MultiPlus Inverter/Charger
... The MultiPlus is a very powerful battery charger. It will therefore draw a lot of current from the generator or shore side supply (nearly 10 A per 5 kVA Multi at 230 VAC). With the Multi Control Panel a maximum generator or shore current can be set. The MultiPlus will then take account of other AC l ...
... The MultiPlus is a very powerful battery charger. It will therefore draw a lot of current from the generator or shore side supply (nearly 10 A per 5 kVA Multi at 230 VAC). With the Multi Control Panel a maximum generator or shore current can be set. The MultiPlus will then take account of other AC l ...
Chapter 5
... Operating console – consists of ALL LOW VOLTAGE components and controls: Quantity – mA/mAs (amount of radiation produced) increases in mA will increase the number of electrons available to be “boiled off” the filament via THERMIONIC EMISSION. FILAMENT CURRENT is usually 3-6 AMPS in order to have eno ...
... Operating console – consists of ALL LOW VOLTAGE components and controls: Quantity – mA/mAs (amount of radiation produced) increases in mA will increase the number of electrons available to be “boiled off” the filament via THERMIONIC EMISSION. FILAMENT CURRENT is usually 3-6 AMPS in order to have eno ...
servo control facts
... motor to rotate at the same speed (in synchronization) as the stator field. There are basically two types of synchronous motors: self excited ( as the induction motor) and directly excited (as with permanent magnets). The self excited motor (may be called reluctance synchronous) includes a rotor wit ...
... motor to rotate at the same speed (in synchronization) as the stator field. There are basically two types of synchronous motors: self excited ( as the induction motor) and directly excited (as with permanent magnets). The self excited motor (may be called reluctance synchronous) includes a rotor wit ...
How to Set Control Voltage In an Application Circuit
... shows the 1.2kΩ resistor would drop the voltage from 3V to about 1.4V in this case. The same plot shows that at Vcont=1.4V, Pout and IDD are only slightly lowered. In conclusion, a single serial resistor of 1.2 to 1.5kΩ can lower a supply voltage of 3 to 3.3V to the appropriate range for Vcont. The ...
... shows the 1.2kΩ resistor would drop the voltage from 3V to about 1.4V in this case. The same plot shows that at Vcont=1.4V, Pout and IDD are only slightly lowered. In conclusion, a single serial resistor of 1.2 to 1.5kΩ can lower a supply voltage of 3 to 3.3V to the appropriate range for Vcont. The ...
70 Watt AM Shortwave Transmitter Circuit
... This is truly a 'Rig-in-the-Box'! The rig itself is placed in a well rugged cabinet for field operations. The VU meter (left) is available on the chassis that shows the peak modulation. (0VU = 100% modulation) On the right metering is provided for Grid current and Kathode current on the 807s, ...
... This is truly a 'Rig-in-the-Box'! The rig itself is placed in a well rugged cabinet for field operations. The VU meter (left) is available on the chassis that shows the peak modulation. (0VU = 100% modulation) On the right metering is provided for Grid current and Kathode current on the 807s, ...
Chapter 16: Lower Motor Neuron Circuits
... provide their efferent input. Peripheral nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy) Mononeuropathy-Mononeuropathy and radiculopathy is most often due to trauma of some type. Radiculopathy-Radiculopathy indicates damage to nerve root(s), and typically occurs as a component of several spinal diseases. Polyn ...
... provide their efferent input. Peripheral nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy) Mononeuropathy-Mononeuropathy and radiculopathy is most often due to trauma of some type. Radiculopathy-Radiculopathy indicates damage to nerve root(s), and typically occurs as a component of several spinal diseases. Polyn ...
1-MHz, 3.3-V High-Efficiency Synchronous Buck
... Design Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 ...
... Design Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 ...
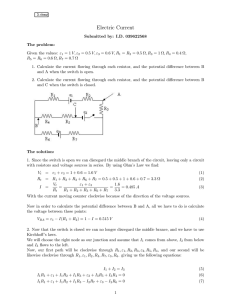
Direct current - Sackville School
... In the UK, the frequency of mains electricity is 50 hertz: this alternating current flows backwards and forwards 50 times per second. This frequency is the same at any point in the electricity supply system but the voltage varies in different parts of the national grid. The voltage of mains electric ...
... In the UK, the frequency of mains electricity is 50 hertz: this alternating current flows backwards and forwards 50 times per second. This frequency is the same at any point in the electricity supply system but the voltage varies in different parts of the national grid. The voltage of mains electric ...
