William Stallings Data and Computer
... or 56-Kbps data lines higher speeds are available with T-3 (45Mbps) [sometimes referred to a DS-3 lines; can be multiplexed into 28 T-1 signals; T-3 consists of 672 individual channels, each of which supports 64-Kbps] and T-4 services (274Mbps) in Europe, E-1 (2.048Mbps) is used instead of T-1 ...
... or 56-Kbps data lines higher speeds are available with T-3 (45Mbps) [sometimes referred to a DS-3 lines; can be multiplexed into 28 T-1 signals; T-3 consists of 672 individual channels, each of which supports 64-Kbps] and T-4 services (274Mbps) in Europe, E-1 (2.048Mbps) is used instead of T-1 ...
Single-Mode Photonic Band Gap Guidance of Light in Air
... comparison with the wavelength, the PBGs responsible for the guidance are of high order. By selecting lengths of fiber that had been found to guide light at appropriate wavelengths, we excited this mode using laser sources. The laser light guided in the air core formed a stable, smoothly varying, si ...
... comparison with the wavelength, the PBGs responsible for the guidance are of high order. By selecting lengths of fiber that had been found to guide light at appropriate wavelengths, we excited this mode using laser sources. The laser light guided in the air core formed a stable, smoothly varying, si ...
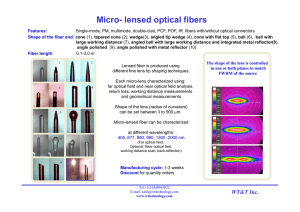
lensed fiber
... Focusing of light into small spot at working distance of ~200 -3000 um Introduction of angled interface in the light-pass results in deflection of light, emitting from the fiber. Resultant deflected optical field is Focused at working distance of 0.4-2 mm ...
... Focusing of light into small spot at working distance of ~200 -3000 um Introduction of angled interface in the light-pass results in deflection of light, emitting from the fiber. Resultant deflected optical field is Focused at working distance of 0.4-2 mm ...
What is total internal reflection?
... some of the basic concepts and principles. The groups will be assigned (three to four students per group). Hand out the assignments. Day 3: Laser safety test will be administered. Group 1 – Design a set-up that shows total internal reflection. This group will have one or two laser pointers (differen ...
... some of the basic concepts and principles. The groups will be assigned (three to four students per group). Hand out the assignments. Day 3: Laser safety test will be administered. Group 1 – Design a set-up that shows total internal reflection. This group will have one or two laser pointers (differen ...
Photonics Systems - Introduction Sergiusz Patela, Dr Sc
... 2000 - L-band system introduced (1570-1610nm) 40 Gb/s transmission in one channel. ...
... 2000 - L-band system introduced (1570-1610nm) 40 Gb/s transmission in one channel. ...
Near-field optical micromanipulation
... Light is launched into the 127nm layer 32 times of the incident intensity in the layer 25 times at the surface 5~10 times measured… v = 2~4 vs. 22 ...
... Light is launched into the 127nm layer 32 times of the incident intensity in the layer 25 times at the surface 5~10 times measured… v = 2~4 vs. 22 ...
may11-96 as a Word 6.0 doc - Lyle School of Engineering
... 20. Find the amount of pulse spreading in a single mode fiber if the optical source is a dfb laser operating at a free space wavelength of 1.56 µm. The laser has a spectral emission width of 0.1 nm. The length of the silica fiber is 3000 km. (You may want to refer to one or more of the attached dis ...
... 20. Find the amount of pulse spreading in a single mode fiber if the optical source is a dfb laser operating at a free space wavelength of 1.56 µm. The laser has a spectral emission width of 0.1 nm. The length of the silica fiber is 3000 km. (You may want to refer to one or more of the attached dis ...
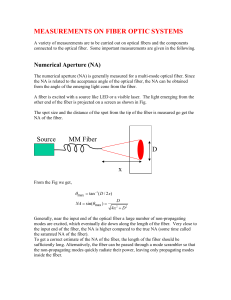
2.7 Optical Fiber Attenuation
... ▪ caused in inhomogeneities which are comparable in size to the guided wavelength. ▪ These result from the non-perfect cylindrical structure of the waveguide and may be caused by fiber imperfections such as irregularities in the core-cladding interface, core-cladding refractive index differences alo ...
... ▪ caused in inhomogeneities which are comparable in size to the guided wavelength. ▪ These result from the non-perfect cylindrical structure of the waveguide and may be caused by fiber imperfections such as irregularities in the core-cladding interface, core-cladding refractive index differences alo ...
