The effect of Steroids in DBA
... implicated in DBA • Absent progenitors in 7 relapsed patients with DBA (Nathan D JCI 1978) • Normal progenitor numbers with impaired development of progenitors to red blood cells (Lipton J et al Blood 1989) ...
... implicated in DBA • Absent progenitors in 7 relapsed patients with DBA (Nathan D JCI 1978) • Normal progenitor numbers with impaired development of progenitors to red blood cells (Lipton J et al Blood 1989) ...
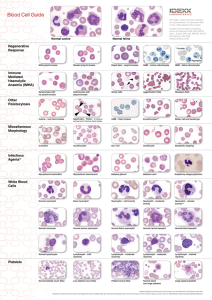
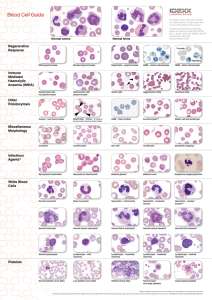
Blood Cell Guide
... **Illustration reproduced with permission from Reagan WJ, Rovira AI, DeNicola DB, eds. Veterinary Haematology: Atlas of Common Domestic and Non-Domestic Species. 2nd ed. Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell; 2008. Copyright 2008 Wiley-Blackwell. ...
... **Illustration reproduced with permission from Reagan WJ, Rovira AI, DeNicola DB, eds. Veterinary Haematology: Atlas of Common Domestic and Non-Domestic Species. 2nd ed. Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell; 2008. Copyright 2008 Wiley-Blackwell. ...
Blood Cell Guide - IDEXX Laboratories
... **Illustration reproduced with permission from Reagan WJ, Rovira AI, DeNicola DB, eds. Veterinary Haematology: Atlas of Common Domestic and Non-Domestic Species. 2nd ed. Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell; 2008. Copyright 2008 Wiley-Blackwell. ...
... **Illustration reproduced with permission from Reagan WJ, Rovira AI, DeNicola DB, eds. Veterinary Haematology: Atlas of Common Domestic and Non-Domestic Species. 2nd ed. Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell; 2008. Copyright 2008 Wiley-Blackwell. ...
blood type A
... Blood group antigens are carbohydrates that are attached to proteins or lipids. An antigen is a substance foreign to the body that causes an immune response. An immune response occurs when antibodies, which are proteins in your immune system, are summoned to attack an antigen. When you say you are b ...
... Blood group antigens are carbohydrates that are attached to proteins or lipids. An antigen is a substance foreign to the body that causes an immune response. An immune response occurs when antibodies, which are proteins in your immune system, are summoned to attack an antigen. When you say you are b ...
Blood Types and Transfusion
... The jaundiced, erythroblastotic newborn baby is usually anemic at birth, and the antiRh agglutinins from the mother usually circulate in the infant’s blood for another 1 to 2 months after birth, destroying more and more red blood cells. The hematopoietic tissues of the infant attempt to replace the ...
... The jaundiced, erythroblastotic newborn baby is usually anemic at birth, and the antiRh agglutinins from the mother usually circulate in the infant’s blood for another 1 to 2 months after birth, destroying more and more red blood cells. The hematopoietic tissues of the infant attempt to replace the ...
Protein S Deficiency Brochure - University of Iowa Health Care
... health, symptoms, and need for other medications or surgical procedures. The duration of treatment will vary depending on your individual medical history, and the presence of other health problems. Your treatment plan should be discussed with your primary doctor or hematologist. Some people with thr ...
... health, symptoms, and need for other medications or surgical procedures. The duration of treatment will vary depending on your individual medical history, and the presence of other health problems. Your treatment plan should be discussed with your primary doctor or hematologist. Some people with thr ...
Protein C Deficiency Brochure - University of Iowa Health Care
... health, symptoms, and need for other medications or surgical procedures. The duration of treatment will vary depending on your individual medical history, and the presence of other health problems. Your treatment plan should be discussed with your primary doctor or hematologist. Some people with thr ...
