Norman Matloff, Unix Processes
... A process is an instance of running a program. If, for example, three people are running the same program simultaneously, there are three processes there, not just one. In fact, we might have more than one process running even with only person executing the program, because (you will see later) the ...
... A process is an instance of running a program. If, for example, three people are running the same program simultaneously, there are three processes there, not just one. In fact, we might have more than one process running even with only person executing the program, because (you will see later) the ...
Linux-by-Blane-Adcock-Bryan-Knehr-Kevin-Estep-Jason
... of the root directory, symbolized “/” • This forms an inverted tree structure with the root at the top and everything stemming from there • Creates a parent-child relationship between ...
... of the root directory, symbolized “/” • This forms an inverted tree structure with the root at the top and everything stemming from there • Creates a parent-child relationship between ...
Chapter 2: Introduction to the Kernel
... • A process is the execution of a program • A process is consists of text (machine code), data and stack • Many process can run simultaneously as kernel schedules them for execution • Several processes may be instances of one program • A process reads and writes its data and stack sections, but it c ...
... • A process is the execution of a program • A process is consists of text (machine code), data and stack • Many process can run simultaneously as kernel schedules them for execution • Several processes may be instances of one program • A process reads and writes its data and stack sections, but it c ...
operating systems - Computer Science, Columbia University
... • Consider a system consisting of n processes. Each process has a segment of code, called a critical section, in which the process may be changing common variables, updating a table, writing a file, and so on. • Printer allocation example • Solution • Interrupt disable and interrupt enable • Se ...
... • Consider a system consisting of n processes. Each process has a segment of code, called a critical section, in which the process may be changing common variables, updating a table, writing a file, and so on. • Printer allocation example • Solution • Interrupt disable and interrupt enable • Se ...
I. Course code and Title OPERATING SYSTEM CONCEPTS II
... This course covers the basic concepts of Operating Systems. It includes the following topics Overview: Operating System Role, Purpose and Functionality; Computing Environments: Single User, Multi User, Multiple Simultaneous Computations; Goals of Parallelism (e.g., Throughput) versus Concurrency (e. ...
... This course covers the basic concepts of Operating Systems. It includes the following topics Overview: Operating System Role, Purpose and Functionality; Computing Environments: Single User, Multi User, Multiple Simultaneous Computations; Goals of Parallelism (e.g., Throughput) versus Concurrency (e. ...
lecture4-sept13
... • Process executes last statement and asks the operating system to delete it (exit) – Output data from child to parent (via wait) – Process’ resources are deallocated by operating system • Parent may terminate execution of children processes (abort) – Child has exceeded allocated resources – Task as ...
... • Process executes last statement and asks the operating system to delete it (exit) – Output data from child to parent (via wait) – Process’ resources are deallocated by operating system • Parent may terminate execution of children processes (abort) – Child has exceeded allocated resources – Task as ...
Device Drivers - EMU CMPE Home Page
... 0th – for Kernel mode parts of OS, and users applications and some parts of OS run on the 3rd ring of privilege. Protected mode provides means for multitasking and segmented and paged virtual memory. Each user task gets 4G bytes of virtual address space. Maximal size of segment is 4Gb, size of page ...
... 0th – for Kernel mode parts of OS, and users applications and some parts of OS run on the 3rd ring of privilege. Protected mode provides means for multitasking and segmented and paged virtual memory. Each user task gets 4G bytes of virtual address space. Maximal size of segment is 4Gb, size of page ...
Slide 1
... • A process is the execution of a program • A process is consists of text (machine code), data and stack • Many process can run simultaneously as kernel schedules them for execution • Several processes may be instances of one program • A process reads and writes its data and stack sections, but it c ...
... • A process is the execution of a program • A process is consists of text (machine code), data and stack • Many process can run simultaneously as kernel schedules them for execution • Several processes may be instances of one program • A process reads and writes its data and stack sections, but it c ...
kernel-intro
... • A process is the execution of a program • A process is consists of text (machine code), data and stack • Many process can run simultaneously as kernel schedules them for execution • Several processes may be instances of one program • A process reads and writes its data and stack sections, but it c ...
... • A process is the execution of a program • A process is consists of text (machine code), data and stack • Many process can run simultaneously as kernel schedules them for execution • Several processes may be instances of one program • A process reads and writes its data and stack sections, but it c ...
Introduction - Stanford Secure Computer Systems Group
... • Protection mechanism to prevent monopolizing CPU • E.g., kernel programs timer to interrupt every 10 ms - Must be in supervisor mode to write appropriate I/O registers - User code cannot re-program interval timer • Kernel sets interrupt to vector back to kernel - Regains control whenever interval ...
... • Protection mechanism to prevent monopolizing CPU • E.g., kernel programs timer to interrupt every 10 ms - Must be in supervisor mode to write appropriate I/O registers - User code cannot re-program interval timer • Kernel sets interrupt to vector back to kernel - Regains control whenever interval ...
