* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hydraulics training module 1
Hydraulic jumps in rectangular channels wikipedia , lookup
Wind-turbine aerodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Blaise Pascal wikipedia , lookup
Flow measurement wikipedia , lookup
Coandă effect wikipedia , lookup
Flow conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Lift (force) wikipedia , lookup
Compressible flow wikipedia , lookup
Reynolds number wikipedia , lookup
Aerodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hydraulic power network wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli's principle wikipedia , lookup
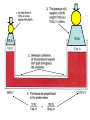
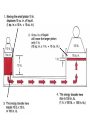
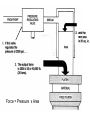
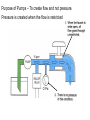
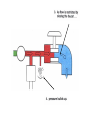
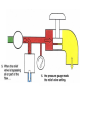
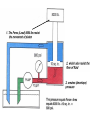
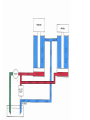
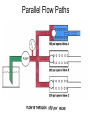
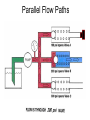
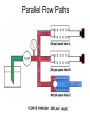
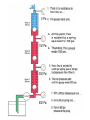
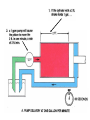
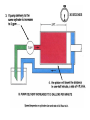
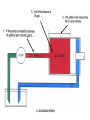
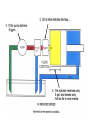
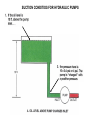
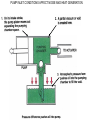
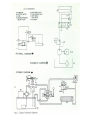
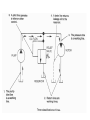
HYDRAULICS TRAINING MODULE 1 Hydraulic Systems Transmit power from one point to another Pascal’s Law Pressure applied on a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished in all directions, and acts with equal force on equal areas, and at right angles to them Pascal’s Law A 10 lb force is applied to a stopper with an area of one square inch Results in 10 lb force on every square inch of the container wall This bottle is filled with liquid that is noncompressible If the bottom has an area of 20 sq. in. and each square inch is pushed by a 10 lb of force, the entire bottom receives a 200 lb push PASCAL’S LAW • Pressure = Force / Area Pressure = lb/in2 (psi) Area = in2 Force = pounds (lb) 10 lb INPUT 100 lb OUTPUT Force = Pressure x Area Purpose of Pumps – To create flow and not pressure. Pressure is created when the flow is restricted O Psi Parallel Flow Paths Parallel Flow Paths Parallel Flow Paths 0 Psi 100 Psi 300 Psi 600 Psi SUCTION CONDITIOS FOR HYDRAULIC PUMPS SUCTION CONDITIOS FOR HYDRAULIC PUMPS PUMP INLET CONDITIONS AFFECT NOISE AND HEAT GENERATION