Semiconductor Basics
... longer) its resistance would also increase. Likewise, if we increased its diameter (making it fatter) its resistance would then decrease. So we want to be able to define the material in such a way as to indicate its ability to either conduct or oppose the flow of electrical current through it no mat ...
... longer) its resistance would also increase. Likewise, if we increased its diameter (making it fatter) its resistance would then decrease. So we want to be able to define the material in such a way as to indicate its ability to either conduct or oppose the flow of electrical current through it no mat ...
Preview to Mole Activity #2 preview_to_mole_activity_21
... A long time ago chemists discovered what you just discovered by answering question 8. If they were talking about the mass of one atom of an element they talked about its mass in amu’s. This was not very helpful as most often they were dealing with many more atoms than just one or two. What they foun ...
... A long time ago chemists discovered what you just discovered by answering question 8. If they were talking about the mass of one atom of an element they talked about its mass in amu’s. This was not very helpful as most often they were dealing with many more atoms than just one or two. What they foun ...
Metallic Crystal Structure
... All elements can exist as solids, liquids, or gases depending up on the conditions of temperature and pressure that in. Solid materials may be classified according to the regularity with which atoms or ions are arranged with respect to one another. A crystalline material is one in which the atoms ar ...
... All elements can exist as solids, liquids, or gases depending up on the conditions of temperature and pressure that in. Solid materials may be classified according to the regularity with which atoms or ions are arranged with respect to one another. A crystalline material is one in which the atoms ar ...
Period #2 Notes: Electronic Structure of Atoms
... positive side with relatively few electrons, and a negative side with relatively many electrons. The inter-attraction between the opposite poles of different molecules is called van der Waals bonding. Usually, the strength of such bonds is very small relative to the strengths of the primary bonds. A ...
... positive side with relatively few electrons, and a negative side with relatively many electrons. The inter-attraction between the opposite poles of different molecules is called van der Waals bonding. Usually, the strength of such bonds is very small relative to the strengths of the primary bonds. A ...
Nylon+and+the+Atomic+bomb+have+a+surprising+number+of+
... a day to day basis. It is used most commonly in “clothing, laces, toothbrushes, strings on musical instruments, sails, fish nets, carpets, and other products requiring strong lightweight fibers” (Schmittroth 756). The Atomic Bomb, however, is used only in the most serious times of war because of it ...
... a day to day basis. It is used most commonly in “clothing, laces, toothbrushes, strings on musical instruments, sails, fish nets, carpets, and other products requiring strong lightweight fibers” (Schmittroth 756). The Atomic Bomb, however, is used only in the most serious times of war because of it ...
Covalent Bonds
... • Both atoms have very high ionization energies so neither atom will be able to take valence electrons completely off the other…they will share them • Because no electrons are transferred, there are no ...
... • Both atoms have very high ionization energies so neither atom will be able to take valence electrons completely off the other…they will share them • Because no electrons are transferred, there are no ...
Chemistry 1 Lectures
... Electron pairs align at 0, 120, and 360º around the central atom, A # of atoms bonded to central atom ...
... Electron pairs align at 0, 120, and 360º around the central atom, A # of atoms bonded to central atom ...
Weak Interactions
... Ice crystallizes in many polymorphic forms (12 crystal structures and 2 amorphous forms known)- we consider one form here ...
... Ice crystallizes in many polymorphic forms (12 crystal structures and 2 amorphous forms known)- we consider one form here ...
PROJECT CLIL
... In semiconductors there are two types of current. The first type of current is the classic electric current drift current, the second one happens for the phenomenon of the spread electrical worker. ...
... In semiconductors there are two types of current. The first type of current is the classic electric current drift current, the second one happens for the phenomenon of the spread electrical worker. ...
chapter11 Paramagnetism and Diamagnetism
... Classical theory of paramagnetism In 1905, Langevin also tried to explain paramagnetism qualitatively. He assumed that paramagnetic materials have molecules or atoms with the same non-zero net magnetic moment µ. In the absence of magnetic field, these atomic moments point at random and cancel one a ...
