Comparing Means in Two Populations
... • The horizontal spreading of the values is done so that you can see each school’s scores better (called “Jittered Points”). The amount of horizontal spread is random; so, don’t try to interpret the scores for points farther to the right or left than scores closer to the center (horizontally). • Of ...
... • The horizontal spreading of the values is done so that you can see each school’s scores better (called “Jittered Points”). The amount of horizontal spread is random; so, don’t try to interpret the scores for points farther to the right or left than scores closer to the center (horizontally). • Of ...
1. Discrete Distributions
... The distribution defined by the density function in Exercise 13 is the hypergeometric distributions with parameters m, r , and n. The distribution defined by the density function in Exercise 14 is the bivariate hypergeometric distribution with parameters m, r , s, and n. Clearly, the same general pa ...
... The distribution defined by the density function in Exercise 13 is the hypergeometric distributions with parameters m, r , and n. The distribution defined by the density function in Exercise 14 is the bivariate hypergeometric distribution with parameters m, r , s, and n. Clearly, the same general pa ...
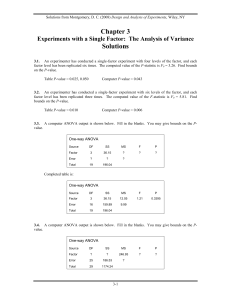
Combining Analysis Results from Multiply Imputed Categorical Data
... earlier versions of SAS, there is a way to deal with non-monotone categorical missing data, namely by using Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method for partial imputation of non-monotone missing records while treating categorical variables as if they were continuous and modeling them with a multivari ...
... earlier versions of SAS, there is a way to deal with non-monotone categorical missing data, namely by using Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method for partial imputation of non-monotone missing records while treating categorical variables as if they were continuous and modeling them with a multivari ...