Introduction - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Scale Changes: multiplying or dividing each of the values by a number. ...
... • Scale Changes: multiplying or dividing each of the values by a number. ...
confidence interval
... ● If we have a process for calculating confidence intervals with a 90% level of confidence Assume that we know the population mean We then obtain a series of 50 random samples We apply our process to the data from each random sample to obtain a confidence interval for each ...
... ● If we have a process for calculating confidence intervals with a 90% level of confidence Assume that we know the population mean We then obtain a series of 50 random samples We apply our process to the data from each random sample to obtain a confidence interval for each ...
Understanding Variability
... A histogram is a way of summarising data that are measured on an interval scale (either discrete or continuous). It is often used in exploratory data analysis to illustrate the major features of the distribution of the data in a convenient form. It divides up the range of possible values in a data s ...
... A histogram is a way of summarising data that are measured on an interval scale (either discrete or continuous). It is often used in exploratory data analysis to illustrate the major features of the distribution of the data in a convenient form. It divides up the range of possible values in a data s ...
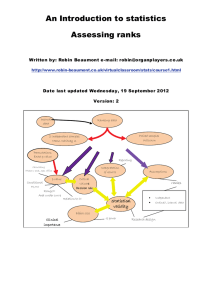
ordinal data
... Currently we have a statistic so the next question is can we draw inferences from it (i.e. provide an associated P-value) to do this we must be able to show that it either follows a sampling distribution or somehow actually calculate the associated probabilities (see latter). For small values of n ( ...
... Currently we have a statistic so the next question is can we draw inferences from it (i.e. provide an associated P-value) to do this we must be able to show that it either follows a sampling distribution or somehow actually calculate the associated probabilities (see latter). For small values of n ( ...
Forward Samplers - Carnegie Mellon University
... P(xi | ui) are the transition probability (neighboring states differ only in one variable) Given the transition matrix you could compute the exact stationary distribution ...
... P(xi | ui) are the transition probability (neighboring states differ only in one variable) Given the transition matrix you could compute the exact stationary distribution ...
lec11 - Biostatistics
... If you still do, we can use a t distribution to approximate the actual sampling distribution of the two-sample t-statistic. The degrees of freedom is not n1 + n2 − 2. It is smaller, and there are several possible formulae for calculating it. Typically we use either ...
... If you still do, we can use a t distribution to approximate the actual sampling distribution of the two-sample t-statistic. The degrees of freedom is not n1 + n2 − 2. It is smaller, and there are several possible formulae for calculating it. Typically we use either ...
The Central Limit Theorem
... The central limit theorem (cont’d) Furthermore, as we have seen, knowing the mean and standard deviation of a distribution that is approximately normal allows us to calculate anything we wish to know with tremendous accuracy – and the sampling distribution of the mean is always approximately normal ...
... The central limit theorem (cont’d) Furthermore, as we have seen, knowing the mean and standard deviation of a distribution that is approximately normal allows us to calculate anything we wish to know with tremendous accuracy – and the sampling distribution of the mean is always approximately normal ...
Introduction: exponential family, conjugacy, and sufficiency (9/2/13)
... • The exponential family is the only family of distributions for which conjugate priors exist, which simplifies the computation of the posterior. • They are the core of generalized linear models and variational methods, which we will learn about in this course. • Expectations are simple to compute, ...
... • The exponential family is the only family of distributions for which conjugate priors exist, which simplifies the computation of the posterior. • They are the core of generalized linear models and variational methods, which we will learn about in this course. • Expectations are simple to compute, ...