Biotechnology
... similar to humans. As a result they can be used to study human diseases and gene function. ...
... similar to humans. As a result they can be used to study human diseases and gene function. ...
COMP.350/580.202 LAB: GENOME ANNOTATION 2/3/16 Reference
... 9. If you find different predictions leading to conflicting models, explain what would be required to be able to decide which gene prediction got it right. 10. To conclude your work click menu tab File and select Upload to DNA Subway. 11. Close the Apollo to return to DNA Subway. Experiment 5: Ident ...
... 9. If you find different predictions leading to conflicting models, explain what would be required to be able to decide which gene prediction got it right. 10. To conclude your work click menu tab File and select Upload to DNA Subway. 11. Close the Apollo to return to DNA Subway. Experiment 5: Ident ...
NMPDRposter - Edwards @ SDSU
... Clicking the GBrowse button displays a layout of genes against the genome. You can zoom in and out. You may select to map pathogenicity islands, homologous regions from related genomes, and so forth. Clicking on a gene of interest in this display will open the NMPDR context page, just like clicking ...
... Clicking the GBrowse button displays a layout of genes against the genome. You can zoom in and out. You may select to map pathogenicity islands, homologous regions from related genomes, and so forth. Clicking on a gene of interest in this display will open the NMPDR context page, just like clicking ...
How many genes are responsible for phenotypic differences
... What are these genes??? (TFs, enzymes, etc.) What are their normal developmental/biochemical functions? Why do changes in these genes cause phenotypic differences? What are these changes at the molecular level? (coding or noncoding, how many mutations per gene, etc.) ...
... What are these genes??? (TFs, enzymes, etc.) What are their normal developmental/biochemical functions? Why do changes in these genes cause phenotypic differences? What are these changes at the molecular level? (coding or noncoding, how many mutations per gene, etc.) ...
supplement 3 - Springer Static Content Server
... even it captures the largest amount of variance in data (57%). This agrees with existing arguments (Yeung and Ruzzo 2001, Chang 1983) that the component with largest variance is not necessary to be the most informative component for classification. The precise description of the six class separating ...
... even it captures the largest amount of variance in data (57%). This agrees with existing arguments (Yeung and Ruzzo 2001, Chang 1983) that the component with largest variance is not necessary to be the most informative component for classification. The precise description of the six class separating ...
Presenter 18 - Florida International University
... ccguggacgc gagcgcgcuu gagggugcug gguuggaaag uacguuucau cuggguugac gacuugaggu cgcagugacc ccg ...
... ccguggacgc gagcgcgcuu gagggugcug gguuggaaag uacguuucau cuggguugac gacuugaggu cgcagugacc ccg ...
Nature Nurture
... – complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes – has two strands-forming a “double helix”- held together by bonds between pairs of nucleotides ...
... – complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes – has two strands-forming a “double helix”- held together by bonds between pairs of nucleotides ...
Study Guide: Lecture 1 1. What does “GMO” stand for and what does
... 1. What does “GMO” stand for and what does it mean? 2. What is the meaning of a formula such as 2n = 2x = 18? a. How many chromosomes are there in a pollen grain of a plant with this formula? b. How many chromosomes are there in a leaf cell of a plant with this formula? c. What ploidy level is a pla ...
... 1. What does “GMO” stand for and what does it mean? 2. What is the meaning of a formula such as 2n = 2x = 18? a. How many chromosomes are there in a pollen grain of a plant with this formula? b. How many chromosomes are there in a leaf cell of a plant with this formula? c. What ploidy level is a pla ...
ALE #7
... a. What are the two most widely known epigenetic processes? 1.DNA methylation – adding methyl groups to DNA to turn genes on or off without mutating the gene itself. 2. Histone modification – loosens the DNA coils to enhance transcription of genes. b. How does lunasin kill cancer cells? It modifies ...
... a. What are the two most widely known epigenetic processes? 1.DNA methylation – adding methyl groups to DNA to turn genes on or off without mutating the gene itself. 2. Histone modification – loosens the DNA coils to enhance transcription of genes. b. How does lunasin kill cancer cells? It modifies ...
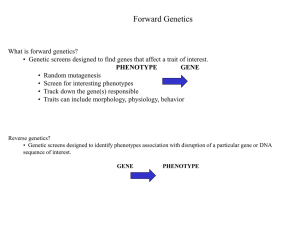
Complementation
... • Genetic screens designed to identify phenotypes association with disruption of a particular gene or DNA sequence of interest. GENE ...
... • Genetic screens designed to identify phenotypes association with disruption of a particular gene or DNA sequence of interest. GENE ...
