* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Warm – Up Chapter 16-2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
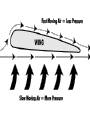
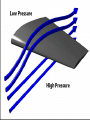
Warm – Up Chapter 3-2 1. How do particle change from a solid to a liquid? 2. What is the difference between evaporation and boiling? 3. What is sublimation? 4. What state of matter is the most common in the universe? Chapter 3-2 States of Matter Fluids Fluids Fluid – nonsolid state of matter Atoms free to move past each other Gas or liquid How do ships float? Buoyant Force – upward force exerted on an object in a fluid How do ships float? If buoyant force < object’s weight, the object will sink. Pressure Pressure – amount of force exerted per unit area of a surface Increases as depth increases Pressure below is greater than pressure above – upward buoyant force Archimedes’ Principal Buoyant force on an object in a fluid is an upward force equal to the weight of the volume of a fluid that the object displaces Density Density = mass / volume Pressure Formula Pressure = force (N) / area (m2) SI Unit - pascal Pascal’s Principal Hydraulic machines to toothpaste A fluid in a vessel exerts a pressure of equal intensity in all directions. Pascal’s Principal P1 = P2 F1 = F2 A1 = A2 Cross Multiply! Force is measured in Newton’s (N) Area is in cm2 Calculating Pascal’s Principal A hydraulic lift is used to lift a heavy machine that is pushing down on a 2.8 m2 piston (A1) with a force (F1) of 3,700 N. What force (F2) needs to be exerted on a 0.072 m2 piston (A2) to lift the machine? Calculating Pascal’s Principle In a hydraulic system, a force of 7,500 N is exerted on a piston with an area of 10 m2. If the force exerted on a second piston in the hydraulic system is 1,500 N, what is the area of the second piston? Fluids in Motion Fluids move faster in smaller areas compared to larger areas Viscosity – the resistance of a gas or liquid to flow High – slow Low – fast Bernoulli’s Principle As the velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure exerted by the fluid decreases. Flying! Velocity of the air blown over the top surface of the wing is greater than that of the air below it. Air pressure pushing down on the top of the wing is lower than the air pressure pushing up on the wing. Net force below the wing pushes the plane upward. Try it! Blow on the top of a sheet of paper.