Optical Fiber Communication
... • The specific attenuation ( power loss in dB per unit length ) actually depends on the wavelength of the radiation travelling along the optic fibre • The graph shows minima at 1310nm and 1550nm, which implies that these are desirable wavelengths for optimal transmission • These are infra red wavele ...
... • The specific attenuation ( power loss in dB per unit length ) actually depends on the wavelength of the radiation travelling along the optic fibre • The graph shows minima at 1310nm and 1550nm, which implies that these are desirable wavelengths for optimal transmission • These are infra red wavele ...
Activity: Emission spectroscopy and smart sensors
... A “Red Tide” spectrometer connected to an optical fiber(red/blue) and a USB computer interface (clay ). The USB link is used to bring power the spectrometer and transmit data to the computer. Light is brought to the spectrometer using the optical fiber. ...
... A “Red Tide” spectrometer connected to an optical fiber(red/blue) and a USB computer interface (clay ). The USB link is used to bring power the spectrometer and transmit data to the computer. Light is brought to the spectrometer using the optical fiber. ...
TrueWave® SRS Ocean Optical Fiber
... festoons and deep-water crossings, can also take advantage of the fiber’s high bandwidth capacity. For longer regional and trans-oceanic applications, TrueWave SRS Fiber can be combined in spans with the large effective area TrueWave XL Fibers and the positive dispersion of AllWave® Single-Mode Ocea ...
... festoons and deep-water crossings, can also take advantage of the fiber’s high bandwidth capacity. For longer regional and trans-oceanic applications, TrueWave SRS Fiber can be combined in spans with the large effective area TrueWave XL Fibers and the positive dispersion of AllWave® Single-Mode Ocea ...
Optical fibers - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... Optical fibers work on the principle of total internal reflection of light. When a beam of light traveling in an optically denser medium falls on a surface separating a relatively less denser medium at an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle (C) for the pair of media, the light undergo ...
... Optical fibers work on the principle of total internal reflection of light. When a beam of light traveling in an optically denser medium falls on a surface separating a relatively less denser medium at an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle (C) for the pair of media, the light undergo ...
Optical fiber communication
... Glass produced were too lossy for modern long distance communications. ...
... Glass produced were too lossy for modern long distance communications. ...
Cladding
... Optical fiber is a long thin transparent dielectric material which carries EM waves of visible and IR frequencies from one end to the other end of the fiber by means of TIR. ...
... Optical fiber is a long thin transparent dielectric material which carries EM waves of visible and IR frequencies from one end to the other end of the fiber by means of TIR. ...
OPTICAL TIME DOMAIN REFLECTOMETRY
... diameter and cladding are chosen such that light will remain within the fiber. This is due to the fact that the light wave introduced into the fiber core has a fixed frequency. As such, the light wave’s angle of incidence to the fiber walls is also fixed within a given range. Thus, the core diameter ...
... diameter and cladding are chosen such that light will remain within the fiber. This is due to the fact that the light wave introduced into the fiber core has a fixed frequency. As such, the light wave’s angle of incidence to the fiber walls is also fixed within a given range. Thus, the core diameter ...
About Optical Fiber - University of Vaasa
... When the Light Ray pass from a higher index material to a lower index material, light refraction occurs. When light incidents at interface between the core and the cladding has differents angles some power are reflacting back and some power enter into the cladding Cladding ...
... When the Light Ray pass from a higher index material to a lower index material, light refraction occurs. When light incidents at interface between the core and the cladding has differents angles some power are reflacting back and some power enter into the cladding Cladding ...
Photodetecting Fiber Webs—Y. Fink, J. Joannopoulos
... (MRSEC) program of the NSF with use of their Shared Experimental Facilities. Modal decomposition in multimode optical waveguides plays an important role in the study of multimode wave propagation by providing insight to the nature of mode interactions due to structural perturbation. Nevertheless, to ...
