Micro_1b, Microscopy Overview, part 1b
... Specimens for Electron Backscattered Diffraction (EBSD) analysis or Orientation Imaging Microscopy (OIM) may require special specimen preparation methods. This will be discussed latter. ...
... Specimens for Electron Backscattered Diffraction (EBSD) analysis or Orientation Imaging Microscopy (OIM) may require special specimen preparation methods. This will be discussed latter. ...
L13-B_Micro_1b
... Specimens for Electron Backscattered Diffraction (EBSD) analysis or Orientation Imaging Microscopy (OIM) may require special specimen preparation methods. This will be discussed latter. ...
... Specimens for Electron Backscattered Diffraction (EBSD) analysis or Orientation Imaging Microscopy (OIM) may require special specimen preparation methods. This will be discussed latter. ...
Practice Problem Set #6
... 1. Write balanced chemical equations for the reaction of hydrogen gas with oxygen, chlorine, and nitrogen. 2. Write a balanced chemical equation for the preparation of H2 (and CO) by the reaction of CH4 and water. Using a table of thermodynamic data, calculate ∆H°, ∆G°, and ∆S° for this reaction. ...
... 1. Write balanced chemical equations for the reaction of hydrogen gas with oxygen, chlorine, and nitrogen. 2. Write a balanced chemical equation for the preparation of H2 (and CO) by the reaction of CH4 and water. Using a table of thermodynamic data, calculate ∆H°, ∆G°, and ∆S° for this reaction. ...
Secondary Ion-Mass Spectroscopy (SIMS)
... respect to the A rods, and RF field is phase shifted by 180. Ions travel down the quadrupole between the rods. Only ions of a certain mass-to-charge ratio m/z will reach the detector for a given ratio of voltages: other ions have unstable trajectories and will collide with the rods. This permit ...
... respect to the A rods, and RF field is phase shifted by 180. Ions travel down the quadrupole between the rods. Only ions of a certain mass-to-charge ratio m/z will reach the detector for a given ratio of voltages: other ions have unstable trajectories and will collide with the rods. This permit ...
MISE - Physical Basis of Chemistry
... Up to now, we’ve been talking about relative atomic weights and we have been working in ratio - using the “triangle”. Since individual weights appear in the periodic table, there has to be a mass standard, i.e., a reference mass - so that the ratio of atomic weights can become individual values. Sin ...
... Up to now, we’ve been talking about relative atomic weights and we have been working in ratio - using the “triangle”. Since individual weights appear in the periodic table, there has to be a mass standard, i.e., a reference mass - so that the ratio of atomic weights can become individual values. Sin ...
Damage in hydrogen plasma implanted silicon
... 共4兲 The ion energy distribution is broad due to multiple ion species as well as the low-energy component arising from the nonzero rise and fall times of the sample voltage pulse. In general, a surface dislocation density of less than 50 cm⫺2 is desired in a production environment.1 Hence, damage in ...
... 共4兲 The ion energy distribution is broad due to multiple ion species as well as the low-energy component arising from the nonzero rise and fall times of the sample voltage pulse. In general, a surface dislocation density of less than 50 cm⫺2 is desired in a production environment.1 Hence, damage in ...
Page 1 MISE - Physical Basis of Chemistry First Set of Problems
... (2c) Through painstaking labor - and some luck - you determine that the atomic weight of Z (relative to unity for hydrogen) is about 32. Using this value for the atomic weight of Z, determine the atomic weight of X. Referring to a modern periodic table of the elements (which also lists hydrogen with ...
... (2c) Through painstaking labor - and some luck - you determine that the atomic weight of Z (relative to unity for hydrogen) is about 32. Using this value for the atomic weight of Z, determine the atomic weight of X. Referring to a modern periodic table of the elements (which also lists hydrogen with ...
Homework 1 - Devin Gatherwright IET 307 Portfolio
... 1. What is metallic bonding? How is it formed? What are its characteristics? Answer: According to our Materials Science textbook, metallic bonding can be defined as a “primary interatomic bond that involves the non-directional sharing of valence electrons that are shared mutually between all atoms i ...
... 1. What is metallic bonding? How is it formed? What are its characteristics? Answer: According to our Materials Science textbook, metallic bonding can be defined as a “primary interatomic bond that involves the non-directional sharing of valence electrons that are shared mutually between all atoms i ...
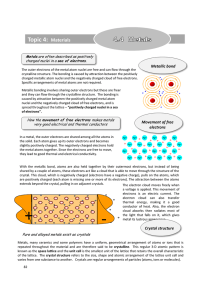
Topic 4: Materials - Education Umbrella
... extends beyond the crystal, pulling in on adjacent crystals. The electron cloud moves freely when ...