... health, symptoms, and need for other medications or surgical procedures. The duration of treatment will vary depending on your individual medical history, and the presence of other health problems. Your treatment plan should be discussed with your primary doctor or hematologist. Some people with thr ...
Standard Precautions
... Sharps with engineered sharps injury protections means a nonneedle sharp or a needle device used for withdrawing body fluids, accessing a vein or artery, or administering medications or other fluids, with a built‐in safety feature or mechanism that effectively reduces the risk of an exposure incid ...
... Sharps with engineered sharps injury protections means a nonneedle sharp or a needle device used for withdrawing body fluids, accessing a vein or artery, or administering medications or other fluids, with a built‐in safety feature or mechanism that effectively reduces the risk of an exposure incid ...
Shock
... Shock occurs when a diminished amount of blood is available to the circulatory system The vascular system fails to hold the fluid portion of the blood Vasodilation of the blood vessels occurs and disrupts the osmotic fluid balance in the body ...
... Shock occurs when a diminished amount of blood is available to the circulatory system The vascular system fails to hold the fluid portion of the blood Vasodilation of the blood vessels occurs and disrupts the osmotic fluid balance in the body ...
Blood Notes - Moodle d128
... BloodRed Blood Cells (erythrocytes)White Blood Cells (leukocytes)PlasmaPlatelets- ...
... BloodRed Blood Cells (erythrocytes)White Blood Cells (leukocytes)PlasmaPlatelets- ...
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Brochure
... health, symptoms, and need for other medications or surgical procedures. The duration of treatment will vary depending on your individual medical history, and the presence of other health problems. Your treatment plan should be discussed with your primary doctor or hematologist. Some people with thr ...
... health, symptoms, and need for other medications or surgical procedures. The duration of treatment will vary depending on your individual medical history, and the presence of other health problems. Your treatment plan should be discussed with your primary doctor or hematologist. Some people with thr ...
Antithrombin Deficiency Brochure
... health, symptoms, and need for other medications or surgical procedures. The duration of treatment will vary depending on your individual medical history, and the presence of other health problems. Your treatment plan should be discussed with your primary doctor or hematologist. Some people with thr ...
... health, symptoms, and need for other medications or surgical procedures. The duration of treatment will vary depending on your individual medical history, and the presence of other health problems. Your treatment plan should be discussed with your primary doctor or hematologist. Some people with thr ...
Dental students-hemodynamics
... : tightly regulated processes that maintain blood in a fluid, clot-free state in normal vessels while inducing the rapid formation of a localized hemostatic plug at the site of vascular injury. The pathologic form of hemostasis is ...
... : tightly regulated processes that maintain blood in a fluid, clot-free state in normal vessels while inducing the rapid formation of a localized hemostatic plug at the site of vascular injury. The pathologic form of hemostasis is ...
information for requesting doctors
... However, if other causes of raised ferritin have been excluded, such as malignancy, significant liver disease, chronic systemic or inflammatory disease or autoimmune disease, the person may be eligible to become a regular whole blood donor, donating at intervals of 12 weeks or more. ...
... However, if other causes of raised ferritin have been excluded, such as malignancy, significant liver disease, chronic systemic or inflammatory disease or autoimmune disease, the person may be eligible to become a regular whole blood donor, donating at intervals of 12 weeks or more. ...
Handwriting analysis takes many years of dedicated study
... Which blood type would be considered a universal donor (someone who can give blood to anyone)? Genetics of Blood Types Your blood type is established before you are born, by specific genes inherited from your parents. You receive one blood type gene from your mother and one from your father. These t ...
... Which blood type would be considered a universal donor (someone who can give blood to anyone)? Genetics of Blood Types Your blood type is established before you are born, by specific genes inherited from your parents. You receive one blood type gene from your mother and one from your father. These t ...
Blood transfusion Part 1 - Basics - e-safe
... Calcium: Each unit of blood contains approximately 3g citrate, which binds ionized calcium. However, the liver is able to metabolise 3g of citrate every 5 minutes, so that only when transfusion rates are greater than one unit per five minutes or in the presence of impaired liver function is there a ...
