The nervous system - Science for Yr9@E
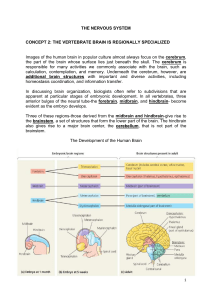
... hemispheres and has a highly folded surface or cortex. This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. ...
... hemispheres and has a highly folded surface or cortex. This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. ...
Sample
... (subjects cannot be randomly assigned to either condition). Cause is difficult to surmise in quasiexperimental designs due to the fact that subjects are not randomly assigned to groups, opening up the possibility that factors other than the manipulated ones may be correlated with the experimental gr ...
... (subjects cannot be randomly assigned to either condition). Cause is difficult to surmise in quasiexperimental designs due to the fact that subjects are not randomly assigned to groups, opening up the possibility that factors other than the manipulated ones may be correlated with the experimental gr ...
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury
... brain that tells where things are found and where they are situated in respect to the body. (greater risk of losing their way). 0 The third part and most important function is its high level of processing all the brain’s input data. ...
... brain that tells where things are found and where they are situated in respect to the body. (greater risk of losing their way). 0 The third part and most important function is its high level of processing all the brain’s input data. ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... serotonin and melatonin, thus aiding sleep. Although we know very little about the function of sleep, it is clear that sleep is essential for survival. Sleep is an active state, at least for the brain. By placing electrodes at multiple sites on the scalp, we can record patterns of electrical activit ...
... serotonin and melatonin, thus aiding sleep. Although we know very little about the function of sleep, it is clear that sleep is essential for survival. Sleep is an active state, at least for the brain. By placing electrodes at multiple sites on the scalp, we can record patterns of electrical activit ...
Multiple Intelligences: Gardner`s Theory Amy C. Brualdi
... revolutionary war songs, organize a role play of the signing of the Declaration of Independence, and have the students read a novel about life during that period. This kind of presentation not only excites students about learning, but it also allows a teacher to reinforce the same material in a vari ...
... revolutionary war songs, organize a role play of the signing of the Declaration of Independence, and have the students read a novel about life during that period. This kind of presentation not only excites students about learning, but it also allows a teacher to reinforce the same material in a vari ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... they become helpful once you gain familiarity with what they are and how and when to use them. What might be slowing you down in your learning is that the words used to help navigate through the brain may seem more confusing than what they are describing. Thus, the first step in navigating the brain ...
... they become helpful once you gain familiarity with what they are and how and when to use them. What might be slowing you down in your learning is that the words used to help navigate through the brain may seem more confusing than what they are describing. Thus, the first step in navigating the brain ...
Brain Development
... literally feels good to eat them – they induce pleasurable sensations in the body In addition to its calming effects, sugar is known to make babies more alert and to encourage their hand-to-mouth coordination ...
... literally feels good to eat them – they induce pleasurable sensations in the body In addition to its calming effects, sugar is known to make babies more alert and to encourage their hand-to-mouth coordination ...
Revised Lesson Plan 1 - The Brain
... Group students by asking them to count 1 – 6. Students with the same number will form a group. There should be at least 3 – 4 members in a group. Ask students to name five ways in which they use their brain every day. Have them write their answers on sticky notes and post them on the poster board pr ...
... Group students by asking them to count 1 – 6. Students with the same number will form a group. There should be at least 3 – 4 members in a group. Ask students to name five ways in which they use their brain every day. Have them write their answers on sticky notes and post them on the poster board pr ...
the version of this backgrounder
... The human brain is one part of our nervous system, which is the control system through which all other body systems receive their instructions. Much like the engine of a car, the brain is made up of many different parts. These parts have different functions, but they work closely together, to coordi ...
... The human brain is one part of our nervous system, which is the control system through which all other body systems receive their instructions. Much like the engine of a car, the brain is made up of many different parts. These parts have different functions, but they work closely together, to coordi ...
