Life 101 - findyourtao2011
... Definition: A change in the DNA. Remember, DNA is the code of life. It determines what traits will be expressed and what traits won’t be expressed. A single change in the sequence of DNA is a mutation. A mutation can be neutral, positive or negative for an organism. A negative mutation means it is h ...
... Definition: A change in the DNA. Remember, DNA is the code of life. It determines what traits will be expressed and what traits won’t be expressed. A single change in the sequence of DNA is a mutation. A mutation can be neutral, positive or negative for an organism. A negative mutation means it is h ...
Topic 4: Genetics - Peoria Public Schools
... 8. Base substitution is the simplest type of mutation in which one base in a gene is replaced by another. 9. An example of a disease caused by a base substitution mutation in humans is sickle cell anemia. 10. Natural selection has maintained the sickle cell allele because when it occurs singly, it r ...
... 8. Base substitution is the simplest type of mutation in which one base in a gene is replaced by another. 9. An example of a disease caused by a base substitution mutation in humans is sickle cell anemia. 10. Natural selection has maintained the sickle cell allele because when it occurs singly, it r ...
6.4 Manipulating the Genome - Hutchison
... mammals, but plasmid vectors are not. • A cold virus is a good choice to target lung cells but not bone cells. ...
... mammals, but plasmid vectors are not. • A cold virus is a good choice to target lung cells but not bone cells. ...
African Regional Training of Trainers workshop on the Identification and
... • Chromosomes are Chapters in the Book • Genes are like Individual Recipes • Genes act as the Blue Print for Life ...
... • Chromosomes are Chapters in the Book • Genes are like Individual Recipes • Genes act as the Blue Print for Life ...
Problem Set
... 2) Describe the pros and cons of using spotted cDNA arrays vs. short oligonucleotide microarrays for your studies on wookie starwarius. 3) The goal of these studies is to identify gene expression patterns that might be relevant for treatment of human baldness. How will you use expression data on ten ...
... 2) Describe the pros and cons of using spotted cDNA arrays vs. short oligonucleotide microarrays for your studies on wookie starwarius. 3) The goal of these studies is to identify gene expression patterns that might be relevant for treatment of human baldness. How will you use expression data on ten ...
Developmental Biology 8/e - Florida International University
... A mutation in a particular enhancer can delete its particular stripe and no other. The placement of the stripes can be altered by deleting the gap genes that regulate them. ...
... A mutation in a particular enhancer can delete its particular stripe and no other. The placement of the stripes can be altered by deleting the gap genes that regulate them. ...
Human Genetics
... Where do our genes come from? • We had said that a pair of genes determines which traits we will inherit from our parents • Why would it be a pair of genes? •Each parent provides a sex cell in order for fertilization to occur •The father will provide a sperm cell that has 23 chromosomes •The mother ...
... Where do our genes come from? • We had said that a pair of genes determines which traits we will inherit from our parents • Why would it be a pair of genes? •Each parent provides a sex cell in order for fertilization to occur •The father will provide a sperm cell that has 23 chromosomes •The mother ...
Genes
... blindness, and death during early childhood. Cystic Fibrosis: Makes breathing and digestion difficult, its caused by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome). As a result, the a ...
... blindness, and death during early childhood. Cystic Fibrosis: Makes breathing and digestion difficult, its caused by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome). As a result, the a ...
Supplementary
... Figure S2. Evaluation of resistance for wild-type (Nb wt) and transgenic N. benthamiana against V. dahliae. (A) Region (189–836 bp) of VdAAC gene was amplified and cloned into pK7GW1WG2(I) by LR recombination reaction. Numbers indicate nucleotide positions; (B) Schematic representation of the pK7GWI ...
... Figure S2. Evaluation of resistance for wild-type (Nb wt) and transgenic N. benthamiana against V. dahliae. (A) Region (189–836 bp) of VdAAC gene was amplified and cloned into pK7GW1WG2(I) by LR recombination reaction. Numbers indicate nucleotide positions; (B) Schematic representation of the pK7GWI ...
Word Doc
... 2) Describe the pros and cons of using spotted cDNA arrays vs. short oligonucleotide microarrays for your studies on wookie starwarius. 3) Using the dataset provided (BBSIarraydata7_06.xls), explore your primary data. Using scattergram analysis (to be demonstrated in class), determine if any of the ...
... 2) Describe the pros and cons of using spotted cDNA arrays vs. short oligonucleotide microarrays for your studies on wookie starwarius. 3) Using the dataset provided (BBSIarraydata7_06.xls), explore your primary data. Using scattergram analysis (to be demonstrated in class), determine if any of the ...
B1 You and Your Genes
... Why people can be carriers of cystic fibrosis, but not Huntington’s disorder Doctors can test embryos, foetuses and adults for certain alleles by genetic tests What happens during embryo selection (pre-implantation genetic diagnosis) The implications of the use of genetic testing by others ( ...
... Why people can be carriers of cystic fibrosis, but not Huntington’s disorder Doctors can test embryos, foetuses and adults for certain alleles by genetic tests What happens during embryo selection (pre-implantation genetic diagnosis) The implications of the use of genetic testing by others ( ...
Unit 6: Inheritance
... In humans, hypercholesterolemia is an example of incomplete dominance. CHCH= normal CHCh= elevated cholesterol (2x’s the normal level ChCh= extremely high cholesterol (5x’s the normal level, VERY dangerous). ...
... In humans, hypercholesterolemia is an example of incomplete dominance. CHCH= normal CHCh= elevated cholesterol (2x’s the normal level ChCh= extremely high cholesterol (5x’s the normal level, VERY dangerous). ...
