OS_Structure
... loaded into memory in various locations, how an individual OS use storage varies greatly. • Normally resident components are loaded into the areas of memory with the lowest addresses. • Application programs begin being loaded at a location just beyond the portion of the os in low memory. • Some OS’s ...
... loaded into memory in various locations, how an individual OS use storage varies greatly. • Normally resident components are loaded into the areas of memory with the lowest addresses. • Application programs begin being loaded at a location just beyond the portion of the os in low memory. • Some OS’s ...
Introduction to Operating Systems
... • Batch of jobs given to OS at one time. • OS optimizes resource utilization & throughput. • This was the first step in allowing multiple users to share a machine. • No real-time interaction between users and computer. CS4315 A. Berrached:CMS:UHD ...
... • Batch of jobs given to OS at one time. • OS optimizes resource utilization & throughput. • This was the first step in allowing multiple users to share a machine. • No real-time interaction between users and computer. CS4315 A. Berrached:CMS:UHD ...
Operating System Architecture and Distributed Systems
... Threads support treating of requests with varying priorities. Various types of architectures can be used in current processing: ...
... Threads support treating of requests with varying priorities. Various types of architectures can be used in current processing: ...
Module 3: Processes and Process management
... Process states: Management issues An important point to ponder is: what role does an OS play as processes migrate from one state to another? When a process is created the OS assigns it an id and also creates a data structure to record its progress. At some point in time OS makes this newly created p ...
... Process states: Management issues An important point to ponder is: what role does an OS play as processes migrate from one state to another? When a process is created the OS assigns it an id and also creates a data structure to record its progress. At some point in time OS makes this newly created p ...
Operating Systems Principles Lecture 1: Introduction
... interposed between a running program and a lowspeed device involved with the program in input/output. Example: Instead of writing directly to a printer, outputs are written to the disk. ...
... interposed between a running program and a lowspeed device involved with the program in input/output. Example: Instead of writing directly to a printer, outputs are written to the disk. ...
Unit I Introduction
... have the function to coordinate to the other parts of an OS such as : I/O Devices, Process, Memory and File Systems. • The structure of and OS could be different but in most of the time are very similar because some OS use Open Standards. ...
... have the function to coordinate to the other parts of an OS such as : I/O Devices, Process, Memory and File Systems. • The structure of and OS could be different but in most of the time are very similar because some OS use Open Standards. ...
Operating Systems
... • A timesharing system allows multiple users to interact with a computer at the same time • Multiprogramming allowed multiple processes to be active at once, which gave rise to the ability for programmers to interact with the computer system directly, while still sharing its resources • In a timesha ...
... • A timesharing system allows multiple users to interact with a computer at the same time • Multiprogramming allowed multiple processes to be active at once, which gave rise to the ability for programmers to interact with the computer system directly, while still sharing its resources • In a timesha ...
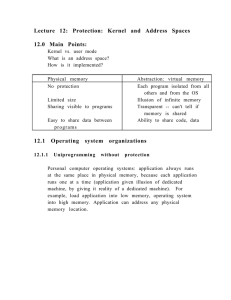
Lecture 12: Protection: Kernel and Address Spaces 12.0 Main Points
... sets processor status to kernel changes execution stack to kernel saves current program counter jumps to handler in kernel handler saves previous state of any registers it uses Context switching between programs: same as with threads, except now also save and restore pointer to translation table. To ...
... sets processor status to kernel changes execution stack to kernel saves current program counter jumps to handler in kernel handler saves previous state of any registers it uses Context switching between programs: same as with threads, except now also save and restore pointer to translation table. To ...
pdf
... can occur at any time -- causing code to execute that interferes with code that was interrupted • OS must be able to synchronize concurrent processes • This requires guaranteeing that certain instruction sequences (read-modify-write) execute atomically • One way to guarantee this is to turn off inte ...
... can occur at any time -- causing code to execute that interferes with code that was interrupted • OS must be able to synchronize concurrent processes • This requires guaranteeing that certain instruction sequences (read-modify-write) execute atomically • One way to guarantee this is to turn off inte ...
Operating systems
... History of operating system A major drawback to using a computer operator as intermediary is that the users have no interaction with their jobs once they are submitted to the operator. New operating systems were developed that allowed a program being executed to carry on a dialogue with the user ...
... History of operating system A major drawback to using a computer operator as intermediary is that the users have no interaction with their jobs once they are submitted to the operator. New operating systems were developed that allowed a program being executed to carry on a dialogue with the user ...
PowerPoint
... z Batch job issues Halt instruction z User logs off z Process executes a service request to terminate z Error and fault conditions ...
... z Batch job issues Halt instruction z User logs off z Process executes a service request to terminate z Error and fault conditions ...
Introduction
... • Inter-Processes Communication • Most modern operating systems are multiprocessing systems – Several processes can be run at the “same time” ...
... • Inter-Processes Communication • Most modern operating systems are multiprocessing systems – Several processes can be run at the “same time” ...
Chapter 1 - OS Overview
... – total amount of time – CPU time – main memory usage – secondary storage used during program execution or during billing period – use of system software – number of I/O operations & time spent waiting for I/O completion – Number of input records read, number of output records printed – number of pa ...
