Chapter 2 – Operating System Overview
... derived by the way the users were forced to access the systems. ...
... derived by the way the users were forced to access the systems. ...
process control block
... during process run time. The structure of a process in memory is shown in Figure 3.1. We emphasize that a program by itself is not a process; a program is a passive entity, such as a file containing a list of instructions stored on disk (often called an executable file), whereas a process is an acti ...
... during process run time. The structure of a process in memory is shown in Figure 3.1. We emphasize that a program by itself is not a process; a program is a passive entity, such as a file containing a list of instructions stored on disk (often called an executable file), whereas a process is an acti ...
Lecture1
... dedicated resources but frequently use shared resources from servers Handheld computers are resource poor, optimized for usability and battery life Some computers have little or no user interface, such as embedded computers in devices and automobiles ...
... dedicated resources but frequently use shared resources from servers Handheld computers are resource poor, optimized for usability and battery life Some computers have little or no user interface, such as embedded computers in devices and automobiles ...
cs459 - Operating Systems: Introduction
... • Multiprogramming: Concurrent process execution – A set of jobs is kept in memory (or partially on disk) – The OS job scheduler module picks one to execute – A OS switch occurs when it blocks (ex: for I/O) ...
... • Multiprogramming: Concurrent process execution – A set of jobs is kept in memory (or partially on disk) – The OS job scheduler module picks one to execute – A OS switch occurs when it blocks (ex: for I/O) ...
interrupt
... When it has to wait (for I/O for example), OS switches to another job Timesharing (multitasking) is logical extension in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing Response time should be < 1 second Each user ...
... When it has to wait (for I/O for example), OS switches to another job Timesharing (multitasking) is logical extension in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing Response time should be < 1 second Each user ...
Operating System Structures
... − Huge range, including denial-of-service, worms, viruses, identity theft, theft of service Systems generally first distinguish among users, to determine who can do what − User identities (user IDs, security IDs) include name and associated number, one per user − User ID then associated with all fil ...
... − Huge range, including denial-of-service, worms, viruses, identity theft, theft of service Systems generally first distinguish among users, to determine who can do what − User identities (user IDs, security IDs) include name and associated number, one per user − User ID then associated with all fil ...
PDF
... (a) You have just installed a new webcam for your laptop. In order to use the webcam, you must install both a device driver and a chat application. Describe the purposes of and differences between these two pieces of software. (b) While installing the driver, the operating system asks you for admini ...
... (a) You have just installed a new webcam for your laptop. In order to use the webcam, you must install both a device driver and a chat application. Describe the purposes of and differences between these two pieces of software. (b) While installing the driver, the operating system asks you for admini ...
Lecture 2
... Operating System Structure • Basic idea of multiprogramming: – Keep multiple jobs in memory. – When one job blocks on I/O (or other events), the operating system: • Starts the I/O operation. • Switches to another job that is ready to execute. • Now the CPU and I/O device are executing in parallel. ...
... Operating System Structure • Basic idea of multiprogramming: – Keep multiple jobs in memory. – When one job blocks on I/O (or other events), the operating system: • Starts the I/O operation. • Switches to another job that is ready to execute. • Now the CPU and I/O device are executing in parallel. ...
Solaris System Management - Understanding System Concepts -
... Root filesystem (/) is the parent of all filesystems. Mount Point – the directory name on the parent file system where a separate file system may be attached. Operating System – the set of programs that manage all system operations and user communications. va-scan ...
... Root filesystem (/) is the parent of all filesystems. Mount Point – the directory name on the parent file system where a separate file system may be attached. Operating System – the set of programs that manage all system operations and user communications. va-scan ...
ITS 225 (Operating Systems) Lecture Notes
... – CPU stops what it is doing and transfers control to an interrupt service routine (ISR) – May be different ISRs for different types of interrupts. The list of ISR locations is called the interrupt vector. – Example: the Intel 386 architecture contains 16 interrupt lines (IRQ0-IRQ15), requiring a 16 ...
... – CPU stops what it is doing and transfers control to an interrupt service routine (ISR) – May be different ISRs for different types of interrupts. The list of ISR locations is called the interrupt vector. – Example: the Intel 386 architecture contains 16 interrupt lines (IRQ0-IRQ15), requiring a 16 ...
