Lecture 39
... Stagnation pressure Pstag = pressure at a stagnation point where the velocity is slowed down to zero nearly isentropically. This is the pressure at the nose (stagnation point) of a probe in the flow. Static pressure P = pressure that would be measured by an infinitesimal pressure sensor moving with ...
... Stagnation pressure Pstag = pressure at a stagnation point where the velocity is slowed down to zero nearly isentropically. This is the pressure at the nose (stagnation point) of a probe in the flow. Static pressure P = pressure that would be measured by an infinitesimal pressure sensor moving with ...
Unit Operations Test 2 (answer)
... pressure drop of the fluid flows through a granular beds or porous medium. In considering the effect of surface area, there is a difference between the specific surface or particle (S) and the specific surface area of bed (SB). Explain why these two parameters cannot be assumed similar. ...
... pressure drop of the fluid flows through a granular beds or porous medium. In considering the effect of surface area, there is a difference between the specific surface or particle (S) and the specific surface area of bed (SB). Explain why these two parameters cannot be assumed similar. ...
1P1, 2013-14, Thermofluid Mechanics: examples paper 2
... The figure below shows air flowing through a nozzle. The inlet pressure is p1 = 105 kPa and the pressure in the exhausting jet is p2 =101.3 kPa (which is equal to the ambient pressure at the nozzle exit). The nozzle has an inlet diameter of 60 mm, an exit diameter of 10 mm, and the nozzle is connect ...
... The figure below shows air flowing through a nozzle. The inlet pressure is p1 = 105 kPa and the pressure in the exhausting jet is p2 =101.3 kPa (which is equal to the ambient pressure at the nozzle exit). The nozzle has an inlet diameter of 60 mm, an exit diameter of 10 mm, and the nozzle is connect ...
Lab 3: Motor-Pump System Measurements and LabView Interface
... state and the ambient pressure and temperature data. You will assume the density and temperature to have been constant throughout the experiment. Calculate air flow in m^3/sec for all data points by using the velocity probe data and an area corresponding to a 2-inch diameter pipe section. Use the fo ...
... state and the ambient pressure and temperature data. You will assume the density and temperature to have been constant throughout the experiment. Calculate air flow in m^3/sec for all data points by using the velocity probe data and an area corresponding to a 2-inch diameter pipe section. Use the fo ...
The Bernoulli equation
... the top of the reservoir to the nozzle and gains a velocity u2. KE is 0.5mv22 and PE is mgh2. Now mgh1 = 0.5mv22 + mgh2 so v2 = ( 2g(h1- h2))0.5 This gives an expression for the velocity of the water as it flows from of a pipe nozzle at a height (h1- h2) below the surface of the reservoir.(Ignoring ...
... the top of the reservoir to the nozzle and gains a velocity u2. KE is 0.5mv22 and PE is mgh2. Now mgh1 = 0.5mv22 + mgh2 so v2 = ( 2g(h1- h2))0.5 This gives an expression for the velocity of the water as it flows from of a pipe nozzle at a height (h1- h2) below the surface of the reservoir.(Ignoring ...
Warm – Up Chapter 16-2
... machine that is pushing down on a 2.8 m2 piston (A1) with a force (F1) of 3,700 N. What force (F2) needs to be exerted on a 0.072 m2 piston (A2) to lift the machine? ...
... machine that is pushing down on a 2.8 m2 piston (A1) with a force (F1) of 3,700 N. What force (F2) needs to be exerted on a 0.072 m2 piston (A2) to lift the machine? ...
Electrohydrodynamic atomization of fat milk.
... technique for the production of this item is spray drying. The process is highly depending on the droplet size because it dictates the evaporation level and consequently the quality of the p ...
... technique for the production of this item is spray drying. The process is highly depending on the droplet size because it dictates the evaporation level and consequently the quality of the p ...
MMV211, March 9, 2005 P1. The figure below shows a vane with a
... exit plane there must be a shock wave upstream of the Pitot-static tube. There are two possibilities, either there is (i) a normal shock wave standing in the diverging section, or there is (ii) a curved shock wave just upstream of the Pitot-static tube (supersonic outlet). Assume that it is alternat ...
... exit plane there must be a shock wave upstream of the Pitot-static tube. There are two possibilities, either there is (i) a normal shock wave standing in the diverging section, or there is (ii) a curved shock wave just upstream of the Pitot-static tube (supersonic outlet). Assume that it is alternat ...
Solids and Fluids
... A spherical helium filled balloon was a radius of 1.10m. Does the buoyant force on the balloon depend on the density of 1) helium 2) air or 3) the weight of the rubber skin? Compute the magnitude of the buoyant force on the balloon. ρair = 1.29 kg/m3 and ρHe = 0.18 kg/m3. If the rubber skin of ...
... A spherical helium filled balloon was a radius of 1.10m. Does the buoyant force on the balloon depend on the density of 1) helium 2) air or 3) the weight of the rubber skin? Compute the magnitude of the buoyant force on the balloon. ρair = 1.29 kg/m3 and ρHe = 0.18 kg/m3. If the rubber skin of ...
Teacher Vocabulary Guide
... Barometer: a scientific instrument used in meteorology to measure atmospheric (barometric) pressure, which is the amount of pressure exerted by air over a given area. ...
... Barometer: a scientific instrument used in meteorology to measure atmospheric (barometric) pressure, which is the amount of pressure exerted by air over a given area. ...
