Authentication is the process of determining whether someone or
... but cannot use it until all other resources are available. Resource Holding is A process is currently holding at least one resource and requesting additional resources which are being held by other processes. ...
... but cannot use it until all other resources are available. Resource Holding is A process is currently holding at least one resource and requesting additional resources which are being held by other processes. ...
university of helsinki 24.8.2001
... In a multiprogramming environment the applications are not allowed to mess each other and they are not allowed to use resources not owned by themselves without given permissions. To implement a multiprogramming operating system certain hardware level features are desirable. Explain what kind of supp ...
... In a multiprogramming environment the applications are not allowed to mess each other and they are not allowed to use resources not owned by themselves without given permissions. To implement a multiprogramming operating system certain hardware level features are desirable. Explain what kind of supp ...
process.
... I/O requests -Typical interactive user programs. CPU-bound process – large amount of computation before it needs to do some I/O; few I/O requests - Programs that require sustained periods of calculation e.g. modelling applications ...
... I/O requests -Typical interactive user programs. CPU-bound process – large amount of computation before it needs to do some I/O; few I/O requests - Programs that require sustained periods of calculation e.g. modelling applications ...
What is an Operating System?
... may overwrite another file or folder on disk. A process may get the CPU and never relinquish it. So the issues of hardware protection are: I/O protection, memory protection, and CPU protection. We will discuss them one by one, but first we talk about the dual-mode operation of a CPU. a) Dual Mode Op ...
... may overwrite another file or folder on disk. A process may get the CPU and never relinquish it. So the issues of hardware protection are: I/O protection, memory protection, and CPU protection. We will discuss them one by one, but first we talk about the dual-mode operation of a CPU. a) Dual Mode Op ...
ppt - Dave Reed
... must at least provide process & memory management, communications communications between client programs and services via message passing e.g., client program & file server send messages through microkernel advantages: easier to extend a microkernel; easier to port the OS to new architectures; m ...
... must at least provide process & memory management, communications communications between client programs and services via message passing e.g., client program & file server send messages through microkernel advantages: easier to extend a microkernel; easier to port the OS to new architectures; m ...
Overview and History
... must at least provide process & memory management, communications communications between client programs and services via message passing e.g., client program & file server send messages through microkernel advantages: easier to extend a microkernel; easier to port the OS to new architectures; m ...
... must at least provide process & memory management, communications communications between client programs and services via message passing e.g., client program & file server send messages through microkernel advantages: easier to extend a microkernel; easier to port the OS to new architectures; m ...
L02_OperatingSystemEvolution
... A program containing even a very small number of I/O ops, will spend most of its time waiting for them Hence: poor CPU usage when only one program is present in memory ...
... A program containing even a very small number of I/O ops, will spend most of its time waiting for them Hence: poor CPU usage when only one program is present in memory ...
CSE 5431 (Approved): Systems II: Introduction to Operating Systems
... Process concepts, process control block, memory and CPU protection, process hierarchy, shell, process (Unix-like) related system calls, interactions between systems calls, context switching and underlying interrupt, timer mechanisms. ...
... Process concepts, process control block, memory and CPU protection, process hierarchy, shell, process (Unix-like) related system calls, interactions between systems calls, context switching and underlying interrupt, timer mechanisms. ...
No Slide Title - ECE Users Pages
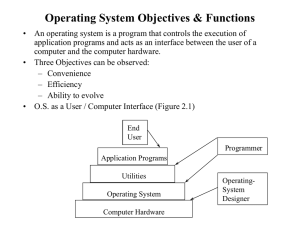
... 1. Hardware – provides basic computing resources (CPU, memory, I/O devices). 2. Operating system – controls and coordinates the use of the hardware among the various application programs for the various users. 3. Applications programs – define the ways in which the system resources are used to solve ...
... 1. Hardware – provides basic computing resources (CPU, memory, I/O devices). 2. Operating system – controls and coordinates the use of the hardware among the various application programs for the various users. 3. Applications programs – define the ways in which the system resources are used to solve ...
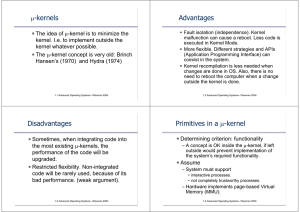
μ-kernels Advantages Disadvantages Primitives in a μ
... kernel aid-processes. benchmarking the context switch overhead is usually done by the execution time of getpid(). Cost of kernel-user mode switches is very high on x86 processors. – 71 CPU cycles for entering kernel mode – 36 CPU cycles for returning to user mode. ...
... kernel aid-processes. benchmarking the context switch overhead is usually done by the execution time of getpid(). Cost of kernel-user mode switches is very high on x86 processors. – 71 CPU cycles for entering kernel mode – 36 CPU cycles for returning to user mode. ...
Operating System
... 2. learn several types of operating system such as Windows and Linux environment; and 3. identify main module in operating system ...
... 2. learn several types of operating system such as Windows and Linux environment; and 3. identify main module in operating system ...