... extends beyond the crystal, pulling in on adjacent crystals. The electron cloud moves freely when ...
Microscopy with Electron Diffraction Overview
... • Since the diffraction zone is shallow, the specimen surface must no be obscured by: ...
... • Since the diffraction zone is shallow, the specimen surface must no be obscured by: ...
Inorganic Analysis Methods - Armstrong State University
... Six Techniques • Six main techniques are available to forensic scientists for determining the elemental composition of materials: – Emission spectroscopy – Inductively coupled plasma – Atomic absorption spectrophotometry – Neutron activation analysis – X-ray diffraction – X-ray Fluorescence ...
... Six Techniques • Six main techniques are available to forensic scientists for determining the elemental composition of materials: – Emission spectroscopy – Inductively coupled plasma – Atomic absorption spectrophotometry – Neutron activation analysis – X-ray diffraction – X-ray Fluorescence ...
ch6 - ChemistryVCE
... Both metallic and ionic lattices do contain positive ions in a regular arrangement. In a metallic lattice, the positive ions are surrounded by delocalised electrons; in an ionic lattice, negative ions alternate with the positive ions. Agree. In a metallic lattice, each positive ion attracts the delo ...
... Both metallic and ionic lattices do contain positive ions in a regular arrangement. In a metallic lattice, the positive ions are surrounded by delocalised electrons; in an ionic lattice, negative ions alternate with the positive ions. Agree. In a metallic lattice, each positive ion attracts the delo ...
the Language of Chemistry
... 3. Four atoms of hydrogen combine with one atom of carbon to form a molecule of methane (CH4). Hence, the valency of carbon is 4. 4. The valency of noble gas is zero as they do not undergo chemical reactions under normal conditions. Modern definition of valency ...
... 3. Four atoms of hydrogen combine with one atom of carbon to form a molecule of methane (CH4). Hence, the valency of carbon is 4. 4. The valency of noble gas is zero as they do not undergo chemical reactions under normal conditions. Modern definition of valency ...
the effect of a magnetic field on the her, the ph
... The electrodeposition of less noble metals is usually overlapped by the reduction of hydrogen ions. This leads to an increase of the pH value in front of the electrode surface which can result in spontaneous formation of hydroxides. This changes the deposition behaviour, the morphology and the prope ...
... The electrodeposition of less noble metals is usually overlapped by the reduction of hydrogen ions. This leads to an increase of the pH value in front of the electrode surface which can result in spontaneous formation of hydroxides. This changes the deposition behaviour, the morphology and the prope ...
ionization 12.3.1
... and electronic states and the electron has zero potential and kinetic energy. Electron energy The potential difference through which electrons are accelerated before they are used to bring about electron ionization. Fast atom bombardment ionization This term refers to the ionization of any species b ...
... and electronic states and the electron has zero potential and kinetic energy. Electron energy The potential difference through which electrons are accelerated before they are used to bring about electron ionization. Fast atom bombardment ionization This term refers to the ionization of any species b ...
Final Exam - Dawson College
... Condensed ground-state electron configuration is [Ne] 3s23p2 The period 4 member whose (2-) ion is isoelectronic with Kr A transition metal ion with a charge of 1+ having 5 unpaired “4d” electrons The element with the highest first ionization energy in period 4 The excited electron configuration is ...
... Condensed ground-state electron configuration is [Ne] 3s23p2 The period 4 member whose (2-) ion is isoelectronic with Kr A transition metal ion with a charge of 1+ having 5 unpaired “4d” electrons The element with the highest first ionization energy in period 4 The excited electron configuration is ...
Chemistry and Material Science 1. Physical Properties of Materials
... The Secondary/ van der Waals bond The major source of cohesion in a given engineering material is one or more of the three primary bonds just covered. Typical primary bond energies range from 200-700 kJ/mol. Secondary/ van der Waals bonding – some atomic bonding without electron transfer or shar ...
... The Secondary/ van der Waals bond The major source of cohesion in a given engineering material is one or more of the three primary bonds just covered. Typical primary bond energies range from 200-700 kJ/mol. Secondary/ van der Waals bonding – some atomic bonding without electron transfer or shar ...
Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)
... The name of the technique arises from the quantum mechanical tunnelling-type mechanism by which the electrons can move between the tip and substrate. Quantum mechanical tunnelling permits particles to tunnel through a potential barrier which they could not surmount according to the classical laws o ...
... The name of the technique arises from the quantum mechanical tunnelling-type mechanism by which the electrons can move between the tip and substrate. Quantum mechanical tunnelling permits particles to tunnel through a potential barrier which they could not surmount according to the classical laws o ...