Technological Education Institute (TEI) of Piraeus
... Light transmission - Light is totally reflected from the cladding back into the core - This is achieved with a higher refractive index in the core - Transmission with minimal loss. - The outer buffer coating protects the fiber from external conditions and physical damage. ...
... Light transmission - Light is totally reflected from the cladding back into the core - This is achieved with a higher refractive index in the core - Transmission with minimal loss. - The outer buffer coating protects the fiber from external conditions and physical damage. ...
Lecture 13-15
... Optical fiber Loss Absorption Scattering Connectors Low loss : 0.2 dB/Km Color dependent ...
... Optical fiber Loss Absorption Scattering Connectors Low loss : 0.2 dB/Km Color dependent ...
Full Material(s)-Please Click here
... multiple fixed rate channels. For example, the payload of an OC-48 link may be subdivided into four OC-12 channels. In this case the data rate of a single cell or packet flow is limited by the bandwidth of an individual channel. Protocol Layers The SONET/SDH standard includes a definition of a trans ...
... multiple fixed rate channels. For example, the payload of an OC-48 link may be subdivided into four OC-12 channels. In this case the data rate of a single cell or packet flow is limited by the bandwidth of an individual channel. Protocol Layers The SONET/SDH standard includes a definition of a trans ...
Fiber Waveguide
... of fiber, known as graded-index fiber, the refractive index decreases gradually inside the core. Considerable insight in the guiding properties of optical fibers can be gained by using a ray picture based on geometrical optics. The geometrical-optics description, although approximate, is valid when ...
... of fiber, known as graded-index fiber, the refractive index decreases gradually inside the core. Considerable insight in the guiding properties of optical fibers can be gained by using a ray picture based on geometrical optics. The geometrical-optics description, although approximate, is valid when ...
Chapter two_part B
... ▪ caused in inhomogeneities which are comparable in size to the guided wavelength. ▪ These result from the non-perfect cylindrical structure of the waveguide and may be caused by fiber imperfections such as irregularities in the core-cladding interface, core-cladding refractive index differences alo ...
... ▪ caused in inhomogeneities which are comparable in size to the guided wavelength. ▪ These result from the non-perfect cylindrical structure of the waveguide and may be caused by fiber imperfections such as irregularities in the core-cladding interface, core-cladding refractive index differences alo ...
EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 7
... Amplifiers are used to overcome fiber loss They are used in 4 basic applications: ...
... Amplifiers are used to overcome fiber loss They are used in 4 basic applications: ...
MC-4TX Series
... 3.03 INSTALLATION A. General: Locate fiber optic modules as indicated on the approved detail drawings and install module in compliance with the IFS User’s manual. ...
... 3.03 INSTALLATION A. General: Locate fiber optic modules as indicated on the approved detail drawings and install module in compliance with the IFS User’s manual. ...
5. Optical fiber
... where I0 is the minimum displacement current and I is the corresponding detector current. THEORY: (1) Communication implies transfer of information from one point to another. The information can be speech, images, data etc. The carrier wave is modulated by the information which is then transmitted t ...
... where I0 is the minimum displacement current and I is the corresponding detector current. THEORY: (1) Communication implies transfer of information from one point to another. The information can be speech, images, data etc. The carrier wave is modulated by the information which is then transmitted t ...
2. Measurement of refractive index of liquids using fiber optic
... The paper describes a technique to determine the refractive index of liquids using reflective type fiber optic displacement sensor. The sensor consists of two multimode step index fibers and a mirror. The output light intensity from the receiving fiber is measured as a function of displacement of th ...
... The paper describes a technique to determine the refractive index of liquids using reflective type fiber optic displacement sensor. The sensor consists of two multimode step index fibers and a mirror. The output light intensity from the receiving fiber is measured as a function of displacement of th ...
Optical losses
... The term launching loss refers to an optical fiber not being able to propagate all the incoming light rays from an optical source. These occur during the process of coupling light into the fiber (e.g., losses at the interface stages). Rays launched outside the angle of acceptance excite only dissipa ...
... The term launching loss refers to an optical fiber not being able to propagate all the incoming light rays from an optical source. These occur during the process of coupling light into the fiber (e.g., losses at the interface stages). Rays launched outside the angle of acceptance excite only dissipa ...
Parallel Optic Technology - Accu-Tech
... Duplex fiber serial transmission with a directly modulated 850 nm vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) has been used to date for data rates up to 10G. Duplex fiber serial transmission becomes impractical at data rates beyond 16G due to reliability concerns when the VCSEL is directly modula ...