CG7b-PSSM
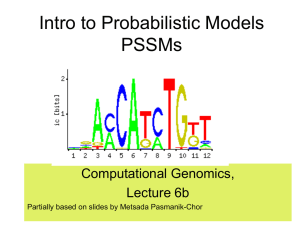
... Computational Genomics, Lecture 6b Partially based on slides by Metsada Pasmanik-Chor ...
... Computational Genomics, Lecture 6b Partially based on slides by Metsada Pasmanik-Chor ...
Cloze passage 3
... o) The twisted shape of a DNA molecule p) A biologist who worked with fruit fly to identify sex-linkage q) The features or traits of an organism are controlled by both genes and the ……………. r) The base complementary to thymine s) A model we used to represent chromosomes t) A biological name for a fam ...
... o) The twisted shape of a DNA molecule p) A biologist who worked with fruit fly to identify sex-linkage q) The features or traits of an organism are controlled by both genes and the ……………. r) The base complementary to thymine s) A model we used to represent chromosomes t) A biological name for a fam ...
Obesity caused BBC tumors to form at a faster rate compared to lean
... • 2,919 genes exhibited differential methylation in response to arsenic exposure • 334 gene exhibited corresponding changes in gene expression (mRNA transcripts) • Only 16 genes exhibited a significant linear relationship between methylation and gene expression • Seven of these genes were related to ...
... • 2,919 genes exhibited differential methylation in response to arsenic exposure • 334 gene exhibited corresponding changes in gene expression (mRNA transcripts) • Only 16 genes exhibited a significant linear relationship between methylation and gene expression • Seven of these genes were related to ...
SEX-RELATED INHERITANCE
... and female gametogenesis; different regions are condensed in oogenesis than in spermatogenesis. The inactivated regions are not expressed in the fetus, so if the normally "active" gene(s) donated by the other parent is/are defective, an aberrant phenotype may result. Human examples include Prader-Wi ...
... and female gametogenesis; different regions are condensed in oogenesis than in spermatogenesis. The inactivated regions are not expressed in the fetus, so if the normally "active" gene(s) donated by the other parent is/are defective, an aberrant phenotype may result. Human examples include Prader-Wi ...
Lecture
... Glimmer uses interpolated Markov models (IMMs) to identify the coding regions; it uses ATG, GTG, and TTG as potential starts. Critica uses blastn to produce alignments from the entire dataset and derives dicodon statistics to recognize coding sequences. It uses an SD sensor with ATG, GTG, and TTG as ...
... Glimmer uses interpolated Markov models (IMMs) to identify the coding regions; it uses ATG, GTG, and TTG as potential starts. Critica uses blastn to produce alignments from the entire dataset and derives dicodon statistics to recognize coding sequences. It uses an SD sensor with ATG, GTG, and TTG as ...
Law of Independent Assortment
... Epistasis: One gene masks the expression of a different gene for a different trait Dominance: One allele masks the expression of another allele of the same gene ...
... Epistasis: One gene masks the expression of a different gene for a different trait Dominance: One allele masks the expression of another allele of the same gene ...
Inferring Function From Known Genes
... used to infer the function of unknown genes in a microarray experiment. 3) Pathway analysis If the genes are sufficiently well understood, they may be assembled into networks showing which genes regulate other genes. Unknown genes that have expression patterns similar to those in the network can be ...
... used to infer the function of unknown genes in a microarray experiment. 3) Pathway analysis If the genes are sufficiently well understood, they may be assembled into networks showing which genes regulate other genes. Unknown genes that have expression patterns similar to those in the network can be ...
Inferring Function From Known Genes
... used to infer the function of unknown genes in a microarray experiment. 3) Pathway analysis If the genes are sufficiently well understood, they may be assembled into networks showing which genes regulate other genes. Unknown genes that have expression patterns similar to those in the network can be ...
... used to infer the function of unknown genes in a microarray experiment. 3) Pathway analysis If the genes are sufficiently well understood, they may be assembled into networks showing which genes regulate other genes. Unknown genes that have expression patterns similar to those in the network can be ...
Linked Genes - Deepwater.org
... A male could receive the trait from a mother that does not express the trait. But for a female to receive the trait, her father would have to be a hemophiliac. This is why sex-linked traits are so much more common in males. Baldness is slightly different. Baldness isn’t fatal, it often doesn’t appea ...
... A male could receive the trait from a mother that does not express the trait. But for a female to receive the trait, her father would have to be a hemophiliac. This is why sex-linked traits are so much more common in males. Baldness is slightly different. Baldness isn’t fatal, it often doesn’t appea ...
Genekids - CICO TEAM
... you may have inherited factors that put you at risk. Inherited risk factors are passed down from parent to child by way of genes. All humans have the same genes, but different people have different versions of these genes. Sometimes genetic differences cause disease. In rare cases, changing a single ...
... you may have inherited factors that put you at risk. Inherited risk factors are passed down from parent to child by way of genes. All humans have the same genes, but different people have different versions of these genes. Sometimes genetic differences cause disease. In rare cases, changing a single ...
Gene expression profiling

In the field of molecular biology, gene expression profiling is the measurement of the activity (the expression) of thousands of genes at once, to create a global picture of cellular function. These profiles can, for example, distinguish between cells that are actively dividing, or show how the cells react to a particular treatment. Many experiments of this sort measure an entire genome simultaneously, that is, every gene present in a particular cell.DNA microarray technology measures the relative activity of previously identified target genes. Sequence based techniques, like serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE, SuperSAGE) are also used for gene expression profiling. SuperSAGE is especially accurate and can measure any active gene, not just a predefined set. The advent of next-generation sequencing has made sequence based expression analysis an increasingly popular, ""digital"" alternative to microarrays called RNA-Seq. However, microarrays are far more common, accounting for 17,000 PubMed articles by 2006.