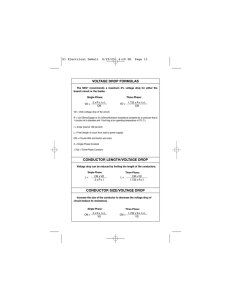
Voltage Drop Formula Sheet
... VD = Volts (voltage drop of the circuit) R = 12.9 Ohms/Copper or 21.2 Ohms/Aluminum (resistance constants for a conductor that is 1 circular mil in diameter and 1 foot long at an operating temperature of 75O C.) I = Amps (load at 100 percent) L = Feet (length of circuit from load to power supply) CM ...
... VD = Volts (voltage drop of the circuit) R = 12.9 Ohms/Copper or 21.2 Ohms/Aluminum (resistance constants for a conductor that is 1 circular mil in diameter and 1 foot long at an operating temperature of 75O C.) I = Amps (load at 100 percent) L = Feet (length of circuit from load to power supply) CM ...
Zener diode voltage regulator File
... albeit with a voltage reduction equal to the base emitter junction voltage - 0.6 volts for a silicon transistor It is a simple matter to design a series pass voltage regulator circuit like this. Knowing the maximum current required by the load, it is possible to calculate the maximum emitter current ...
... albeit with a voltage reduction equal to the base emitter junction voltage - 0.6 volts for a silicon transistor It is a simple matter to design a series pass voltage regulator circuit like this. Knowing the maximum current required by the load, it is possible to calculate the maximum emitter current ...
A voltage controlled adjustable speed
... In this paper, a buck half-bridge DC-DC converter is used as a single-stage power factor correction (PFC)converter for feeding a voltage source inverter (VSI) based permanent magnet brushless ...
... In this paper, a buck half-bridge DC-DC converter is used as a single-stage power factor correction (PFC)converter for feeding a voltage source inverter (VSI) based permanent magnet brushless ...
555 switchmode instructions.PM6
... his kit allows you to make a very simple switchmode boost (step-up) converter for powering nixie tubes and similar displays that require voltages between 100 and 200 Volt DC. It uses very readily available parts which can be bought from almost any electronics components store should the need arise f ...
... his kit allows you to make a very simple switchmode boost (step-up) converter for powering nixie tubes and similar displays that require voltages between 100 and 200 Volt DC. It uses very readily available parts which can be bought from almost any electronics components store should the need arise f ...
1. Black Box Electronics
... May have specs for various conditions (voltage, temperature, etc). Trend now away from Greek, towards more readable descriptions (e.g. β now hFE) ...
... May have specs for various conditions (voltage, temperature, etc). Trend now away from Greek, towards more readable descriptions (e.g. β now hFE) ...
Voltage Current Dividers Impedance
... Voltage Division The voltage associated with one impedance Zn in a chain of multiple impedances in series is: ...
... Voltage Division The voltage associated with one impedance Zn in a chain of multiple impedances in series is: ...
BAT85 Schottky Diodes FEATURES ♦
... BAT85 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS Ratings at 25 °C ambient temperature unless otherwise specified ...
... BAT85 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS Ratings at 25 °C ambient temperature unless otherwise specified ...
EE302 Lesson 1: Introduction
... This positive region created by separating the free electron from the basic atomic structure is called a positive ion. In general, every source of voltage is established by simply creating a separation of positive and negative ...
... This positive region created by separating the free electron from the basic atomic structure is called a positive ion. In general, every source of voltage is established by simply creating a separation of positive and negative ...
Voltage Current (electric) Resistance (electric) direct current
... the time rate of flow of electric charge, in the direction that a positive moving charge would take and having magnitude equal to the quantity of charge per unit time: measured in amperes. ...
... the time rate of flow of electric charge, in the direction that a positive moving charge would take and having magnitude equal to the quantity of charge per unit time: measured in amperes. ...
Control and Grid Synchronization for Distributed Power Generation
... Unity Power Factor Control Strategy Positive-Sequence Control Strategy Constant Active Power Control Strategy Constant Reactive Power Control Strategy ...
... Unity Power Factor Control Strategy Positive-Sequence Control Strategy Constant Active Power Control Strategy Constant Reactive Power Control Strategy ...
Abstract - PG Embedded systems
... op-amp, there may be fluctuation in output voltage between two saturation states (+ Vsat and – Vsat voltages). Thus zero crossings may be detected for noise voltages as well as input signal vin. Both of these problems can be overcome, if we use regenerative or positive feeding causing the output vol ...
... op-amp, there may be fluctuation in output voltage between two saturation states (+ Vsat and – Vsat voltages). Thus zero crossings may be detected for noise voltages as well as input signal vin. Both of these problems can be overcome, if we use regenerative or positive feeding causing the output vol ...
Voltage tuning
... For the PAC Chargers Tuning The Output Voltage: If The battery is charged in a very cold place or desired constant voltage didn’t found from the charging algorithm list, then there is a need to tune the output voltage. The output voltage can be tuned +/-5% from its nominal value. ...
... For the PAC Chargers Tuning The Output Voltage: If The battery is charged in a very cold place or desired constant voltage didn’t found from the charging algorithm list, then there is a need to tune the output voltage. The output voltage can be tuned +/-5% from its nominal value. ...
Charging System final pp
... The voltage Rectifier. Rectifiers are consisted with six diodes. Diodes are one way check valves that only allow current to flow one way . ...
... The voltage Rectifier. Rectifiers are consisted with six diodes. Diodes are one way check valves that only allow current to flow one way . ...
Multilayer Varistor Application Note
... MOVs alone have generally high capacitances and lower peak current capabilities. ...
... MOVs alone have generally high capacitances and lower peak current capabilities. ...
Two – wires method: Circuit 1. Two-wire resistance measurement, R
... RX is very small, or when very high accuracy is required. The method is immune to the influence of lead resistance and is limited by the quality of the constant current source and voltage measurement. Thermo-electric voltages can be eliminated by averaging two measurements with the polarity of the e ...
... RX is very small, or when very high accuracy is required. The method is immune to the influence of lead resistance and is limited by the quality of the constant current source and voltage measurement. Thermo-electric voltages can be eliminated by averaging two measurements with the polarity of the e ...
Analog Electronics and Communication lab
... Maximum power is delivered from a source to a load when the load resistance is equal to the source resistance, assuming that the load resistance is a variable. 2. Define Resonance Resonance is defined as a phenomenon in an AC circuit where applied voltage and resulting current are in phase with each ...
... Maximum power is delivered from a source to a load when the load resistance is equal to the source resistance, assuming that the load resistance is a variable. 2. Define Resonance Resonance is defined as a phenomenon in an AC circuit where applied voltage and resulting current are in phase with each ...
Triode

A triode is an electronic amplifying vacuum tube (or valve in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode). Invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest by adding a grid to the Fleming valve, the triode was the first electronic amplification device and the ancestor of other types of vacuum tubes such as the tetrode and pentode. Its invention founded the electronics age, making possible amplified radio technology and long-distance telephony. Triodes were widely used in consumer electronics devices such as radios and televisions until the 1970s, when transistors replaced them. Today, their main remaining use is in high-power RF amplifiers in radio transmitters and industrial RF heating devices. The word is derived from the Greek τρίοδος, tríodos, from tri- (three) and hodós (road, way), originally meaning the place where three roads meet.