Plasma ion-assisted deposition coating system
... external to the ion source which allows for independent or automated control of the ion energy and flux. The energy and flux of ions is composed of neutral atoms which allow either insulating or conducting targets to be sputtered directly onto the substrate; this allows for a wide range of coating o ...
... external to the ion source which allows for independent or automated control of the ion energy and flux. The energy and flux of ions is composed of neutral atoms which allow either insulating or conducting targets to be sputtered directly onto the substrate; this allows for a wide range of coating o ...
Surface Characterization by Spectroscopy and Microscopy
... The surface can be mapped, by moving the primary beam across the surface in a raster patter of measured increments and observing changes in the secondary beam. A beam of ions from an ion gun is used to etch a hole in the surface by sputtering. During this process a finer primary beam is used to ...
... The surface can be mapped, by moving the primary beam across the surface in a raster patter of measured increments and observing changes in the secondary beam. A beam of ions from an ion gun is used to etch a hole in the surface by sputtering. During this process a finer primary beam is used to ...
resonant material processing using (ultra-)short
... resonantly (i.e. with a frequency that is specific to said material) these modes create standing waves leading to a local increase or decrease of the electromagnetic field on the surface. Hills are represented by nodes, valleys by antinodes. The emerging structures have dimensions which are in the o ...
... resonantly (i.e. with a frequency that is specific to said material) these modes create standing waves leading to a local increase or decrease of the electromagnetic field on the surface. Hills are represented by nodes, valleys by antinodes. The emerging structures have dimensions which are in the o ...
Chapter 8 An Introduction to Optical Atomic Spectroscopy
... No Po where, Nj = number of atoms in an excited state No = number of atoms ground state k = Boltzmann constant (1.38 x 10-23J/K) T = temperature in Kelvin Ej = energy difference in joules between Nj and No Pj and Po = statistical factors depend on quantum level ...
... No Po where, Nj = number of atoms in an excited state No = number of atoms ground state k = Boltzmann constant (1.38 x 10-23J/K) T = temperature in Kelvin Ej = energy difference in joules between Nj and No Pj and Po = statistical factors depend on quantum level ...
Radioactive isotopes in solid state physics
... Doping of semiconductors Progress in semiconductor technology is driven by two requirements: Developing new materials with unique optical or electrical features and reducing the size of the individual constituents of an integrated device. These requirements demand a thorough understanding and contro ...
... Doping of semiconductors Progress in semiconductor technology is driven by two requirements: Developing new materials with unique optical or electrical features and reducing the size of the individual constituents of an integrated device. These requirements demand a thorough understanding and contro ...
History of Vacuum Deposition Using Energetic Ions of Condensable
... Arc plasmas and arc vaporization has a long history preceding even the invention of the voltaic pile by Volta (1800) [21]. Bradley used an arc between two carbon rod electrodes in vacuum to deposit thin carbon films in 1954 [22]. In Russia, stable long-lived cathodic continuous arc vaporization from ...
... Arc plasmas and arc vaporization has a long history preceding even the invention of the voltaic pile by Volta (1800) [21]. Bradley used an arc between two carbon rod electrodes in vacuum to deposit thin carbon films in 1954 [22]. In Russia, stable long-lived cathodic continuous arc vaporization from ...
Atom probe

The atom probe was introduced at the 14th International Field Emission Symposium in 1967 by Erwin W. Müller and John Panitz. For the first time an instrument could “... determine the nature of one single atom seen on a metal surface and selected from neighboring atoms at the discretion of the observer”. Erwin Wilhelm Müller, J. A. Panitz, and S. Brooks McLane. The atom probe is closely related to the field ion microscope, the first microscopic instrument capable of atomic resolution, developed in 1951 by Erwin Wilhelm Müller.Atom probes are unlike conventional optical or electron microscopes, in that the magnification effect comes from the magnification provided by a highly curved electric field, rather than by the manipulation of radiation paths. The method is destructive in nature removing ions from a sample surface in order to image and identify them, generating magnifications sufficient to observe individual atoms as they are removed from the sample surface. Through coupling of this magnification method with time of flight mass spectrometry, ions evaporated by application of electric pulses can have their mass-to-charge ratio computed.Through successive evaporation of material, layers of atoms are removed from a specimen, allowing for probing not only of the surface, but also through the material itself. Computer methods are utilised to rebuild a three-dimensional view of the sample, prior to it being evaporated, providing atomic scale information on the structure of a sample, as well as providing the type atomic species information. The instrument allows the three-dimensional reconstruction of up to billions of atoms from a sharp tip (corresponding to specimen volumes of 10,000-10,000,000 nm3).