Unix – Linux
... environment that is separated from other users sharing the computer’s resources. – Access is through a verification process known as logging-in: Enter a user-id and password. – The OS creates an environment known as the “shell” for the user after the login is complete. ...
... environment that is separated from other users sharing the computer’s resources. – Access is through a verification process known as logging-in: Enter a user-id and password. – The OS creates an environment known as the “shell” for the user after the login is complete. ...
pentest
... Each processor is self-scheduling, Common ready queue, or each has its own private queue ...
... Each processor is self-scheduling, Common ready queue, or each has its own private queue ...
Page 1 •Program Execution •I/O Operation •File System
... Operator-console device driver Memory management CPU scheduling hardware ...
... Operator-console device driver Memory management CPU scheduling hardware ...
Introduction and Overview - William & Mary Computer Science
... • use a hardware timer that generates a periodic interrupt • before it transfers to a user program, the OS loads the timer with a time to interrupt – “quantum” – how big should it be set? ...
... • use a hardware timer that generates a periodic interrupt • before it transfers to a user program, the OS loads the timer with a time to interrupt – “quantum” – how big should it be set? ...
Introduction - Stanford Secure Computer Systems Group
... - Address space: all memory locations a program can name - Virtual address: addresses in process’ address space - Physical address: address of real memory - Translation: map virtual to physical addresses ...
... - Address space: all memory locations a program can name - Virtual address: addresses in process’ address space - Physical address: address of real memory - Translation: map virtual to physical addresses ...
I. Introduction, system calls, dual mode
... Timer to prevent infinite loop / process hogging resources – Timer is set to interrupt the computer after some time period – Keep a counter that is decremented by the physical clock. – Operating system set the counter (privileged instruction) – When counter zero generate an interrupt – Set up before ...
... Timer to prevent infinite loop / process hogging resources – Timer is set to interrupt the computer after some time period – Keep a counter that is decremented by the physical clock. – Operating system set the counter (privileged instruction) – When counter zero generate an interrupt – Set up before ...
Chapter 2 Operating System Overview
... Despite overhead, the simple batch system improves utilization of the computer. ...
... Despite overhead, the simple batch system improves utilization of the computer. ...
sample PPT 2 - Virginia Tech
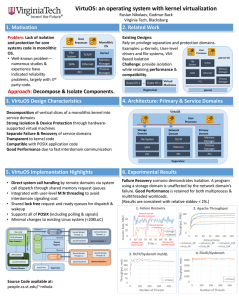
... Compatible with POSIX application code Good Performance due to fast interdomain communication ...
... Compatible with POSIX application code Good Performance due to fast interdomain communication ...
Powerpoint source
... • There must be a system call instruction, which: – causes an exception (throws a software interrupt), which vectors to a kernel handler – passes a parameter indicating which system call to invoke – saves caller’s state (regs, mode bit) so they can be restored – OS must verify caller’s parameters (e ...
... • There must be a system call instruction, which: – causes an exception (throws a software interrupt), which vectors to a kernel handler – passes a parameter indicating which system call to invoke – saves caller’s state (regs, mode bit) so they can be restored – OS must verify caller’s parameters (e ...
Computer Science 8530 Advanced Operating Systems Fall 2016
... 17. Where is it likely that the majority of user-accessible register contents will be saved when a process is moved from the running/current state to the ready state? Where else might some other register contents be saved? Use Xinu on the Galileo as a specific case. 18. The three characteristic p ...
... 17. Where is it likely that the majority of user-accessible register contents will be saved when a process is moved from the running/current state to the ready state? Where else might some other register contents be saved? Use Xinu on the Galileo as a specific case. 18. The three characteristic p ...
Introduction to Object Technology
... Interactive: User quits application or logs off Batch job issues Halt instr. or OS termination call External signal (eg kill() or ctrl-c) Error and fault conditions ...
... Interactive: User quits application or logs off Batch job issues Halt instr. or OS termination call External signal (eg kill() or ctrl-c) Error and fault conditions ...