Chapter 3-The Dynamic Earth
... never reaches, are very cold, just above freezing. Surface waters are stirred up by waves and currents so the warm surface zone may be as much as 350 m deep. Below the surface zone is the thermocline, which is a layer about 300 to 700 m deep where the temperature falls rapidly. ...
... never reaches, are very cold, just above freezing. Surface waters are stirred up by waves and currents so the warm surface zone may be as much as 350 m deep. Below the surface zone is the thermocline, which is a layer about 300 to 700 m deep where the temperature falls rapidly. ...
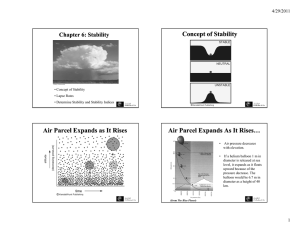
Chapter 6: Stability
... Î The temperature of the air parcel (or balloon) decreases with elevation. The lost energy is used to increase the potential energy of air molecular. • Similarly when the air parcel descends, the potential energy of air molecular is converted back to kinetic energy. Î Air temperature rises. ...
... Î The temperature of the air parcel (or balloon) decreases with elevation. The lost energy is used to increase the potential energy of air molecular. • Similarly when the air parcel descends, the potential energy of air molecular is converted back to kinetic energy. Î Air temperature rises. ...
Mountain Meteorology (powerpoint)
... • Warm air rises! In the summer, the sun’s rays can warm the ground enough that the air near the surface will be much warmer than the surrounding air. • To learn more about rising air, click here: Website of cool air and warm air moving with circulation http://www.prh.noaa.gov/ hnl/kids/activities.p ...
... • Warm air rises! In the summer, the sun’s rays can warm the ground enough that the air near the surface will be much warmer than the surrounding air. • To learn more about rising air, click here: Website of cool air and warm air moving with circulation http://www.prh.noaa.gov/ hnl/kids/activities.p ...
Chapter 6: Stability
... rate at which the air temperature surrounding us (or the air parcels) would be changed if we were to climb upward into the atmosphere. • This rate varies from time to time and from place to place. • A rawinsonde’s thermometer measures the environmental lapse rate. ...
... rate at which the air temperature surrounding us (or the air parcels) would be changed if we were to climb upward into the atmosphere. • This rate varies from time to time and from place to place. • A rawinsonde’s thermometer measures the environmental lapse rate. ...
HS 4572 * Chapter 8 Water, Minerals and Osteoporosis
... CALCIUM SUPPLEMENTS Please read pg 322 – 323, under the heading Calcium Supplements, in the ...
... CALCIUM SUPPLEMENTS Please read pg 322 – 323, under the heading Calcium Supplements, in the ...
Pewaukee River Jayne Jenks, Waukesha County Nancy Sheehan
... Dissolved oxygen (DO) is a gas found in water that is critical for sustaining aquatic life (just as oxygen is required for us to survive). Dissolved oxygen enters water through mixing with air in turbulent waters or through photosynthetic processes by aquatic plants and algae. Dissolved oxygen leave ...
... Dissolved oxygen (DO) is a gas found in water that is critical for sustaining aquatic life (just as oxygen is required for us to survive). Dissolved oxygen enters water through mixing with air in turbulent waters or through photosynthetic processes by aquatic plants and algae. Dissolved oxygen leave ...
C:\Datafiles\CAMM\CAMMS\CAMM-S Manual\Appendix B\glossary
... is heated to approximately 1000 oF for at least one hour. Flocculation - Agglomeration of colloidal materials during water or wastewater treatment. Flushing system - A system that collects and transports or moves waste material with the use of water or wastewater such as in washing of pens and flush ...
... is heated to approximately 1000 oF for at least one hour. Flocculation - Agglomeration of colloidal materials during water or wastewater treatment. Flushing system - A system that collects and transports or moves waste material with the use of water or wastewater such as in washing of pens and flush ...
599KB - NZQA
... The continental crusts of the Pacific and Australian Plates are locked together under the Seddon / Lake Grassmere region (top of the South Island). These two plates are pushing into each other in a transform (strike-slip) fault, as their densities are similar – there are a number of faults in this a ...
... The continental crusts of the Pacific and Australian Plates are locked together under the Seddon / Lake Grassmere region (top of the South Island). These two plates are pushing into each other in a transform (strike-slip) fault, as their densities are similar – there are a number of faults in this a ...
