Settling and Sedimentation
... eventually is deposited as a layer of solid particles on the bed or bottom of a body of water or other liquid. Sedimentation - the deposition by settling of a suspended material. -the separation of a dilute slurry or suspension by gravity settling into a clear fluid and a slurry of higher solids con ...
... eventually is deposited as a layer of solid particles on the bed or bottom of a body of water or other liquid. Sedimentation - the deposition by settling of a suspended material. -the separation of a dilute slurry or suspension by gravity settling into a clear fluid and a slurry of higher solids con ...
Solute
... Freezing point depression and boiling point elevation: adding solute to a solvent lowers the freezing point and raises the boiling point of the solvent. • Solute particles disrupt crystallization and ...
... Freezing point depression and boiling point elevation: adding solute to a solvent lowers the freezing point and raises the boiling point of the solvent. • Solute particles disrupt crystallization and ...
Particle Size Enlargement - Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy
... the particles influences the packing and flow of powders. On a molecular level, the characteristic surface roughness and real area of contact dictates the cohesion and adhesion properties of particles surface.[7-10] Sometimes, cohesive powders that exhibits poor flow property are formed due to incre ...
... the particles influences the packing and flow of powders. On a molecular level, the characteristic surface roughness and real area of contact dictates the cohesion and adhesion properties of particles surface.[7-10] Sometimes, cohesive powders that exhibits poor flow property are formed due to incre ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... However, after 300ºC the reflections mainly signify the hematite phase of the nano particle. In this case, the formation of the maghemite like structure is mainly restricted by the kinetic issue during the growth of hematite nano particle by the sintering process. This means that not only particle ...
... However, after 300ºC the reflections mainly signify the hematite phase of the nano particle. In this case, the formation of the maghemite like structure is mainly restricted by the kinetic issue during the growth of hematite nano particle by the sintering process. This means that not only particle ...
New Liquid Crystalline Tolanes from (-)
... The design and synthesis of new chiral liquid crystals has experienced a great growth, especially of ferroelectric liquid crystals (FLCs). This is due to practical applications of FLCs as high resolution displays and in photonical technologies for storage and reproduction of information based on non ...
... The design and synthesis of new chiral liquid crystals has experienced a great growth, especially of ferroelectric liquid crystals (FLCs). This is due to practical applications of FLCs as high resolution displays and in photonical technologies for storage and reproduction of information based on non ...
Metathesis Problems (and Some Solutions) Identified Through
... water, most of the salt would dissolve but some would remain on the bottom – Ions dissolve by leaving the surface of the crystal and entering the liquid solution – Some crystals may re-deposit on the crystal • Equilibrium is reached at point where particles dissolve at same rate as they return to th ...
... water, most of the salt would dissolve but some would remain on the bottom – Ions dissolve by leaving the surface of the crystal and entering the liquid solution – Some crystals may re-deposit on the crystal • Equilibrium is reached at point where particles dissolve at same rate as they return to th ...
Document
... 12.When 20 gm of an acid (C11H8O2) is dissolved in 50 gm benzene (K f=1.72K kg mol‐1) a freezing point depression of 2K is observed.Thevant Hoff’s factor is ...
... 12.When 20 gm of an acid (C11H8O2) is dissolved in 50 gm benzene (K f=1.72K kg mol‐1) a freezing point depression of 2K is observed.Thevant Hoff’s factor is ...
X04704145151
... application to second order NLO materials than organics. Most commercial materials are inorganic especially for high power use. However, organic materials are perceived as being structurally more diverse and therefore are believed to have more long term promise than inorganics. Recent interest is co ...
... application to second order NLO materials than organics. Most commercial materials are inorganic especially for high power use. However, organic materials are perceived as being structurally more diverse and therefore are believed to have more long term promise than inorganics. Recent interest is co ...
Regents Chemistry
... Be able to describe the effect of polarity, temperature & pressure on the solubility of solids in liquids, liquids in liquids or gas in liquids o remember: pressure only effects solubility of gases in liquids o as temperature increases the solubility of solids tends to increase but the solubility of ...
... Be able to describe the effect of polarity, temperature & pressure on the solubility of solids in liquids, liquids in liquids or gas in liquids o remember: pressure only effects solubility of gases in liquids o as temperature increases the solubility of solids tends to increase but the solubility of ...
Mixtures
... suspensions. These mixtures are known as colloids. A colloid is a mixture in which the particles are dispersed throughout but are not heavy enough to settle out. The particles in a colloid are relatively small and are fairly well mixed. Solids, liquids, and gases can be used to make colloids. Unli ...
... suspensions. These mixtures are known as colloids. A colloid is a mixture in which the particles are dispersed throughout but are not heavy enough to settle out. The particles in a colloid are relatively small and are fairly well mixed. Solids, liquids, and gases can be used to make colloids. Unli ...
Metastability limit for the nucleation of NaCl crystals in confinement
... concentration for which nucleation is first observed, recrystallization experiments were conducted by performing repeated cycles of complete deliquescence (dissolution by water vapour) of the salt crystals followed by drying, a procedure that is known to efficiently expel impurities (6,27). These re ...
... concentration for which nucleation is first observed, recrystallization experiments were conducted by performing repeated cycles of complete deliquescence (dissolution by water vapour) of the salt crystals followed by drying, a procedure that is known to efficiently expel impurities (6,27). These re ...
plumbum thiogallate optical properties
... placed. The wafers were oriented so that they did not change the condition of polarization of incident radiation. Typical number of ob ctory optical quality). A decrease in the number of observed rings is connected with phase distortions introduced by the wafer into the stopped beam of radiation of ...