Regulatory role of hsa-miR-939 on pro
... Transfection of miR-939 resulted in the reduction of IL-6 and NOS2A mRNAs, a decrease in protein levels of IL-6, VEGFA, NOS2A, and an abrogation of NFκB activity. Collectively, our data suggests that downregulation of miR-939 in CRPS patients may enhance target gene expression involved in inflammato ...
... Transfection of miR-939 resulted in the reduction of IL-6 and NOS2A mRNAs, a decrease in protein levels of IL-6, VEGFA, NOS2A, and an abrogation of NFκB activity. Collectively, our data suggests that downregulation of miR-939 in CRPS patients may enhance target gene expression involved in inflammato ...
BIOL 112 – Principles of Zoology
... Eukaryotic genes are divided into exons and introns; in bacteria, genes are almost never divided. In eukaryotes, mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and then processed and exported to the cytoplasm; in bacteria, transcription and translation can take place simultaneously off the same piece of DNA ...
... Eukaryotic genes are divided into exons and introns; in bacteria, genes are almost never divided. In eukaryotes, mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and then processed and exported to the cytoplasm; in bacteria, transcription and translation can take place simultaneously off the same piece of DNA ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch.14 Mendel and the Gene Idea
... while B or b leads to color BBcc would be white even though the genes code for black color. ...
... while B or b leads to color BBcc would be white even though the genes code for black color. ...
Prodigiosin Production in E. Coli
... Known to cause many nosocomial infections Thrives in high moisture environments ...
... Known to cause many nosocomial infections Thrives in high moisture environments ...
PPT File
... a. Organisms that move the recombinant DNA from one organism to another organism. Bacteria- a. contains a circular piece of DNA called a plasmid. b. By splicing a foreign gene into a plasmid. A scientist can transport the gene to a new bacterial cell. c. This technique and vectors are used to produc ...
... a. Organisms that move the recombinant DNA from one organism to another organism. Bacteria- a. contains a circular piece of DNA called a plasmid. b. By splicing a foreign gene into a plasmid. A scientist can transport the gene to a new bacterial cell. c. This technique and vectors are used to produc ...
Andrew Pocklington
... - ISC and MGS data: SNPs with a greater effect on global gene expression generally predict schizophrenia affected status significantly better than those with a lesser effect Alex Richards ...
... - ISC and MGS data: SNPs with a greater effect on global gene expression generally predict schizophrenia affected status significantly better than those with a lesser effect Alex Richards ...
Brain Organization
... Note that it is not the case that the chromosomes just pair off, there is also recombination So, each sex cell is a little bit different ...
... Note that it is not the case that the chromosomes just pair off, there is also recombination So, each sex cell is a little bit different ...
CH11-Summary
... – Gene expression can be controlled through regulatory proteins known as transcription factors. • Dictate placement of RNA polymerase • Enhancers ...
... – Gene expression can be controlled through regulatory proteins known as transcription factors. • Dictate placement of RNA polymerase • Enhancers ...
Chapter 15
... 1. Promoter always capable of binding to RNA polymerase and therefore the genes in question are always transcribed (“on”) >genes that are always on are called constitutive genes 2. Promoter usually incapable of binding to RNA polymerase and therefore the genes are usually not transcribed (“off”) but ...
... 1. Promoter always capable of binding to RNA polymerase and therefore the genes in question are always transcribed (“on”) >genes that are always on are called constitutive genes 2. Promoter usually incapable of binding to RNA polymerase and therefore the genes are usually not transcribed (“off”) but ...
Resistance Gene Management: Concepts and Practice
... • May be needed as a stopgap measure • In general, don’t go there - Puts growers at risk - Disruptive to breeding programs ...
... • May be needed as a stopgap measure • In general, don’t go there - Puts growers at risk - Disruptive to breeding programs ...
Gene expression profiling

In the field of molecular biology, gene expression profiling is the measurement of the activity (the expression) of thousands of genes at once, to create a global picture of cellular function. These profiles can, for example, distinguish between cells that are actively dividing, or show how the cells react to a particular treatment. Many experiments of this sort measure an entire genome simultaneously, that is, every gene present in a particular cell.DNA microarray technology measures the relative activity of previously identified target genes. Sequence based techniques, like serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE, SuperSAGE) are also used for gene expression profiling. SuperSAGE is especially accurate and can measure any active gene, not just a predefined set. The advent of next-generation sequencing has made sequence based expression analysis an increasingly popular, ""digital"" alternative to microarrays called RNA-Seq. However, microarrays are far more common, accounting for 17,000 PubMed articles by 2006.