2.6 Graphing linear Inequalities in 2 Variables
... Graphing an Inequality in Two Variables Graph x < 2 Step 1: Start by graphing the line x = 2 ...
... Graphing an Inequality in Two Variables Graph x < 2 Step 1: Start by graphing the line x = 2 ...
Math 111 Pre-test(Show all work
... Math 111 Pre-test Show all work. No calculators. No books. Take as much time as you like but do it NEATLY!! To be handed in first day of class. This will NOT count toward your grade. 1. Find the area of the region bounded by 2. Find the equation of the line with slope 2 that intersects the x-axis wh ...
... Math 111 Pre-test Show all work. No calculators. No books. Take as much time as you like but do it NEATLY!! To be handed in first day of class. This will NOT count toward your grade. 1. Find the area of the region bounded by 2. Find the equation of the line with slope 2 that intersects the x-axis wh ...
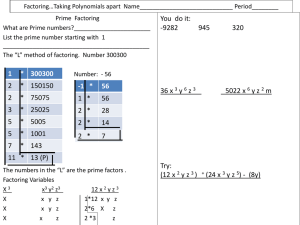
Factoring…Taking Polynomials apart
... zeroes, solutions 15, Y intercept – where a graph touches or crosses the y axis in a quadratic, it is at “c”. 16. Axis of Symmetry – the vertical line that passes through the vertex of a quadratic graph 17. Axis of Symmetry Formula -b/2a (the opposite of b divided by 2 times a 18. Reflection – The m ...
... zeroes, solutions 15, Y intercept – where a graph touches or crosses the y axis in a quadratic, it is at “c”. 16. Axis of Symmetry – the vertical line that passes through the vertex of a quadratic graph 17. Axis of Symmetry Formula -b/2a (the opposite of b divided by 2 times a 18. Reflection – The m ...
Math 20 Module 4 Review - Westwind Alternate School
... y=(x-1)( x2 +x-6) y=(x-1)(x+3)(x-2) Review the remainder theorem This leads us to the Remainder Theorem which states: If a polynomial f(x) is divided by (x − r) and a remainder R is obtained, then f(r) = R. 12) When P(x) = x3 - 3x2 + kx + 2 is divided by x - 2 the remainder is 4. a. Determine the va ...
... y=(x-1)( x2 +x-6) y=(x-1)(x+3)(x-2) Review the remainder theorem This leads us to the Remainder Theorem which states: If a polynomial f(x) is divided by (x − r) and a remainder R is obtained, then f(r) = R. 12) When P(x) = x3 - 3x2 + kx + 2 is divided by x - 2 the remainder is 4. a. Determine the va ...
PART 7 Ordinary Differential Equations ODEs
... A value is assumed for one of the unknowns to solve for the other three. ...
... A value is assumed for one of the unknowns to solve for the other three. ...