... Calcium: Each unit of blood contains approximately 3g citrate, which binds ionized calcium. However, the liver is able to metabolise 3g of citrate every 5 minutes, so that only when transfusion rates are greater than one unit per five minutes or in the presence of impaired liver function is there a ...
242 Blood transfusion part 1 - Basics
... Calcium: Each unit of blood contains approximately 3g citrate, which binds ionized calcium. However, the liver is able to metabolise 3g of citrate every 5 minutes, so that only when transfusion rates are greater than one unit per five minutes or in the presence of impaired liver function is there a ...
... Calcium: Each unit of blood contains approximately 3g citrate, which binds ionized calcium. However, the liver is able to metabolise 3g of citrate every 5 minutes, so that only when transfusion rates are greater than one unit per five minutes or in the presence of impaired liver function is there a ...
I. Blood Collection - Austin Community College
... After interview the donor will place the appropriate bar coded label on the donation record If “no” selected the unit is collected, fully tested, but not used for transfusion Allows donors who know they are at risk to “save face” if pressured to donate by friends and family ...
... After interview the donor will place the appropriate bar coded label on the donation record If “no” selected the unit is collected, fully tested, but not used for transfusion Allows donors who know they are at risk to “save face” if pressured to donate by friends and family ...
Red Blood Plasma Transfusion
... alternatives must be considered whenever time is available for their implementation • In acute blood loss, transfusion should not be used to expand vascular volume when oxygen carrying capacity is adequate • In chronic anemia, physiologic adaptation may be sufficient to allow time for use of tra ...
... alternatives must be considered whenever time is available for their implementation • In acute blood loss, transfusion should not be used to expand vascular volume when oxygen carrying capacity is adequate • In chronic anemia, physiologic adaptation may be sufficient to allow time for use of tra ...
CIRCULATING CELL FREE DNA AND MIRNA EXTRACTION FROM
... rotor (392187 and 392243) within 2 hours after the blood was collected. The plasma supernatant was transferred and pooled into a nuclease free clean tube, and centrifuged at 16,000xg for 15 minutes to prepare supernatant plasma without cell debris and with minimized genomic DNA contamination using a ...
... rotor (392187 and 392243) within 2 hours after the blood was collected. The plasma supernatant was transferred and pooled into a nuclease free clean tube, and centrifuged at 16,000xg for 15 minutes to prepare supernatant plasma without cell debris and with minimized genomic DNA contamination using a ...
New Zealand Blood Service Teaching Units Level 7 Science:
... Test the bloods with antisera A and B to find the blood type of each sample. • The test result is positive if a solid forms when the antisera is mixed with the blood. • The test result is negative if no solid forms when the antisera is mixed with the blood. ...
... Test the bloods with antisera A and B to find the blood type of each sample. • The test result is positive if a solid forms when the antisera is mixed with the blood. • The test result is negative if no solid forms when the antisera is mixed with the blood. ...
08.02.002 e2.0 Blood Processing and Storage CTRNet Standard
... In the area designated by the biobank for processing blood, fractionate the whole blood (blood collected in tubes containing an anticoagulant such as ethylene-diamineteraacetic acid-EDTA or Heparin) by centrifuging at 1500-2000 x g for 15 minutes at room temperature. This will separate the blood int ...
... In the area designated by the biobank for processing blood, fractionate the whole blood (blood collected in tubes containing an anticoagulant such as ethylene-diamineteraacetic acid-EDTA or Heparin) by centrifuging at 1500-2000 x g for 15 minutes at room temperature. This will separate the blood int ...
Factor XIII: sticking it to platelets
... blood smears. Analysis showed that these platelets lacked a class of granules that are now known as a-granules. GPS is a rare autosomal recessive disorder associated with macrothrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, myelofibrosis, increased serum B12, and mildto-moderate bleeding tendencies.3 Although fatal ...
... blood smears. Analysis showed that these platelets lacked a class of granules that are now known as a-granules. GPS is a rare autosomal recessive disorder associated with macrothrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, myelofibrosis, increased serum B12, and mildto-moderate bleeding tendencies.3 Although fatal ...