... Duplex fiber serial transmission with a directly modulated 850 nm vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) has been used to date for data rates up to 10G. Duplex fiber serial transmission becomes impractical at data rates beyond 16G due to reliability concerns when the VCSEL is directly modula ...
FOC-Measurements
... When the wavelength is much smaller than the cut-off wavelength, then both, the first mode and the next higher order get excited in the fiber and both are far from cut-off. So both the modes are well guided and there is not much loss in the fiber. As the wavelength increases, the higher order mode a ...
... When the wavelength is much smaller than the cut-off wavelength, then both, the first mode and the next higher order get excited in the fiber and both are far from cut-off. So both the modes are well guided and there is not much loss in the fiber. As the wavelength increases, the higher order mode a ...
Localization & Rectification of Optical Fiber
... PRINCIPLE OF OPTICAL FIBER An optical fiber is a cylindrical dielectric waveguide (nonconducting waveguide) that transmits light along its axis, by the process of total internal reflection. The fiber consists of a core dielectric materials.To confine the optical signal in the core,the refrative ind ...
... PRINCIPLE OF OPTICAL FIBER An optical fiber is a cylindrical dielectric waveguide (nonconducting waveguide) that transmits light along its axis, by the process of total internal reflection. The fiber consists of a core dielectric materials.To confine the optical signal in the core,the refrative ind ...
part 1 - general
... A. The Industrial Fast Ethernet switch with fiber optical transceiver system shall be an MC2504T/1FM / MC250-4T/1FS module. B. The module shall support the transmission of 1channel of 100 Mbps over a multimode / single mode fiber. C. The module shall support the Ethernet data IEEE 802.3 protocol usi ...
... A. The Industrial Fast Ethernet switch with fiber optical transceiver system shall be an MC2504T/1FM / MC250-4T/1FS module. B. The module shall support the transmission of 1channel of 100 Mbps over a multimode / single mode fiber. C. The module shall support the Ethernet data IEEE 802.3 protocol usi ...
Modes in Optical Fibers
... The diameter of the laser beam incident on the lens can be determined by d = do*(1+(zΦ+do)2)1/2 where Φ is the angle of divergence ( ≈1.3 mrad) z is the laser to lens distance. d1 is otherwise approximately given by, d1 = 2a [.65 + 1.619/V1.5 + 2.879/V6] Focal point Laser ...
... The diameter of the laser beam incident on the lens can be determined by d = do*(1+(zΦ+do)2)1/2 where Φ is the angle of divergence ( ≈1.3 mrad) z is the laser to lens distance. d1 is otherwise approximately given by, d1 = 2a [.65 + 1.619/V1.5 + 2.879/V6] Focal point Laser ...
Raman tailored photonic-crystal-fiber for telecom band photon
... future quantum communication networks. Indeed, glass fibers are widely investigated for various nonlinear applications [4]. They can exhibit very low absorption, strong confinement over long distance and high nonlinearities according to the chosen glass. Moreover, the various design parameters in mi ...
... future quantum communication networks. Indeed, glass fibers are widely investigated for various nonlinear applications [4]. They can exhibit very low absorption, strong confinement over long distance and high nonlinearities according to the chosen glass. Moreover, the various design parameters in mi ...
Optical fiber

An optical fiber (or optical fibre) is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than wire cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with lesser amounts of loss; in addition, fibers are also immune to electromagnetic interference, a problem which metal wires suffer from excessively. Fibers are also used for illumination, and are wrapped in bundles so that they may be used to carry images, thus allowing viewing in confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, some of them being fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers.Optical fibers typically include a transparent core surrounded by a transparent cladding material with a lower index of refraction. Light is kept in the core by the phenomenon of total internal reflection which causes the fiber to act as a waveguide. Fibers that support many propagation paths or transverse modes are called multi-mode fibers (MMF), while those that support a single mode are called single-mode fibers (SMF). Multi-mode fibers generally have a wider core diameter and are used for short-distance communication links and for applications where high power must be transmitted. Single-mode fibers are used for most communication links longer than 1,000 meters (3,300 ft).An important aspect of a fiber optic communication is that of extension of the fiber optic cables such that the losses brought about by joining two different cables is kept to a minimum. Joining lengths of optical fiber often proves to be more complex than joining electrical wire or cable and involves careful cleaving of the fibers, perfect alignment of the fiber cores, and the splicing of these aligned fiber cores. For applications that demand a permanent connection a mechanical splice which holds the ends of the fibers together mechanically could be used or a fusion splice that uses heat to fuse the ends of the fibers together could be used. Temporary or semi-permanent connections are made by means of specialized optical fiber connectors.The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of optical fibers is known as fiber optics.