The Use of the Primitive Equations of Motion in Numerical Prediction
... An obstacle to the use of the primitive hydrodynamical equations for numerical prediction is that the initial wind and pressure fields determined by conventional means give rise to spurious large-amplitude inertio-gravitational oscillations which obscure the nieteorologically Eignificant large-scale ...
... An obstacle to the use of the primitive hydrodynamical equations for numerical prediction is that the initial wind and pressure fields determined by conventional means give rise to spurious large-amplitude inertio-gravitational oscillations which obscure the nieteorologically Eignificant large-scale ...
國立臺北科技大學九十一學年度
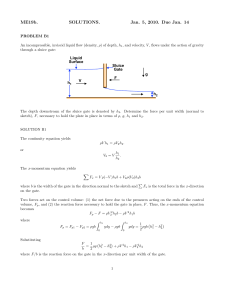
... the x-component of fluid velocity u as a function of time t, fluid viscosity μ, top plate speed V, distance h, fluid densityρ, and distance y (i.e. u= f(t,μ, V, h,ρ, y)). Show details of your work. 5) An incompressible, viscous fluid is placed between two horizontal, infinite, parallel plates as is ...
... the x-component of fluid velocity u as a function of time t, fluid viscosity μ, top plate speed V, distance h, fluid densityρ, and distance y (i.e. u= f(t,μ, V, h,ρ, y)). Show details of your work. 5) An incompressible, viscous fluid is placed between two horizontal, infinite, parallel plates as is ...
Momentum (Newton`s 2nd Law of Motion)
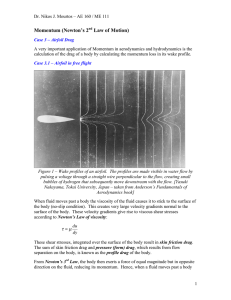
... Figure 4 – Schematic of a different control volume around an airfoil in free flight. The airfoil is again excluded from the control volume. Assumptions: Steady flow Incompressible flow 2- D flow Viscous effects along the control surface are negligible What else is going on: One flow stream ...
... Figure 4 – Schematic of a different control volume around an airfoil in free flight. The airfoil is again excluded from the control volume. Assumptions: Steady flow Incompressible flow 2- D flow Viscous effects along the control surface are negligible What else is going on: One flow stream ...
Surficial Processes Take Home Problems
... Problem 3. Consider a soil particle on a moderately steep hillslope in the Boise foothills. Summarize 4 different processes by which that particle can move downslope. Include qualitative descriptions of the driving forces and resisting forces for each process. Problem 4. List 4 physical variables (l ...
... Problem 3. Consider a soil particle on a moderately steep hillslope in the Boise foothills. Summarize 4 different processes by which that particle can move downslope. Include qualitative descriptions of the driving forces and resisting forces for each process. Problem 4. List 4 physical variables (l ...
Lecture Presentation Chp-10
... Coriolis Mass Flowmeter The Coriolis force is a force that occurs when dynamic problems are analyzed within a rotating reference frame. Useful flowmeters based on this effect are now widely used in the process industries. Consider a fluid flowing through the U-shaped tube shown in Figure 10.13(a ...
... Coriolis Mass Flowmeter The Coriolis force is a force that occurs when dynamic problems are analyzed within a rotating reference frame. Useful flowmeters based on this effect are now widely used in the process industries. Consider a fluid flowing through the U-shaped tube shown in Figure 10.13(a ...
Propeller Efficiency and the SolidWater™ Propeller
... draft interference as the blades are not distributed around a central shaft and massive hub. ! The blade is designed to be slow but can move faster than foil-chorded propellers without penalty due to the elimination of the precavitational state. This is a state of flow where there is a perpetual and ...
... draft interference as the blades are not distributed around a central shaft and massive hub. ! The blade is designed to be slow but can move faster than foil-chorded propellers without penalty due to the elimination of the precavitational state. This is a state of flow where there is a perpetual and ...
File - The Physics Doctor
... As the air moves faster over the top, this means that there is a difference in pressure on the wing. This means that there is more force applied to the bottom of the wing, resulting in uplift (and drag) ...
... As the air moves faster over the top, this means that there is a difference in pressure on the wing. This means that there is more force applied to the bottom of the wing, resulting in uplift (and drag) ...
Factors Affecting Wind - School of Engineering
... centre. Therefore, the resultant winds blow into and counterclockwise about a surface cyclone. In an anticyclone the oppose is true: the pressure decreases outward and thus friction causes a net flow away from the centre. Therefore, the resultant winds blow outward and clockwise about a surface anti ...
... centre. Therefore, the resultant winds blow into and counterclockwise about a surface cyclone. In an anticyclone the oppose is true: the pressure decreases outward and thus friction causes a net flow away from the centre. Therefore, the resultant winds blow outward and clockwise about a surface anti ...
WIND MEASURING AND HUMIDITY SENSORS.
... unequal, the warmer air tends to rise and flow over the colder, heavier air. Winds initiated in this way are usually greatly modified by earth’s rotation. ...
... unequal, the warmer air tends to rise and flow over the colder, heavier air. Winds initiated in this way are usually greatly modified by earth’s rotation. ...
Physics 2053C – Fall 2001
... Water heater in the basement, faucet on the 2nd floor Basement: dpipe = 4.0cm v = 0.50m/s P = 3 atm 2nd floor: dpipe = 2.6cm height = 5m ...
... Water heater in the basement, faucet on the 2nd floor Basement: dpipe = 4.0cm v = 0.50m/s P = 3 atm 2nd floor: dpipe = 2.6cm height = 5m ...
Xie-EGM-RPI-2011.pdf
... • Steady Laminar Flow around a Backward Facing Step. A conducting fluid flows between two large parallel plates and it comes into a backward facing step where a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the plane of the plates. Electric field (if any) applied perpendicular to the plane formed by th ...
... • Steady Laminar Flow around a Backward Facing Step. A conducting fluid flows between two large parallel plates and it comes into a backward facing step where a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the plane of the plates. Electric field (if any) applied perpendicular to the plane formed by th ...
Chapter 2 - CP Physics
... An airplane’s wings each have an area of 4.0 m2. When flying level, the speed of the air over the wings is 245 m/s, while the speed of the air under the wings is 222 m/s. What is the mass of the plane? ...
... An airplane’s wings each have an area of 4.0 m2. When flying level, the speed of the air over the wings is 245 m/s, while the speed of the air under the wings is 222 m/s. What is the mass of the plane? ...
MCAT Fluid dynamics
... 6:-When a body is moving with terminal velocity then it has zero acceleration. 7:-At terminal velocity fluid friction is maximum. 8:-At terminal velocity the net force acting on the body is zero. 9:-Terminal velocity of the body is directly proportional to its mass & density. 10:-Strokes law holds g ...
... 6:-When a body is moving with terminal velocity then it has zero acceleration. 7:-At terminal velocity fluid friction is maximum. 8:-At terminal velocity the net force acting on the body is zero. 9:-Terminal velocity of the body is directly proportional to its mass & density. 10:-Strokes law holds g ...