... (MRSEC) program of the NSF with use of their Shared Experimental Facilities. Modal decomposition in multimode optical waveguides plays an important role in the study of multimode wave propagation by providing insight to the nature of mode interactions due to structural perturbation. Nevertheless, to ...
Document
... 2. A step-index single-mode fiber for transmitting a signal at λ = 1.35 μm is 100 km long. At this wavelength, the fiber has the following parameters for its silica cladding: n2 = 1.446, N2 = 1.466, and D2 = −0.0027. Its core has a radius of a = 4 μm and an index of n1 = 1.450. What are the propagat ...
... 2. A step-index single-mode fiber for transmitting a signal at λ = 1.35 μm is 100 km long. At this wavelength, the fiber has the following parameters for its silica cladding: n2 = 1.446, N2 = 1.466, and D2 = −0.0027. Its core has a radius of a = 4 μm and an index of n1 = 1.450. What are the propagat ...
1895 wireless telegraph (radiotelegraph) and request in Italy having been turned down.
... "Optical Waveguide Fibers" capable of carrying 65,000 times more information than copper wire, through which information carried by a pattern of light waves could be decoded at a destination even a thousand miles away. The team had solved the problems presented by Dr. Kao. 1970 First continuous-wave ...
... "Optical Waveguide Fibers" capable of carrying 65,000 times more information than copper wire, through which information carried by a pattern of light waves could be decoded at a destination even a thousand miles away. The team had solved the problems presented by Dr. Kao. 1970 First continuous-wave ...
optical fiber communication
... components and interconnection methods, but allows much longer, higher-performance links. ...
... components and interconnection methods, but allows much longer, higher-performance links. ...
Optical Fiber Communication
... components and interconnection methods, but allows much longer, higher-performance ...
... components and interconnection methods, but allows much longer, higher-performance ...
Multimode optical fiber - BSNL Durg SSA(Connecting India)
... various materials depending on the choice of user and application in use. They act as a mechanical protection to the core and cladding inside ...
... various materials depending on the choice of user and application in use. They act as a mechanical protection to the core and cladding inside ...
DWDM Technology
... Light emitters and light detectors are active devices at opposite ends of an optical transmission system. Light sources, or light emitters, are transmit-side devices that convert electrical signals to light pulses. The process of this conversion, or modulation, can be accomplished by externally modu ...
... Light emitters and light detectors are active devices at opposite ends of an optical transmission system. Light sources, or light emitters, are transmit-side devices that convert electrical signals to light pulses. The process of this conversion, or modulation, can be accomplished by externally modu ...
Lab 14 - FIber Optics Principles and Position Sensor
... Starting from zero displacement, why does the detected light intensity first INCREASE from zero (region 1) in above figure and then decrease (region 2)? Is there any displacement region where this displacement sensor is linear? What the range of detection (not necessarily when the sensor is line ...
... Starting from zero displacement, why does the detected light intensity first INCREASE from zero (region 1) in above figure and then decrease (region 2)? Is there any displacement region where this displacement sensor is linear? What the range of detection (not necessarily when the sensor is line ...
Fiber Optics Communications
... communicate with their fleets • Lightwave communication started with the invention of photophone by Alexander Graham Bell in 1880, which used Sun light as carrier and air as transmission media. Sound information is transmitted this way up to 200 meters. • The biggest obstacle for using optic fibers ...
... communicate with their fleets • Lightwave communication started with the invention of photophone by Alexander Graham Bell in 1880, which used Sun light as carrier and air as transmission media. Sound information is transmitted this way up to 200 meters. • The biggest obstacle for using optic fibers ...
A Project Report on- *OPTICAL FIBRE CABLE*
... • An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of very pure glass (silica) not much wider than a human hair that acts as "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber • Optical fiber typically consists of a transparent core surrounded by a transparent cladding material ...
... • An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of very pure glass (silica) not much wider than a human hair that acts as "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber • Optical fiber typically consists of a transparent core surrounded by a transparent cladding material ...