Purpose
... Neuropsychology is the field of study that seeks to understand how brain processes make human behavior and psychological functions possible. Neuropsychologists are interested in a wide range of human abilities, including aspects of cognitive functioning (e.g., language, memory attention, mathematica ...
... Neuropsychology is the field of study that seeks to understand how brain processes make human behavior and psychological functions possible. Neuropsychologists are interested in a wide range of human abilities, including aspects of cognitive functioning (e.g., language, memory attention, mathematica ...
Lecture 1 (Neuroscience History)
... Darwin includes behavior among heritable traits. He observed that many mammals show similar behavior when frightened. Concluded animal nervous system probably share common wiring and underlying mechanisms. ...
... Darwin includes behavior among heritable traits. He observed that many mammals show similar behavior when frightened. Concluded animal nervous system probably share common wiring and underlying mechanisms. ...
6. Brain Lateralization
... RH, on the other hand, attends strictly to the Gestalt perceptual characteristics of the stimulus (parts or whole but not relation between) The above mentioned difference is usually understood better by terms called analytical (LH) and holistic (RH). Thus the RH should not be regarded as the minor h ...
... RH, on the other hand, attends strictly to the Gestalt perceptual characteristics of the stimulus (parts or whole but not relation between) The above mentioned difference is usually understood better by terms called analytical (LH) and holistic (RH). Thus the RH should not be regarded as the minor h ...
Brain
... Person can speak clearly, but the words that are put together make no sense. “Word salad” because it appears that the words are all mixed up like the vegetables in a salad ...
... Person can speak clearly, but the words that are put together make no sense. “Word salad” because it appears that the words are all mixed up like the vegetables in a salad ...
natural selection
... population following some change in the environment. There are many types of environmental changes, including man-made changes, natural disasters, seasonal changes, and introductions of species into new environments. For example, from the changes in the peppered moth following a change in pollution ...
... population following some change in the environment. There are many types of environmental changes, including man-made changes, natural disasters, seasonal changes, and introductions of species into new environments. For example, from the changes in the peppered moth following a change in pollution ...
lab 8: central nervous system
... dendrites, axon, axon hillock, myelin sheath (Schwann cell), Nodes of Ranvier (myelin sheath gaps), cell body, nucleus, terminal arborizations (telodendria), synaptic knobs (terminal boutons). ...
... dendrites, axon, axon hillock, myelin sheath (Schwann cell), Nodes of Ranvier (myelin sheath gaps), cell body, nucleus, terminal arborizations (telodendria), synaptic knobs (terminal boutons). ...
Science of Self Awareness and Foundation of Memory
... captured during shooting. The light from the projector passes through the film frames and converts according to matrix of dots into those light frequencies which were received during shooting, these then in totality covering screen appear as images and action. Similarly, the data created by laser li ...
... captured during shooting. The light from the projector passes through the film frames and converts according to matrix of dots into those light frequencies which were received during shooting, these then in totality covering screen appear as images and action. Similarly, the data created by laser li ...
Inkwell @ SMUG - Indiana University
... • No he didn't. • Every consistent formalisation of number theory is incomplete. • It is a huge leap to "AI is impossible". • Indeed, the fact that human brains are capable of both expressing arithmetical relationships and contemplating "I am lying" bodes well for machine minds. • The (formal) consi ...
... • No he didn't. • Every consistent formalisation of number theory is incomplete. • It is a huge leap to "AI is impossible". • Indeed, the fact that human brains are capable of both expressing arithmetical relationships and contemplating "I am lying" bodes well for machine minds. • The (formal) consi ...
AAAS Summary
... humans it extends from the sixth month of gestation to several years after birth. Thus, it appears that there is a period of several years, encompassing portions of both pre and postnatal human development, during which immature neurons are prone to commit suicide if exposed to certain drugs that in ...
... humans it extends from the sixth month of gestation to several years after birth. Thus, it appears that there is a period of several years, encompassing portions of both pre and postnatal human development, during which immature neurons are prone to commit suicide if exposed to certain drugs that in ...