244KB - NZQA
... The continental crusts of the Pacific and Australian Plates are locked together under the Seddon / Lake Grassmere region (top of the South Island). These two plates are pushing into each other in a transform (strike-slip) fault, as their densities are similar – there are a number of faults in this a ...
... The continental crusts of the Pacific and Australian Plates are locked together under the Seddon / Lake Grassmere region (top of the South Island). These two plates are pushing into each other in a transform (strike-slip) fault, as their densities are similar – there are a number of faults in this a ...
Earth Science EOG Review
... Aquifers are large reservoirs of ground water. These can be accessed by wells, some natural springs bring water out of aquifers through the force of gravity. Water in an aquifer is usually cleaner than surface water, b/c it filters through rocks and sand (recharge area) on it’s way to the aquifer. ...
... Aquifers are large reservoirs of ground water. These can be accessed by wells, some natural springs bring water out of aquifers through the force of gravity. Water in an aquifer is usually cleaner than surface water, b/c it filters through rocks and sand (recharge area) on it’s way to the aquifer. ...
Water intake recommendations
... without water. The body has no capacity to store “spare” water, so it must quickly replace lost fluid. Overall, water makes up between 50 and 75 percent of body weight. The main constituent of the body is water. Adult males have more lean tissue and less fat than adult females. An adult male is appr ...
... without water. The body has no capacity to store “spare” water, so it must quickly replace lost fluid. Overall, water makes up between 50 and 75 percent of body weight. The main constituent of the body is water. Adult males have more lean tissue and less fat than adult females. An adult male is appr ...
SURFACE WATER
... 4. watershed (drainage basin) = all of land area whose water drains into a stream system a. can be small or extremely large areas b. divides = ridges or elevated regions of high ground that separate watersheds c. each tributary has its own watershed and divides but are all part of larger stream syst ...
... 4. watershed (drainage basin) = all of land area whose water drains into a stream system a. can be small or extremely large areas b. divides = ridges or elevated regions of high ground that separate watersheds c. each tributary has its own watershed and divides but are all part of larger stream syst ...
EUGENIDIO CLINIC UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS
... The absolute offered technology used by the Active Cool paint demonstrates a dual continuous action: When regularly applied on exterior walls, it transforms air pollution into harmless residues and, at the same time, performs a reflective barrier, which allows the limitation of energy use for coolin ...
... The absolute offered technology used by the Active Cool paint demonstrates a dual continuous action: When regularly applied on exterior walls, it transforms air pollution into harmless residues and, at the same time, performs a reflective barrier, which allows the limitation of energy use for coolin ...
Chapter 11: Water- Notes Packet Vocabulary Terms are in italics
... Instead of dumping used water into the nearby river, the industries recycle and reuse the water. - http://youtu.be/s0idPxypG1w ...
... Instead of dumping used water into the nearby river, the industries recycle and reuse the water. - http://youtu.be/s0idPxypG1w ...
Pond Fertilization
... minimize effluent release to the extent possible. Do not fertilize ponds 1 or 2 days before expected periods of significant precipitation if overflow is expected. A pply agricultural limestone to ponds with total alkalinity below 20 ppm. Store fertilizers under a roof in a dry place to prevent rain ...
... minimize effluent release to the extent possible. Do not fertilize ponds 1 or 2 days before expected periods of significant precipitation if overflow is expected. A pply agricultural limestone to ponds with total alkalinity below 20 ppm. Store fertilizers under a roof in a dry place to prevent rain ...
NRP: Oxygen Requirements
... Toilets were connected to existing storm sewers The storm drain systems discharged directly to streams, lakes, and estuaries without treatment Treatment of wastewater only became an issue after the self-purification capacity of the receiving waters was exceeded and ________ nuisance __________ c ...
... Toilets were connected to existing storm sewers The storm drain systems discharged directly to streams, lakes, and estuaries without treatment Treatment of wastewater only became an issue after the self-purification capacity of the receiving waters was exceeded and ________ nuisance __________ c ...
Chaper 9
... 1. True Your body constantly loses water through insensible perspiration, a form of water loss that is not the same as sweat. 2. False Ounce per ounce, cottage cheese contains less calcium than plain yogurt. 3. True Potassium, sodium, and chloride ions are among the ions involved in fluid balance. 4 ...
