Operating system organization - cs.rochester.edu
... After I/O starts, control returns to user program without waiting for I/O completion. Device controller later informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt. When an interrupt occur, current execution is put on hold; the CPU jumps to a service routine called “interrupt handle ...
... After I/O starts, control returns to user program without waiting for I/O completion. Device controller later informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt. When an interrupt occur, current execution is put on hold; the CPU jumps to a service routine called “interrupt handle ...
CHAPTER 13: I/O SYSTEMS
... Key to performance Different policy for update: write-through, delayed write, etc. ...
... Key to performance Different policy for update: write-through, delayed write, etc. ...
Operating System Kernel More Virtual Stuff
... Does timesharing causes CPU use to be less efficient? • COST: Scheduling, context-switching overhead; but • GAIN: Productive use of idle time of one process by running another. 6.004 – Fall 2002 ...
... Does timesharing causes CPU use to be less efficient? • COST: Scheduling, context-switching overhead; but • GAIN: Productive use of idle time of one process by running another. 6.004 – Fall 2002 ...
Process Control Management
... • At the end of this lecture YOU should be able to: - explain the importance of CPU scheduling - distinguish between preemptive and non-preemptive algorithms - calculate waiting time and turnaround time ...
... • At the end of this lecture YOU should be able to: - explain the importance of CPU scheduling - distinguish between preemptive and non-preemptive algorithms - calculate waiting time and turnaround time ...
Module 4: Processes
... Processes switch between different states based on internal and external events Each process is in exactly one state at a time As a process executes, it changes state (Typical States of Processes (varies with OS)) new: The process is being created running: Instructions are being executed (only o ...
... Processes switch between different states based on internal and external events Each process is in exactly one state at a time As a process executes, it changes state (Typical States of Processes (varies with OS)) new: The process is being created running: Instructions are being executed (only o ...
Operating Systems
... for groups or individual users to access certain files. NTFS supports compression of individual files and folders which can be read and written to while they are ...
... for groups or individual users to access certain files. NTFS supports compression of individual files and folders which can be read and written to while they are ...
operating system
... several jobs in memory at a time, and only assign a resource to a job that needs it on the condition that the resource is available. ...
... several jobs in memory at a time, and only assign a resource to a job that needs it on the condition that the resource is available. ...
Multiprocessor and Real
... • Central queue needs mutual exclusion – May be a bottleneck when more than one processor looks for work at the same time ...
... • Central queue needs mutual exclusion – May be a bottleneck when more than one processor looks for work at the same time ...
Operating Systems
... concerning the modern operating systems design. More specifically, the operating system most important functions and their main associated concepts are presented - process management, process communication, deadlocks, memory management, file systems and input/output management. Practical knowledge o ...
... concerning the modern operating systems design. More specifically, the operating system most important functions and their main associated concepts are presented - process management, process communication, deadlocks, memory management, file systems and input/output management. Practical knowledge o ...
Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures • Operating-System
... Additional Operating-System Functions Additional functions exist not for helping the user, but rather for ensuring efficient system operations. • Resource allocation – allocating resources, such as CPU cycles, main memory, file storage, I/O devices, to multiple users or multiple jobs running at the ...
... Additional Operating-System Functions Additional functions exist not for helping the user, but rather for ensuring efficient system operations. • Resource allocation – allocating resources, such as CPU cycles, main memory, file storage, I/O devices, to multiple users or multiple jobs running at the ...
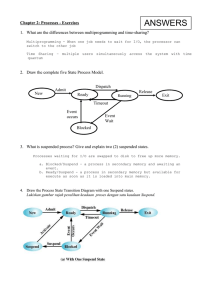
Chapter 2: Processes - Exercises
... elements of the PCB that characterize the process Blok Pengawalan Proses (PCB) mengandungi maklumat tertentu yang disimpan di dalam struktur data. Terangkan empat (4) elemen PCB yang memperincikan sesuatu proses. ...
... elements of the PCB that characterize the process Blok Pengawalan Proses (PCB) mengandungi maklumat tertentu yang disimpan di dalam struktur data. Terangkan empat (4) elemen PCB yang memperincikan sesuatu proses. ...
