COS 318: Midterm Exam (October 23, 2012) (80 Minutes) Name:
... Yes. This is because any programs can use such instructions at any time. b. (1 point) Are the registers for I/O devices part of the context of a process? No. I/O devices are accessed via device driver calls in the kernel. c. (2 point) Can Monitors deadlock? ...
... Yes. This is because any programs can use such instructions at any time. b. (1 point) Are the registers for I/O devices part of the context of a process? No. I/O devices are accessed via device driver calls in the kernel. c. (2 point) Can Monitors deadlock? ...
Processes
... A process will need certain resources-such as CPU time, memory, files, and I/O devices to accomplish its task. These resources are allocated to the process either when it is created or while it is executing. All these processes may execute concurrently. The operating system is responsible for th ...
... A process will need certain resources-such as CPU time, memory, files, and I/O devices to accomplish its task. These resources are allocated to the process either when it is created or while it is executing. All these processes may execute concurrently. The operating system is responsible for th ...
Computer Network and Infrastructure
... Determines which programs are admitted to the system for processing Controls the degree of multiprogramming More processes, smaller percentage of time each process is executed. This is the decision that the LT-scheduler will make. In some sense this also limits the degree of multi programming. The p ...
... Determines which programs are admitted to the system for processing Controls the degree of multiprogramming More processes, smaller percentage of time each process is executed. This is the decision that the LT-scheduler will make. In some sense this also limits the degree of multi programming. The p ...
Functions of the operating systems
... 2. also manages the use of main memory by splitting main memory into two parts (user area, system area). 3. Time sharing: operating system can allow more than one user to work on the same computer, and run more than one program at the same time. ...
... 2. also manages the use of main memory by splitting main memory into two parts (user area, system area). 3. Time sharing: operating system can allow more than one user to work on the same computer, and run more than one program at the same time. ...
OPERATING SYSTEMS: DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION
... Figure 1-15. (a) File system before the mount. (b) File system ...
... Figure 1-15. (a) File system before the mount. (b) File system ...
Process Management in xv6
... point to a generic function to handle all traps (line 3254) that we will examine soon. • When an interrupt / trap / system call occurs in xv6, the interrupting hardware causes the processor to execute the int instruction, with a specific interrupt number (IRQ) as argument. This special instruction m ...
... point to a generic function to handle all traps (line 3254) that we will examine soon. • When an interrupt / trap / system call occurs in xv6, the interrupting hardware causes the processor to execute the int instruction, with a specific interrupt number (IRQ) as argument. This special instruction m ...
04-Scheduling - AIT CSIM Program
... New problem: how to split time between the queues? – Absolute priority: can cause starvation – Time division: e.g. 80% foreground, 20% background ...
... New problem: how to split time between the queues? – Absolute priority: can cause starvation – Time division: e.g. 80% foreground, 20% background ...
Chapter 2 Operating System Overview Operating System Overview
... – The Evolution of Operating Systems – Major Achievements – Developments Leading to Modern Operating Systems – Microsoft Windows Overview – UNIX Systems – Linux ...
... – The Evolution of Operating Systems – Major Achievements – Developments Leading to Modern Operating Systems – Microsoft Windows Overview – UNIX Systems – Linux ...
Operating System Overview
... – The Evolution of Operating Systems – Major Achievements – Developments Leading to Modern Operating Systems – Microsoft Windows Overview – UNIX Systems – Linux ...
... – The Evolution of Operating Systems – Major Achievements – Developments Leading to Modern Operating Systems – Microsoft Windows Overview – UNIX Systems – Linux ...
scheduling
... Operating system is a software which is essential for the user to interact with the computer systems. It is used to manage the software and hardware resources of the computer efficiently and coordinate the use of system components. Process: Process is defined as program in execution. It is used to a ...
... Operating system is a software which is essential for the user to interact with the computer systems. It is used to manage the software and hardware resources of the computer efficiently and coordinate the use of system components. Process: Process is defined as program in execution. It is used to a ...
Chapter 2Operating System Overview
... – The Evolution of Operating Systems – Major Achievements – Developments Leading to Modern Operating Systems – Microsoft Windows Overview – UNIX Systems – Linux ...
... – The Evolution of Operating Systems – Major Achievements – Developments Leading to Modern Operating Systems – Microsoft Windows Overview – UNIX Systems – Linux ...
PowerPoint XP
... Clean virtual machine Hardware independence Resource sharing and management Long term data storage Protection, security, accounting Real time support, parallelism, human interface ...