1. Which of the following statement are true about "LED life" term?
... chromatic dispersion operates is a kind of fiber that operate in the 1370 nm band is done by manipulating the core profile to introduce dispersion in the opposite direction (with the opposite sign) from the direction in which chromatic dispersion operates is a kind of fiber that operate in the 1370 ...
... chromatic dispersion operates is a kind of fiber that operate in the 1370 nm band is done by manipulating the core profile to introduce dispersion in the opposite direction (with the opposite sign) from the direction in which chromatic dispersion operates is a kind of fiber that operate in the 1370 ...
Light Tree.pdf - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... The concept of light tree is introduced in a wavelength routed optical network, which employs wavelength -division multiplexing (WDM). Light Tree was designed by Omar Ivan Huerta Cardoso. Cardoso designed a plastic tree with some water in it which is used to conduce the light from Light Emitting Dio ...
... The concept of light tree is introduced in a wavelength routed optical network, which employs wavelength -division multiplexing (WDM). Light Tree was designed by Omar Ivan Huerta Cardoso. Cardoso designed a plastic tree with some water in it which is used to conduce the light from Light Emitting Dio ...
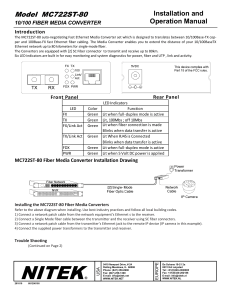
MC722ST-80
... per and 100Base‐FX fast Ethernet fiber cabling. The Media Converter enables you to extend the distance of your 10/100BaseTX Ethernet network up to 80 kilometers for single‐mode fiber. The Converters are equipped with [2] SC Fiber connector to transmit and receive up to 80km. Six LE ...
... per and 100Base‐FX fast Ethernet fiber cabling. The Media Converter enables you to extend the distance of your 10/100BaseTX Ethernet network up to 80 kilometers for single‐mode fiber. The Converters are equipped with [2] SC Fiber connector to transmit and receive up to 80km. Six LE ...
unit –iii fiber optics and applications part-a 2
... 1. What is optical fiber? Optical fiber is a wave guide made up of transparent dielectric like glass or plastics in cylindrical form through which light is transmitted by total internal reflection. An optical fiber consists of a central core glass about 50μm diameter surrounded by a cladding about 1 ...
... 1. What is optical fiber? Optical fiber is a wave guide made up of transparent dielectric like glass or plastics in cylindrical form through which light is transmitted by total internal reflection. An optical fiber consists of a central core glass about 50μm diameter surrounded by a cladding about 1 ...
Optical fiber

An optical fiber (or optical fibre) is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than wire cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with lesser amounts of loss; in addition, fibers are also immune to electromagnetic interference, a problem which metal wires suffer from excessively. Fibers are also used for illumination, and are wrapped in bundles so that they may be used to carry images, thus allowing viewing in confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, some of them being fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers.Optical fibers typically include a transparent core surrounded by a transparent cladding material with a lower index of refraction. Light is kept in the core by the phenomenon of total internal reflection which causes the fiber to act as a waveguide. Fibers that support many propagation paths or transverse modes are called multi-mode fibers (MMF), while those that support a single mode are called single-mode fibers (SMF). Multi-mode fibers generally have a wider core diameter and are used for short-distance communication links and for applications where high power must be transmitted. Single-mode fibers are used for most communication links longer than 1,000 meters (3,300 ft).An important aspect of a fiber optic communication is that of extension of the fiber optic cables such that the losses brought about by joining two different cables is kept to a minimum. Joining lengths of optical fiber often proves to be more complex than joining electrical wire or cable and involves careful cleaving of the fibers, perfect alignment of the fiber cores, and the splicing of these aligned fiber cores. For applications that demand a permanent connection a mechanical splice which holds the ends of the fibers together mechanically could be used or a fusion splice that uses heat to fuse the ends of the fibers together could be used. Temporary or semi-permanent connections are made by means of specialized optical fiber connectors.The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of optical fibers is known as fiber optics.