulled apart, one block lies above the fault (hanging wall), while the other lies below the fault (f ...
EART 118 Seismotectonics
... characteristics (location, size/energy release, faulting mechanism) are obtained by analysis of seismic waves recorded by ground motion sensing instruments called seismometers. ...
... characteristics (location, size/energy release, faulting mechanism) are obtained by analysis of seismic waves recorded by ground motion sensing instruments called seismometers. ...
Earth’s Sub-Surface Processes
... Crustal rocks are pressed together Occurs at convergent boundaries Pushes rock higher up or deeper down in the crust ...
... Crustal rocks are pressed together Occurs at convergent boundaries Pushes rock higher up or deeper down in the crust ...
Aging Earth`s Layers
... Tension, compression and shearing cause crustal deformation Faults Shearing Causes transform or lateral faults Compression Causes reverse faults Tension Causes normal faults May form fault bock mountains Sharp angular and steep on one side Gradual slope on other Plateaus Flat topped May also be form ...
... Tension, compression and shearing cause crustal deformation Faults Shearing Causes transform or lateral faults Compression Causes reverse faults Tension Causes normal faults May form fault bock mountains Sharp angular and steep on one side Gradual slope on other Plateaus Flat topped May also be form ...
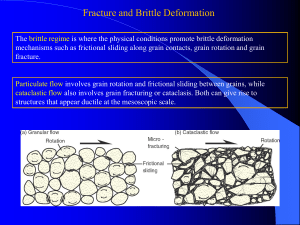
Fracture and Brittle Deformation
... don’t fractures form at 45o. When the shear stress is at a maximum the normal stress is also very high. As the angle decreases, the normal stress decreases more rapidly than the shear stress. The optimal balance between normal stress and shear stress depends on the angle of internal friction. The Co ...
... don’t fractures form at 45o. When the shear stress is at a maximum the normal stress is also very high. As the angle decreases, the normal stress decreases more rapidly than the shear stress. The optimal balance between normal stress and shear stress depends on the angle of internal friction. The Co ...
Section 19.1 Forces Within Earth
... Elastic Deformation • Elastic deformation is caused under conditions of low stress when a material is compressed, bent, or stretched. • When the stress is removed, material returns to its original shape. • Think about a rubber band. ...
... Elastic Deformation • Elastic deformation is caused under conditions of low stress when a material is compressed, bent, or stretched. • When the stress is removed, material returns to its original shape. • Think about a rubber band. ...
Deforming the Earth`s Crust
... • The two sides of a fault are known as the hanging wall and the footwall • The type of fault that forms is dependent on where the hanging and footwall are ...
... • The two sides of a fault are known as the hanging wall and the footwall • The type of fault that forms is dependent on where the hanging and footwall are ...