Powerpoint
... Roles of an Operating System Operating system System software that – manages computer resources, such as memory and input/output devices – provides an interface through which a human can interact with the computer – allows an application program to interact with these other system resources ...
... Roles of an Operating System Operating system System software that – manages computer resources, such as memory and input/output devices – provides an interface through which a human can interact with the computer – allows an application program to interact with these other system resources ...
OS-DS-Arch
... Threads support treating of requests with varying priorities. Various types of architectures can be used in current processing: ...
... Threads support treating of requests with varying priorities. Various types of architectures can be used in current processing: ...
Processes and Threads - University of Waterloo
... In addition to system calls, exceptions are another way of transferring control from a user space process to the kernel. Exceptions occur when a thread is trying to execute an instruction that is either not permitted or requires some additional work before it can be executed: ● arithmetic error (e.g ...
... In addition to system calls, exceptions are another way of transferring control from a user space process to the kernel. Exceptions occur when a thread is trying to execute an instruction that is either not permitted or requires some additional work before it can be executed: ● arithmetic error (e.g ...
Homework: OS Organization
... Submit: In lab 4 you completed building the core of an exokernel-based operating system. In class you studied xv6, a monolithic operating systems. Both are intend to support the UNIX API, but their internal organizations are different. A good example is the virtual memory implementation: JOS impleme ...
... Submit: In lab 4 you completed building the core of an exokernel-based operating system. In class you studied xv6, a monolithic operating systems. Both are intend to support the UNIX API, but their internal organizations are different. A good example is the virtual memory implementation: JOS impleme ...
Chapter10
... • Process A program in execution • Process management keeping track of processes and the states they are in • CPU scheduling determines which process in memory is executed by the CPU at any given instant in time ...
... • Process A program in execution • Process management keeping track of processes and the states they are in • CPU scheduling determines which process in memory is executed by the CPU at any given instant in time ...
Slide set 14
... The trap function switches the machine into supervisory mode and begins executing the dispatcher. This requires a context switch. The dispatcher looks at the system call number, and uses it to locate the executable code for the function call. The system call code executes, control is returned to the ...
... The trap function switches the machine into supervisory mode and begins executing the dispatcher. This requires a context switch. The dispatcher looks at the system call number, and uses it to locate the executable code for the function call. The system call code executes, control is returned to the ...
Processes - United International College
... Process State … • The steps in a process switch are: 1. Save context of processor including program counter and other registers 2. Update the process control block of the process that is currently in the Running state 3. Move process control block to appropriate queue – ready; blocked; ready/suspend ...
... Process State … • The steps in a process switch are: 1. Save context of processor including program counter and other registers 2. Update the process control block of the process that is currently in the Running state 3. Move process control block to appropriate queue – ready; blocked; ready/suspend ...
Processes in Unix, Linux, and Windows
... Process Creation – Unix & Linux • Create a new (child) process – fork(); – Allocates new PCB – Clones the calling process (almost exactly) • Copy of parent process address space • Copies resources in kernel (e.g. files) ...
... Process Creation – Unix & Linux • Create a new (child) process – fork(); – Allocates new PCB – Clones the calling process (almost exactly) • Copy of parent process address space • Copies resources in kernel (e.g. files) ...
(MSWindows, LINUX, UNIX) (China)
... - Interprets the command users enter - Selects and runs the command or program - Provides the results to the screen or file as directed by the command -C shell, Bourne shell, Korn shell The main part of operating system, and responsible for controlling system resources. -Loaded into memory when the ...
... - Interprets the command users enter - Selects and runs the command or program - Provides the results to the screen or file as directed by the command -C shell, Bourne shell, Korn shell The main part of operating system, and responsible for controlling system resources. -Loaded into memory when the ...
Types of services
... functions may be desired (such as to rewind a tape drive, or to blank a CRT screen). For efficiency and protection, users usually cannot control I/0 devices directly. ...
... functions may be desired (such as to rewind a tape drive, or to blank a CRT screen). For efficiency and protection, users usually cannot control I/0 devices directly. ...
Chapter I Introduction
... – We will lose data if the system or the program crashes • After the program issued a write but • Before the data were saved to disk ...
... – We will lose data if the system or the program crashes • After the program issued a write but • Before the data were saved to disk ...