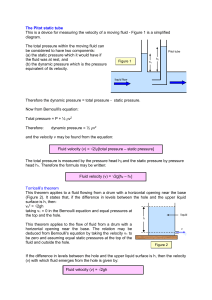
Pitot and Toricelli
... Fluid velocity (v) = √2/[total pressure – static pressure] The total pressure is measured by the pressure head h2 and the static pressure by pressure head h1. Therefore the formula may be written: Fluid velocity (v) = √2g[h2 – h1] Torricelli’s theorem This theorem applies to a fluid flowing from a ...
... Fluid velocity (v) = √2/[total pressure – static pressure] The total pressure is measured by the pressure head h2 and the static pressure by pressure head h1. Therefore the formula may be written: Fluid velocity (v) = √2g[h2 – h1] Torricelli’s theorem This theorem applies to a fluid flowing from a ...
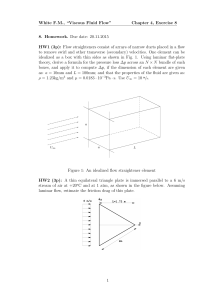
White FM, “Viscous Fluid Flow”
... stream of air at +20o C and at 1 atm, as shown in the figure below. Assuming laminar flow, estimate the friction drag of this plate. ...
... stream of air at +20o C and at 1 atm, as shown in the figure below. Assuming laminar flow, estimate the friction drag of this plate. ...
Question 2
... Problem: A jet of liquid issues horizontally from a small orifice in the vertical side of the tank. Derive an expression for the actual velocity of the jet v if the jet falls a distance y vertically in a horizontal distance x measured from the vena contracta. If the head of liquid above the orifice ...
... Problem: A jet of liquid issues horizontally from a small orifice in the vertical side of the tank. Derive an expression for the actual velocity of the jet v if the jet falls a distance y vertically in a horizontal distance x measured from the vena contracta. If the head of liquid above the orifice ...
Sample Paper
... (a) The centerline velocity increases monotonically with the streamwise coordinate (b) The developing length increases as the Reynolds number increases provided that the flow remains laminar (c) The developing length reduces if the flow transits to turbulence (d) The pressure gradient in the develop ...
... (a) The centerline velocity increases monotonically with the streamwise coordinate (b) The developing length increases as the Reynolds number increases provided that the flow remains laminar (c) The developing length reduces if the flow transits to turbulence (d) The pressure gradient in the develop ...
Forces Acting on a Control Volume
... Example 2 • Water flows through a horizontal 1800 pipe end. The cross sectional area of flow is constant at 0.1 ft2. The flow velocity everywhere in the bend is axial and 50 ft/s. The absolute pressures at the entrance and exit are 30 psia and 24 psia, respectively. Calculate the horizontal compone ...
... Example 2 • Water flows through a horizontal 1800 pipe end. The cross sectional area of flow is constant at 0.1 ft2. The flow velocity everywhere in the bend is axial and 50 ft/s. The absolute pressures at the entrance and exit are 30 psia and 24 psia, respectively. Calculate the horizontal compone ...
Jet`s Scrapbook from Bortron 7
... come from Earth, but instead they come from a make-believe planet called Bortron 7. Bortron 7 is the 7th planet orbiting a make-believe red dwarf star called Bortron. Although Bortron 7 isn't a real place, scientists have evidence that some actual red dwarf stars have planets too. But a planet orbit ...
... come from Earth, but instead they come from a make-believe planet called Bortron 7. Bortron 7 is the 7th planet orbiting a make-believe red dwarf star called Bortron. Although Bortron 7 isn't a real place, scientists have evidence that some actual red dwarf stars have planets too. But a planet orbit ...
山东大学 流体力学 课程试卷 2006-2007 学年 一 学期 题号 一 二 三 四
... (1) The pressure at any point in a static fluid depends only on the; A. Depth, surface pressure, and specific weight. B. Depth and container shape. C. Pressure and depth. (2) When is an inclined-tube manometer used? A. It can be used at any time. B. When the fluid to be measured has a very low densi ...
... (1) The pressure at any point in a static fluid depends only on the; A. Depth, surface pressure, and specific weight. B. Depth and container shape. C. Pressure and depth. (2) When is an inclined-tube manometer used? A. It can be used at any time. B. When the fluid to be measured has a very low densi ...
Slides from the lecture
... Becomes important for wind velocity v > √2gh (≈ 10 m/s for h ≈ 5 m). ...
... Becomes important for wind velocity v > √2gh (≈ 10 m/s for h ≈ 5 m). ...
Exam2 - Purdue Engineering
... 15) The velocity potential of a uniform flow in the y direction with speed 2 and a source of strength 0.1π located at x=y=0 is: a. 2 x + .05 ln(r) b. 2 y + .05 ln(r) c. 2 x + .05 θ d. 2 y - .05 θ e. 2 y - .05 ln(r) (where r and θ are polar coordinates centered at x=y=0) 16) Water flows through a ci ...
... 15) The velocity potential of a uniform flow in the y direction with speed 2 and a source of strength 0.1π located at x=y=0 is: a. 2 x + .05 ln(r) b. 2 y + .05 ln(r) c. 2 x + .05 θ d. 2 y - .05 θ e. 2 y - .05 ln(r) (where r and θ are polar coordinates centered at x=y=0) 16) Water flows through a ci ...
Coandă effect

The Coandă effect /ˈkwaːndə/ is the tendency of a fluid jet to be attracted to a nearby surface. The principle was named after Romanian aerodynamics pioneer Henri Coandă, who was the first to recognize the practical application of the phenomenon in aircraft development.