Rational Exponents 1 Answers
... One way to solve equations is to think of the equation as a balance and we must work with both sides to “undo” what was done to the variable. For example, if 4x + 7 = 31, we must “undo” adding 7, so subtract 7 from each side, yielding 4x = 24. Then we must “undo” multiplying by 4, so we divide both ...
... One way to solve equations is to think of the equation as a balance and we must work with both sides to “undo” what was done to the variable. For example, if 4x + 7 = 31, we must “undo” adding 7, so subtract 7 from each side, yielding 4x = 24. Then we must “undo” multiplying by 4, so we divide both ...
Slide 1 - Elgin Local Schools
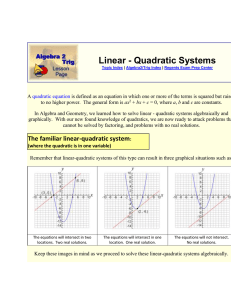
... a) Same line (Concurrent, Or coincident lines) (infinite number of solutions) y = (-5/2)x + 4 5x + 2y = 8 ...
... a) Same line (Concurrent, Or coincident lines) (infinite number of solutions) y = (-5/2)x + 4 5x + 2y = 8 ...
Unit 2
... Simplify & evaluate algebraic expressions, including those with exponents. Solve and interpret algebraic equations and inequalities in 1 variable, including those with absolute values. Graph the solution of an equation or an inequality on a number line. ...
... Simplify & evaluate algebraic expressions, including those with exponents. Solve and interpret algebraic equations and inequalities in 1 variable, including those with absolute values. Graph the solution of an equation or an inequality on a number line. ...
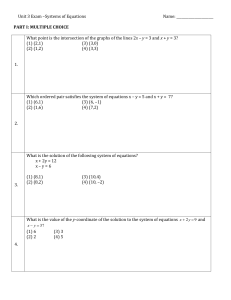
Old Test One
... a) Create a slope field for this diff eq and based on the slope field, explain the end behavior of solutions and/or how the end behavior depends on the choice of initial conditions. ...
... a) Create a slope field for this diff eq and based on the slope field, explain the end behavior of solutions and/or how the end behavior depends on the choice of initial conditions. ...