THE BRAIN & FIVE SENSES
... Just above the Medulla, the brainstem enlarges to form the PONS. PONS mean BRIDGE, and this area of the brain stem contains mostly white matter that provides a link between the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum. Above the PONS and continuous with it is the MIDBRAIN, the smallest division of the lo ...
... Just above the Medulla, the brainstem enlarges to form the PONS. PONS mean BRIDGE, and this area of the brain stem contains mostly white matter that provides a link between the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum. Above the PONS and continuous with it is the MIDBRAIN, the smallest division of the lo ...
The Role of Genetics in Craniofacial Biology
... Evidence for the evolution of mankind has hitherto relied upon paleoanthropological discoveries of fossilized skeletal remains. Evolution takes place in two areas- in the embryo and in the environment. Changes in the embryo have to function cooperatively to form an organism that survives in the envi ...
... Evidence for the evolution of mankind has hitherto relied upon paleoanthropological discoveries of fossilized skeletal remains. Evolution takes place in two areas- in the embryo and in the environment. Changes in the embryo have to function cooperatively to form an organism that survives in the envi ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... • A) Life satisfaction peaks at age 50 and then declines after 65. • B) Most people over 90 are senile. • C) Most women feel relief after going through menopause. • D) older people become more susceptible to short-term illnesses. ...
... • A) Life satisfaction peaks at age 50 and then declines after 65. • B) Most people over 90 are senile. • C) Most women feel relief after going through menopause. • D) older people become more susceptible to short-term illnesses. ...
brain development - EDUC111ChildGrowthDevelopment
... environments impair brain development as well as in all other domains. On the other hand, environments that provide too much stimulation, or stimulation of a type the infant is not yet ready for, also interfere with brain development. During the first two years of life children begin to master their ...
... environments impair brain development as well as in all other domains. On the other hand, environments that provide too much stimulation, or stimulation of a type the infant is not yet ready for, also interfere with brain development. During the first two years of life children begin to master their ...
Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience
... points of the tree) to all the other branches in the tree. In Hennig’s method, evolutionary relationships are reconstructed by a process of “character analysis.” A character is any observable feature or attribute of an organism. A character could be a feature of the brain, such as the corpus callosu ...
... points of the tree) to all the other branches in the tree. In Hennig’s method, evolutionary relationships are reconstructed by a process of “character analysis.” A character is any observable feature or attribute of an organism. A character could be a feature of the brain, such as the corpus callosu ...
What is Anthropology
... t human biological plasticity: the body’s ability to change as it copes with stresses such as heat, cold, and altitude t primatology: the study of the biology, evolution, behavior, and social life of primates. t Biological anthropology is multidisciplinary as it draws on ...
... t human biological plasticity: the body’s ability to change as it copes with stresses such as heat, cold, and altitude t primatology: the study of the biology, evolution, behavior, and social life of primates. t Biological anthropology is multidisciplinary as it draws on ...
New Autism Research
... 1990s, the neurons - also known as "monkey-see, monkey-do cells" - fire both when a monkey performs an action itself and when it observes another living creature perform that same action. Though it has been impossible to directly study the analogue of these neurons in people (since human subjects ca ...
... 1990s, the neurons - also known as "monkey-see, monkey-do cells" - fire both when a monkey performs an action itself and when it observes another living creature perform that same action. Though it has been impossible to directly study the analogue of these neurons in people (since human subjects ca ...
Evolution of human intelligence

The evolution of human intelligence refers to a set of theories that attempt to explain how human intelligence has evolved and are closely tied to the evolution of the human brain and to the origin of language.The timeline of human evolution spans approximately 7 million years, from the separation of the Pan genus until the emergence of behavioral modernity by 50,000 years ago. The first 3 million years of this timeline concern Sahelanthropus, the following 2 million concern Australopithecus and the final 2 million span the history of actual human species in the Paleolithic era.Many traits of human intelligence, such as empathy, theory of mind, mourning, ritual, and the use of symbols and tools, are apparent in great apes although in less sophisticated forms than found in humans, such as Great ape language.