... – total amount of time – CPU time – main memory usage – secondary storage used during program execution or during billing period – use of system software – number of I/O operations & time spent waiting for I/O completion – Number of input records read, number of output records printed – number of pa ...
Introduction
... freed, so the next program can be loaded and executed. To improve response and utilization, few programs reside in the memory, requiring memory management. OS is responsible for the following to manage memory: • Keeping track of which parts of memory are currently being used and who is using them. • ...
... freed, so the next program can be loaded and executed. To improve response and utilization, few programs reside in the memory, requiring memory management. OS is responsible for the following to manage memory: • Keeping track of which parts of memory are currently being used and who is using them. • ...
Test Bank Chapter Three (Operating Systems)
... 7. Why is a “test-and-set” instruction included in most machine languages for CPUs designed for multitasking environments? ANSWER: The “test-and-set” instruction are useful when bits in main memory are used to record whether various nonshareable resources have been allocated because they allow memor ...
... 7. Why is a “test-and-set” instruction included in most machine languages for CPUs designed for multitasking environments? ANSWER: The “test-and-set” instruction are useful when bits in main memory are used to record whether various nonshareable resources have been allocated because they allow memor ...
Operating Systems
... Operating Systems 1. What are the basic functions of an operating system? Program execution, I/O Operation, File System Manipulation( reading and writing), Communications( between processes), Error detection ( in CPU ), Resource Allocation ( for Process ), Protection , Accounting ( which user use ho ...
... Operating Systems 1. What are the basic functions of an operating system? Program execution, I/O Operation, File System Manipulation( reading and writing), Communications( between processes), Error detection ( in CPU ), Resource Allocation ( for Process ), Protection , Accounting ( which user use ho ...
Course Title: Operating System
... explain the objectives and functions of modern operating systems. describe the logical structure of, and facilities provided by, a modern operating system. analyze the tradeoffs inherent in operating system design. differentiate between the concepts of processes, threads and multithreading. demonstr ...
... explain the objectives and functions of modern operating systems. describe the logical structure of, and facilities provided by, a modern operating system. analyze the tradeoffs inherent in operating system design. differentiate between the concepts of processes, threads and multithreading. demonstr ...
Slide 1
... • In Windows a process consists of program code, execution context ( the address space of the process plus such things as the access token) resources allocated to the process i.e. handles, one or more threads • Threads are the units of execution – they execute program code using the processes ...
... • In Windows a process consists of program code, execution context ( the address space of the process plus such things as the access token) resources allocated to the process i.e. handles, one or more threads • Threads are the units of execution – they execute program code using the processes ...
Import Settings:
... 21. Explain why an operating system can be viewed as a resource allocator. 22. Explain the purpose of an interrupt vector. 23. What is a bootstrap program, and where is it stored? 24. What role do device controllers and device drivers play in a computer system? 25. Why are clustered systems consider ...
... 21. Explain why an operating system can be viewed as a resource allocator. 22. Explain the purpose of an interrupt vector. 23. What is a bootstrap program, and where is it stored? 24. What role do device controllers and device drivers play in a computer system? 25. Why are clustered systems consider ...
Final Exam - soe.ucsc.edu
... a. Shared-key cryptography stll requires that some information be sent unencrypted b. Public-key cryptography doesn’t employ a secret key c. Public-key cryptography can also be used to solve the authentication problem 32. A Trojan Horse is: a. A special password that bypasses the regular password sy ...
... a. Shared-key cryptography stll requires that some information be sent unencrypted b. Public-key cryptography doesn’t employ a secret key c. Public-key cryptography can also be used to solve the authentication problem 32. A Trojan Horse is: a. A special password that bypasses the regular password sy ...
Process management
... – allows an application program to interact with these other system resources ...
... – allows an application program to interact with these other system resources ...
Abstract: 16-bit operating systems worth studying
... Abstract: 16-bit operating systems worth studying because it can be a reference for understanding the machine instructions on computer hardware and microcontroller devices. This research aims to develop a 16-bit operating system with functions essentially : the execution process, memory allocation, ...
... Abstract: 16-bit operating systems worth studying because it can be a reference for understanding the machine instructions on computer hardware and microcontroller devices. This research aims to develop a 16-bit operating system with functions essentially : the execution process, memory allocation, ...
OSTEP 13 Address Space
... Only the OS, through its tricky techniques of virtualizing memory, that knows where in the physical memory of the machine these instructions and data values lie If you print out an address in a program, it’s a virtual one, an illusion of how things are laid out in memory; only the OS (and the hardwa ...
... Only the OS, through its tricky techniques of virtualizing memory, that knows where in the physical memory of the machine these instructions and data values lie If you print out an address in a program, it’s a virtual one, an illusion of how things are laid out in memory; only the OS (and the hardwa ...
CSCI 315 Lecture 3
... – Nonpreemptive – once CPU given to the process it cannot be preempted until completes its CPU burst. – Preemptive – if a new process arrives with CPU burst length less than remaining time of current executing process, preempt. This scheme is know as the Shortest-Remaining-Time-First ...
... – Nonpreemptive – once CPU given to the process it cannot be preempted until completes its CPU burst. – Preemptive – if a new process arrives with CPU burst length less than remaining time of current executing process, preempt. This scheme is know as the Shortest-Remaining-Time-First ...