... Clean virtual machine Hardware independence Resource sharing and management Long term data storage Protection, security, accounting Real time support, parallelism, human interface ...
Operating Systems
... • w = time spent in system so far, waiting • e = time spent in execution so far • s = total service time required by the process, including e; ...
... • w = time spent in system so far, waiting • e = time spent in execution so far • s = total service time required by the process, including e; ...
Introduction
... • Interrupts are used to signal an event. • Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally, through the interrupt vector, which contains the addresses of all the service routines. • Interrupt architecture must save the address of the ...
... • Interrupts are used to signal an event. • Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally, through the interrupt vector, which contains the addresses of all the service routines. • Interrupt architecture must save the address of the ...
2015 test - Department of Computer Science
... [1 mark] Which of the following is NOT a true difference between preemptive and non-preemptive (or cooperative) scheduling? ...
... [1 mark] Which of the following is NOT a true difference between preemptive and non-preemptive (or cooperative) scheduling? ...
AOSScheduling
... The dispatch latency must be minimal Context Switching: Saving and loading registers and memory maps, updating various tables and lists, flushing and reloading the memory cache, and so on. ...
... The dispatch latency must be minimal Context Switching: Saving and loading registers and memory maps, updating various tables and lists, flushing and reloading the memory cache, and so on. ...
Chapter 5 Concurrency: Mutual Exclusion and Exclusion and
... Enforce Single Access • If we enforce a rule that only one process may enter the function at a time then: • P1 & P2 run on separate processors • P1 enters echo first, – P2 tries to enter but is blocked – P2 suspends ...
... Enforce Single Access • If we enforce a rule that only one process may enter the function at a time then: • P1 & P2 run on separate processors • P1 enters echo first, – P2 tries to enter but is blocked – P2 suspends ...
Chapter 05: Concurrency: Mutual Exclusion and Synchronization
... Enforce Single Access • If we enforce a rule that only one process may enter the function at a time then: • P1 & P2 run on separate processors • P1 enters echo first, – P2 tries to enter but is blocked – P2 suspends ...
... Enforce Single Access • If we enforce a rule that only one process may enter the function at a time then: • P1 & P2 run on separate processors • P1 enters echo first, – P2 tries to enter but is blocked – P2 suspends ...
What is an Operating System?
... producer and emptied by consumer. Unbounded-buffer places no practical limit on the size of the buffer. Consumer may wait, producer never waits. Bounded-buffer assumes that there is a fixed buffer size. Consumer waits for new item, producer waits if buffer is ...
... producer and emptied by consumer. Unbounded-buffer places no practical limit on the size of the buffer. Consumer may wait, producer never waits. Bounded-buffer assumes that there is a fixed buffer size. Consumer waits for new item, producer waits if buffer is ...
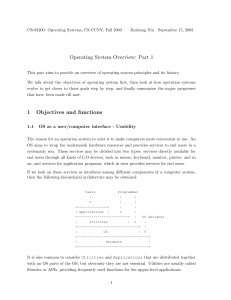
Operating System Overview: Part 1 1 Objectives and functions
... Some programs may even need interaction with users, which requires the processor to switch to these programs frequently. To reach this new goal, a similar technique to multiprogramming can be used, called time sharing. In such a system, multiple users simultaneously access the system through termina ...
... Some programs may even need interaction with users, which requires the processor to switch to these programs frequently. To reach this new goal, a similar technique to multiprogramming can be used, called time sharing. In such a system, multiple users simultaneously access the system through termina ...
CS 111 Processes
... Piece of OS that determines: 1) what process is running now? 2) What process will it run next? RUN QUEUE: Set of processes that are ready to go. "Ready to go" status does not mean that the process is 'useful'. We generally want a small run queue (minimal amount of programs on it). WAIT QUEUE: A queu ...
... Piece of OS that determines: 1) what process is running now? 2) What process will it run next? RUN QUEUE: Set of processes that are ready to go. "Ready to go" status does not mean that the process is 'useful'. We generally want a small run queue (minimal amount of programs on it). WAIT QUEUE: A queu ...
COS 318: Operating Systems Overview Kai Li and Andy Bavier
... Examples that are not provided at user level System calls: file open, close, read and write l Control the CPU so that users won’t get stuck by running l ...
... Examples that are not provided at user level System calls: file open, close, read and write l Control the CPU so that users won’t get stuck by running l ...
Operating Systems
... Problem: lots of wasted computer time! Computer was idle during first and last steps Computers were very expensive! ...
... Problem: lots of wasted computer time! Computer was idle during first and last steps Computers were very expensive! ...