Manual - Custom Audio Electronics
... 1. There is usually no reason to run the Master controls on CH2 and CH3 past #6 mark unless you are driving a direct power amp in jack that needs a hotter signal than +4db. 2. When using a switching system besides our optional controller it is possible to turn on CH2 and CH3 at the same time. There ...
... 1. There is usually no reason to run the Master controls on CH2 and CH3 past #6 mark unless you are driving a direct power amp in jack that needs a hotter signal than +4db. 2. When using a switching system besides our optional controller it is possible to turn on CH2 and CH3 at the same time. There ...
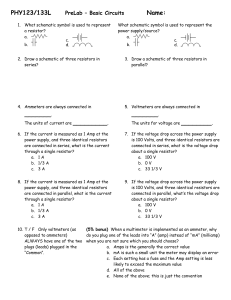
Basic Ciruits
... do you plug one of the leads into “A” (amp) instead of “mA” (milliamp) ALWAYS have one of the two when you are not sure which you should choose? plugs (leads) plugged in the a. Amps is the generally the correct value “Common”. b. mA is such a small unit the meter may display an error c. Each setting ...
... do you plug one of the leads into “A” (amp) instead of “mA” (milliamp) ALWAYS have one of the two when you are not sure which you should choose? plugs (leads) plugged in the a. Amps is the generally the correct value “Common”. b. mA is such a small unit the meter may display an error c. Each setting ...
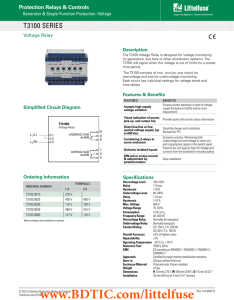
Download T3100 Datasheet
... The T3100 Voltage Relay is designed for voltage monitoring on generators, bus bars or other distribution systems. The T3100 will signal when the voltage is out of limits for a preset time period. The T3100 consists of two circuits, one circuit for overvoltage and one for undervoltage monitoring. Eac ...
... The T3100 Voltage Relay is designed for voltage monitoring on generators, bus bars or other distribution systems. The T3100 will signal when the voltage is out of limits for a preset time period. The T3100 consists of two circuits, one circuit for overvoltage and one for undervoltage monitoring. Eac ...
This wiring diagram
... As with any wiring, voltage and current loss will occur as home run lengths increase and LED fixtures get further away from the power supply. The gauge of wire used plays a major role in the loss prevention. The further you go the thicker the wire should be. Never use smaller wire than 18 awg. The a ...
... As with any wiring, voltage and current loss will occur as home run lengths increase and LED fixtures get further away from the power supply. The gauge of wire used plays a major role in the loss prevention. The further you go the thicker the wire should be. Never use smaller wire than 18 awg. The a ...
Sizing a Generator for a Specific Electric Motor Load, or
... Sizing a generator for single phase motor starting LRA : The formula is: Motor HP x KVA per HP x (1000 / Motor Voltage) = LRA. Example: A 3/4 HP, Code L motor connected to 240 Volts, requires what LRA? Refer to Chart A, and find Code L. Always use the largest KVA/HP number, so select 9.9. The formul ...
... Sizing a generator for single phase motor starting LRA : The formula is: Motor HP x KVA per HP x (1000 / Motor Voltage) = LRA. Example: A 3/4 HP, Code L motor connected to 240 Volts, requires what LRA? Refer to Chart A, and find Code L. Always use the largest KVA/HP number, so select 9.9. The formul ...
Variable-frequency drive

A variable-frequency drive (VFD) (also termed adjustable-frequency drive, variable-speed drive, AC drive, micro drive or inverter drive) is a type of adjustable-speed drive used in electro-mechanical drive systems to control AC motor speed and torque by varying motor input frequency and voltage.VFDs are used in applications ranging from small appliances to the largest of mine mill drives and compressors. However, around 25% of the world's electrical energy is consumed by electric motors in industrial applications, which are especially conducive for energy savings using VFDs in centrifugal load service, and VFDs' global market penetration for all applications is still relatively small. That lack of penetration highlights significant energy efficiency improvement opportunities for retrofitted and new VFD installations.Over the last four decades, power electronics technology has reduced VFD cost and size and has improved performance through advances in semiconductor switching devices, drive topologies, simulation and control techniques, and control hardware and software.VFDs are available in a number of different low- and medium-voltage AC-AC and DC-AC topologies.