AMEE 202 Midterm S14_1 Group 2
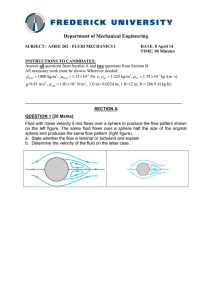
... a spherical shape V r 3 , what would be the required diameter? ...
... a spherical shape V r 3 , what would be the required diameter? ...
Pulmonary Capacity Analyzer - Learn
... released, the timer stops. So to properly use this system, the user must depress the switch as he begins inhaling, and release at the completion of the inhale. This time value (measured in milliseconds) is then multiplied by the volume flow data previously calculated to finally yield a volume of air ...
... released, the timer stops. So to properly use this system, the user must depress the switch as he begins inhaling, and release at the completion of the inhale. This time value (measured in milliseconds) is then multiplied by the volume flow data previously calculated to finally yield a volume of air ...
CVE 304: Hydraulics II (2 Units)
... d) Rectangular, Triangular, Trapezoidal, Circular, Semi-Circular or irregular shape ...
... d) Rectangular, Triangular, Trapezoidal, Circular, Semi-Circular or irregular shape ...
2014
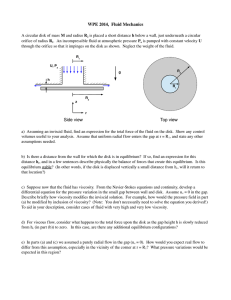
... c) Suppose now that the fluid has viscosity. From the NavierStokes equations and continuity, develop a differential equation for the pressure variation in the small gap between wall and disk. Assume u z = 0 in the gap. Describe briefly how viscosity modifies the inviscid solution. For exampl ...
... c) Suppose now that the fluid has viscosity. From the NavierStokes equations and continuity, develop a differential equation for the pressure variation in the small gap between wall and disk. Assume u z = 0 in the gap. Describe briefly how viscosity modifies the inviscid solution. For exampl ...
Vortex Shedding
... experiences a net pressure force opposite to its direction of motion. • At some point (point C), the momentum of the fluid in the boundary layer is insufficient to carry the element further into the region of increasing pressure. • The fluid layers adjacent to the solid surface are brought to rest ...
... experiences a net pressure force opposite to its direction of motion. • At some point (point C), the momentum of the fluid in the boundary layer is insufficient to carry the element further into the region of increasing pressure. • The fluid layers adjacent to the solid surface are brought to rest ...