Chapter 2: System Structures
... Operating systems provide an environment for execution of programs and services to programs and users ...
... Operating systems provide an environment for execution of programs and services to programs and users ...
DISTRIBUTED OPERATING SYSTEM
... execution may require specialized processor - Software preference – required software may be available at only a particular site - Data access – run process remotely, rather than transfer all data locally ...
... execution may require specialized processor - Software preference – required software may be available at only a particular site - Data access – run process remotely, rather than transfer all data locally ...
Operating Systems
... “no-op” instruction, when no useful work needs execution. An interrupt (e.g., from keyboard, disk, network) will cause the CPU to be reassigned to execute useful work. ...
... “no-op” instruction, when no useful work needs execution. An interrupt (e.g., from keyboard, disk, network) will cause the CPU to be reassigned to execute useful work. ...
ppt
... Hierarchically-named capabilities Requires that these capabilities to be specified explicitly on each system call Example: Buggy child process accidentally requesting write access to the parent’s page ...
... Hierarchically-named capabilities Requires that these capabilities to be specified explicitly on each system call Example: Buggy child process accidentally requesting write access to the parent’s page ...
1.5 In a multiprogramming and time
... queue with a larger quantum, requiring fewer context switches to complete the processing, making more efficient use of the computer. 6.8 Many CPU scheduling algorithms are parameterized. For example, the RR algorithm requires a parameter to indicate the time slice. Multilevel feedback queues require ...
... queue with a larger quantum, requiring fewer context switches to complete the processing, making more efficient use of the computer. 6.8 Many CPU scheduling algorithms are parameterized. For example, the RR algorithm requires a parameter to indicate the time slice. Multilevel feedback queues require ...
The Evolution of OS
... An Example (32 K main memory; 5 K monitor) JOB1: 15K JOB2: 20K JOB3: 5K JOB4: 10K refer to Figure 2.7 Simple => minimize the size of the monitor. A job was always loaded into the same location => no need for relocation at load time. • Minimized disk activity. • Problems Raised: – Multiple jobs in me ...
... An Example (32 K main memory; 5 K monitor) JOB1: 15K JOB2: 20K JOB3: 5K JOB4: 10K refer to Figure 2.7 Simple => minimize the size of the monitor. A job was always loaded into the same location => no need for relocation at load time. • Minimized disk activity. • Problems Raised: – Multiple jobs in me ...
操作系统
... Which one is easer to use Windows / Linux 1. Windows temporarily keeps deleted files in Recycle Bin, while Linux rm delete them instantly. 2. Windows task manager allows us to kill processes with their program names, while Linux uses IDs to kill specific processes. 3. Windows starts an appropriate ...
... Which one is easer to use Windows / Linux 1. Windows temporarily keeps deleted files in Recycle Bin, while Linux rm delete them instantly. 2. Windows task manager allows us to kill processes with their program names, while Linux uses IDs to kill specific processes. 3. Windows starts an appropriate ...
CSC 150 UNGRADED QUIZ - Concordia University Wisconsin
... In typical computer systems, there is always competition for resources. To avoid conflicts and to allow fair usage, resource management is needed for the 4 main resources: (1) MEMORY, (2) PROCESSOR, (3) FILES, (4) DEVICES. ...
... In typical computer systems, there is always competition for resources. To avoid conflicts and to allow fair usage, resource management is needed for the 4 main resources: (1) MEMORY, (2) PROCESSOR, (3) FILES, (4) DEVICES. ...
Operating Systems
... Enforce Single Access • If we enforce a rule that only one process may enter the function at a time then: • P1 & P2 run on separate processors • P1 enters echo first, – P2 tries to enter but is blocked – P2 suspends ...
... Enforce Single Access • If we enforce a rule that only one process may enter the function at a time then: • P1 & P2 run on separate processors • P1 enters echo first, – P2 tries to enter but is blocked – P2 suspends ...
Threads, SMP, and Micro
... Processes and Threads • Resource ownership - process includes a virtual address space to hold the process image • Scheduling/execution- follows an execution path that may be interleaved with other processes ...
... Processes and Threads • Resource ownership - process includes a virtual address space to hold the process image • Scheduling/execution- follows an execution path that may be interleaved with other processes ...
Examination paper
... 1. (max 5 points) Describe the structure of the von Neumann computer architecture and hardware components that an operating system manages to meet its users’ computing needs (CPU and its components, main memory, secondary storage, peripheral controllers and devices, motherboard, BIOS, and buses). 2. ...
... 1. (max 5 points) Describe the structure of the von Neumann computer architecture and hardware components that an operating system manages to meet its users’ computing needs (CPU and its components, main memory, secondary storage, peripheral controllers and devices, motherboard, BIOS, and buses). 2. ...
talk
... { int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY); if (fd < 0) { fprintf(stderr, “Failed to open\n”); exit(-1); ...
... { int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY); if (fd < 0) { fprintf(stderr, “Failed to open\n”); exit(-1); ...