Basic Operating System Concepts
... several processes/threads at a time. The OS keeps several jobs in memory simultaneously. It selects a job from the ready state and starts executing it. When that job needs to wait for some event the CPU is switched to another job. Primary objective: eliminate CPU idle time Time sharing: An extension ...
... several processes/threads at a time. The OS keeps several jobs in memory simultaneously. It selects a job from the ready state and starts executing it. When that job needs to wait for some event the CPU is switched to another job. Primary objective: eliminate CPU idle time Time sharing: An extension ...
Centralized computing
... and executing of the instruction. Single-core processors can only process one instruction at a time • Dual-core processor contains two cores (Such as Intel Core Duo). ...
... and executing of the instruction. Single-core processors can only process one instruction at a time • Dual-core processor contains two cores (Such as Intel Core Duo). ...
Memory Protection: Kernel and User Address Spaces
... Address Translation Each process is associated with an address space, or all the physical addresses a process can touch However, each process believes that it owns the entire memory, starting with the virtual address 0 The missing piece is a translation table Translate every memory referenc ...
... Address Translation Each process is associated with an address space, or all the physical addresses a process can touch However, each process believes that it owns the entire memory, starting with the virtual address 0 The missing piece is a translation table Translate every memory referenc ...
Computers
... Process Management Problems Synchronization: correct management of interrupted processes Mutual exclusion: keeping shared resource use separate Determinate program operation: programs get the same result every time independent of what else is running ...
... Process Management Problems Synchronization: correct management of interrupted processes Mutual exclusion: keeping shared resource use separate Determinate program operation: programs get the same result every time independent of what else is running ...
Operating System Concepts
... – The user has no direct interaction with the computer system but uses a series of instructions to alter the priority of the tasks ...
... – The user has no direct interaction with the computer system but uses a series of instructions to alter the priority of the tasks ...
operating system
... programs (location in memory, stack pointer, program counter). When a program is run, the operating system converts it into a process. It is the process, rather than the simple program, that the processor executes. ...
... programs (location in memory, stack pointer, program counter). When a program is run, the operating system converts it into a process. It is the process, rather than the simple program, that the processor executes. ...
Personal Research of the First Come First Serve Operation in the
... The first come, first served (commonly referred as FIFO: first in, first out) process scheduling algorithm is the simplest process scheduling algorithm. It is one of the BATCH SYSTEMS. It is rarely used in modern operating systems, but it is sometimes in the other scheduling systems. First Come Firs ...
... The first come, first served (commonly referred as FIFO: first in, first out) process scheduling algorithm is the simplest process scheduling algorithm. It is one of the BATCH SYSTEMS. It is rarely used in modern operating systems, but it is sometimes in the other scheduling systems. First Come Firs ...
W. Stallings, Operating Systems Internal and Design Principles
... • privileged instructions: certain machine level instructions can be executed only by the monitor; • memory protection: a user program must not alter memory area containing the monitor. New concept of modes of operations: • user program executes in user mode: certain areas of memory are protected, c ...
... • privileged instructions: certain machine level instructions can be executed only by the monitor; • memory protection: a user program must not alter memory area containing the monitor. New concept of modes of operations: • user program executes in user mode: certain areas of memory are protected, c ...
Document
... include the study of processes and process synchronization, multithreaded applications, deadlocks, memory management, and file systems. UNIX and Windows NT are general purpose operating systems used as examples when studying these concepts. Laboratory assignments of process/thread synchronization, p ...
... include the study of processes and process synchronization, multithreaded applications, deadlocks, memory management, and file systems. UNIX and Windows NT are general purpose operating systems used as examples when studying these concepts. Laboratory assignments of process/thread synchronization, p ...
Operating Systems Concepts Tutorial exercises
... that the details are often unimportant and confusingly complex. This page tries to explain a little of the unimportant detail. ...
... that the details are often unimportant and confusingly complex. This page tries to explain a little of the unimportant detail. ...
OPERATING SYSTEMS DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION Third
... Figure 2-10. A proposed solution to the critical region problem. (a) Process 0. (b) Process 1. In both cases, be sure to note the semicolons terminating the while statements. ...
... Figure 2-10. A proposed solution to the critical region problem. (a) Process 0. (b) Process 1. In both cases, be sure to note the semicolons terminating the while statements. ...
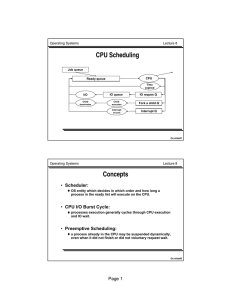
Page 1 • Scheduler: • CPU I/O Burst Cycle: • Preemptive Scheduling:
... OS entity which decides in which order and how long a process in the ready list will execute on the CPU. ...
... OS entity which decides in which order and how long a process in the ready list will execute on the CPU. ...