... 1. True Your body constantly loses water through insensible perspiration, a form of water loss that is not the same as sweat. 2. False Ounce per ounce, cottage cheese contains less calcium than plain yogurt. 3. True Potassium, sodium, and chloride ions are among the ions involved in fluid balance. 4 ...
Why are Rainforests so important
... The role of rainforests in the water cycle is to add water to the atmosphere through the process of transpiration (in which plants release water from their leaves during photosynthesis). This moisture contributes to the formation of rain clouds, which release the water back onto the rainforest. In t ...
... The role of rainforests in the water cycle is to add water to the atmosphere through the process of transpiration (in which plants release water from their leaves during photosynthesis). This moisture contributes to the formation of rain clouds, which release the water back onto the rainforest. In t ...
Breakthrough in Boiler System Efficiencies through New Integrated
... (2) Limit and safety control [2B] responds either to temperature or pressure and provides a maximum limit beyond which the burner will not operate. Boilers require a low-water cutoff to prevent burner operation if the water level drops below safe limits. The control also actuates the feed water or c ...
... (2) Limit and safety control [2B] responds either to temperature or pressure and provides a maximum limit beyond which the burner will not operate. Boilers require a low-water cutoff to prevent burner operation if the water level drops below safe limits. The control also actuates the feed water or c ...
Effect of Land Use on Ground Water Quality
... much closer to the septic tank systems [5]–[7]. In Ciracas sub-district, most of houses are adjacent to one another where the septic systems are certainly near the neighbor’s wells. Moreover, the former land use in Ciracas sub-district were mostly swamp, rice field, and garden where were assumed cau ...
... much closer to the septic tank systems [5]–[7]. In Ciracas sub-district, most of houses are adjacent to one another where the septic systems are certainly near the neighbor’s wells. Moreover, the former land use in Ciracas sub-district were mostly swamp, rice field, and garden where were assumed cau ...
Figure 1 - Variation of Water Transmission with
... As water consumption increases during wet years consumption exceeds the natural resources, the vulnerability to drought therefore, tend to appear more intensive (i.e. Tehran). This has also appeared in some other areas where reservoir dams have completely been emptied and dried out. In year 98-99 go ...
... As water consumption increases during wet years consumption exceeds the natural resources, the vulnerability to drought therefore, tend to appear more intensive (i.e. Tehran). This has also appeared in some other areas where reservoir dams have completely been emptied and dried out. In year 98-99 go ...
Hands-On Hydrology - New Mexico State University
... the effects of such pollution on people and animals that live in or near the "lake." 3. Discuss what actions people might take to prevent some or nearly all of the pollution that took place in the story. ...
... the effects of such pollution on people and animals that live in or near the "lake." 3. Discuss what actions people might take to prevent some or nearly all of the pollution that took place in the story. ...
Solving Common Water Problems With VWP
... Calcium forms scale in every water heater. It forms at the bottom of a water heater or boiler near the flame. The flame no longer can directly heat the water in the tank. It heats the calcium deposit at the bottom of the tank first. The heated calcium then heats the water. Studies of water heaters ...
... Calcium forms scale in every water heater. It forms at the bottom of a water heater or boiler near the flame. The flame no longer can directly heat the water in the tank. It heats the calcium deposit at the bottom of the tank first. The heated calcium then heats the water. Studies of water heaters ...
Correlation of Sky Watchers to the Northwest Territories Science and
... Plan investigations for some of these answers and solutions, identifying variables that need to be held constant to ensure a fair test and identifying criteria for assessing solutions; Use appropriate vocabulary, including correct science and technology terminology, in describing their investigation ...
... Plan investigations for some of these answers and solutions, identifying variables that need to be held constant to ensure a fair test and identifying criteria for assessing solutions; Use appropriate vocabulary, including correct science and technology terminology, in describing their investigation ...
Air well (condenser)

An air well or aerial well is a structure or device that collects water by promoting the condensation of moisture from air. Designs for air wells are many and varied, but the simplest designs are completely passive, require no external energy source and have few, if any, moving parts.Three principal designs are used for air wells, designated as high mass, radiative, and active: High-mass air wells were used in the early 20th century, but the approach failed. From the late 20th century onwards, low-mass, radiative collectors proved to be much more successful. Active collectors collect water in the same way as a dehumidifier; although the designs work well, they require an energy source, making them uneconomical except in special circumstances. New, innovative designs seek to minimise the energy requirements of active condensers or make use of renewable energy resources.↑ ↑ ↑ 3.0 3.1