... placed. The wafers were oriented so that they did not change the condition of polarization of incident radiation. Typical number of ob ctory optical quality). A decrease in the number of observed rings is connected with phase distortions introduced by the wafer into the stopped beam of radiation of ...
Colligative Properties
... Van’t Hoff Factor • Determines the moles of particles that are present when a compound dissolves in a solution • Covalent compounds do not dissociate – C12H22O11 ...
... Van’t Hoff Factor • Determines the moles of particles that are present when a compound dissolves in a solution • Covalent compounds do not dissociate – C12H22O11 ...
The chemistry and physics of interstellar ices
... Distribution of ices in a cloud/envelope/disk. Dust temperatures, radiation fields, density and history of the above parameters. ...
... Distribution of ices in a cloud/envelope/disk. Dust temperatures, radiation fields, density and history of the above parameters. ...
Growth and characterization of Urea Lead nitrate
... which is due to the decrease in mobility of the charge carriers and also it brings changes in the electronic band structure. Electrical conduction is observed in the crystal, as a result of electrons jump from metal ions of lead with low valence state to high valence state. ...
... which is due to the decrease in mobility of the charge carriers and also it brings changes in the electronic band structure. Electrical conduction is observed in the crystal, as a result of electrons jump from metal ions of lead with low valence state to high valence state. ...
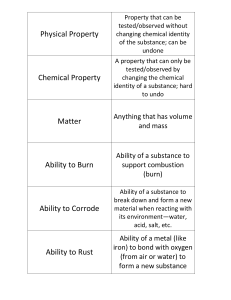
Physical Property
... Temperature at which a solid turns to liquid AND Temperature at which a liquid turns to solid ...
... Temperature at which a solid turns to liquid AND Temperature at which a liquid turns to solid ...
Characteristic Properties Non-Characteristic Properties
... A non-characteristic property is a physical or chemical property that is not unique to one particular substance. Basically: A NCP can be used to describe many substances ...
... A non-characteristic property is a physical or chemical property that is not unique to one particular substance. Basically: A NCP can be used to describe many substances ...
A mechanical model of Markov processes
... However, we have to notice that, even in the model of collisional interactions only, there exists the possibility of re-collision, so the states (i.e., positions and velocities) of small particles at each time are not independent to each other, nor to the history of the system. This becomes more evi ...
... However, we have to notice that, even in the model of collisional interactions only, there exists the possibility of re-collision, so the states (i.e., positions and velocities) of small particles at each time are not independent to each other, nor to the history of the system. This becomes more evi ...
Synthesis and Characterization of Large Colloidal Silver Particles
... Au, Al, Ni, Cu) have been investigated theoretically as possible candidates for metallodielectric photonic crystals.10-14 Because of its low bulk absorption, silver (Ag) is the most suitable metal to create a CPBG in the visible. Recent calculations of Moroz have shown that a CPBG can even be opened ...
... Au, Al, Ni, Cu) have been investigated theoretically as possible candidates for metallodielectric photonic crystals.10-14 Because of its low bulk absorption, silver (Ag) is the most suitable metal to create a CPBG in the visible. Recent calculations of Moroz have shown that a CPBG can even be opened ...
Metamorphic Minerals.
... typically first occurs at medium grade metamorphism. Although not very well illustrated by these specimens, its habit is as dodecahedral crystals, that is, twelve diamond-shaped faces [yellow arrows] with the edges “beveled off” by narrow faces [light blue arrow]. There is no cleavage, so one sees f ...
... typically first occurs at medium grade metamorphism. Although not very well illustrated by these specimens, its habit is as dodecahedral crystals, that is, twelve diamond-shaped faces [yellow arrows] with the edges “beveled off” by narrow faces [light blue arrow]. There is no cleavage, so one sees f ...
E:\My Documents\snc1d\feb12notes.wpd
... Pure substances: uniform and consistent properties in different samples. Mixtures: may or may not be uniform, but properties are variable. Explanation In a pure substance, only one type of particle is present. - every sample is uniform throughout and each is the same as any other. In a mixture, ther ...
... Pure substances: uniform and consistent properties in different samples. Mixtures: may or may not be uniform, but properties are variable. Explanation In a pure substance, only one type of particle is present. - every sample is uniform throughout and each is the same as any other. In a mixture, ther ...
Section3a - Lyle School of Engineering
... temperature dependence of this transformation is in the bottom portion of Figure 9.10. Here, the vertical and horizontal axes are, respectively, temperature and the logarithm of time. Two solid curves are plotted; one represents the time required at each temperature for the initiation or start of th ...
... temperature dependence of this transformation is in the bottom portion of Figure 9.10. Here, the vertical and horizontal axes are, respectively, temperature and the logarithm of time. Two solid curves are plotted; one represents the time required at each temperature for the initiation or start of th ...
PDF
... Solid state parameters are necessary to analyze second harmonic generation efficiency of the grown crystals. The value of valance electron Plasma energy (Ep), Penn gap energy, Fermi energy (EF) and polarizability (α) of the grown crystals were calculated by the formulas given by Vasdevan et al. [21] ...
... Solid state parameters are necessary to analyze second harmonic generation efficiency of the grown crystals. The value of valance electron Plasma energy (Ep), Penn gap energy, Fermi energy (EF) and polarizability (α) of the grown crystals were calculated by the formulas given by Vasdevan et al. [21] ...
Solutions!
... Shows the relationship of grams of solute that may be dissolved at various temperatures. ...
... Shows the relationship of grams of solute that may be dissolved at various temperatures. ...