... Classical theory of paramagnetism In 1905, Langevin also tried to explain paramagnetism qualitatively. He assumed that paramagnetic materials have molecules or atoms with the same non-zero net magnetic moment µ. In the absence of magnetic field, these atomic moments point at random and cancel one a ...
physical setting chemistry
... Base your answers to questions 76 and 77 on the information below. Archimedes (287–212 BC), a Greek inventor and mathematician, made several discoveries important to science today. According to a legend, Hiero, the king of Syracuse, commanded Archimedes to find out if the royal crown was made of go ...
... Base your answers to questions 76 and 77 on the information below. Archimedes (287–212 BC), a Greek inventor and mathematician, made several discoveries important to science today. According to a legend, Hiero, the king of Syracuse, commanded Archimedes to find out if the royal crown was made of go ...
Materials on an Atomic Level
... type of dislocation is when the edge of an extra plane of atoms terminates within the crystal. This is termed an edge dislocation. The line at which the edge terminates is termed the dislocation line. Another type of dislocation, called a screw dislocation, exists, which may be thought of as being f ...
... type of dislocation is when the edge of an extra plane of atoms terminates within the crystal. This is termed an edge dislocation. The line at which the edge terminates is termed the dislocation line. Another type of dislocation, called a screw dislocation, exists, which may be thought of as being f ...
On-surface photo-dissociation of C
... All calculations are based on density functional theory (DFT). The adsorption of DBT molecules on a Au(111) surface was modelled by using the recent Van der Waals density functional vdW-DF2C09x 4 which has been proven to give the best performance for the adsorption distances of graphene on metal sur ...
... All calculations are based on density functional theory (DFT). The adsorption of DBT molecules on a Au(111) surface was modelled by using the recent Van der Waals density functional vdW-DF2C09x 4 which has been proven to give the best performance for the adsorption distances of graphene on metal sur ...
compound having protonated forms of ethylenediaminetetraacetate
... atom by the N(9) donor (as mono-dentate) [1,3,4,7,9,10] or in a m-N(3),N(9) bridging mode (oligomers) [2,5,6,8]. Such coordination modes in non-substituted adenine species are understood on the basis that the N(9) donor atom is the most basic among its five nitrogen atoms, followed by N(1) [1]. Inte ...
... atom by the N(9) donor (as mono-dentate) [1,3,4,7,9,10] or in a m-N(3),N(9) bridging mode (oligomers) [2,5,6,8]. Such coordination modes in non-substituted adenine species are understood on the basis that the N(9) donor atom is the most basic among its five nitrogen atoms, followed by N(1) [1]. Inte ...
Ionizing Systems
... Static electricity in industrial applications can be reduced or eliminated through increased air humidity, soaking, flame treatment or through ionizers. Haug specialises in the manufacture of ionization systems and produces devices, in Switzerland and Germany, for eliminating static electricity as w ...
... Static electricity in industrial applications can be reduced or eliminated through increased air humidity, soaking, flame treatment or through ionizers. Haug specialises in the manufacture of ionization systems and produces devices, in Switzerland and Germany, for eliminating static electricity as w ...
Disordered Structures Lecture 1, Part 1
... • Statistical description of atomic positions • Describes important features of the structure as an input to theories for physical properties • Image analysis of optical or electron microscopy pictures • Scattering experiments (see next lecture) • Convenient for amorphous materials and for compariso ...
... • Statistical description of atomic positions • Describes important features of the structure as an input to theories for physical properties • Image analysis of optical or electron microscopy pictures • Scattering experiments (see next lecture) • Convenient for amorphous materials and for compariso ...
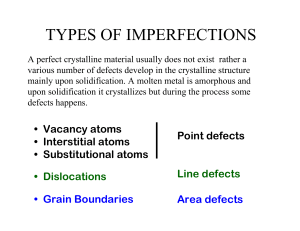
TYPES OF IMPERFECTIONS
... Remarks regarding interstitial solid solutions: •The atomic radius of an interstitial atom must be substantially smaller than that of the host atom. •Metallic materials that have relatively high atomic packing factors crystal structures, the interstitial positions are relatively small. •Normally th ...
... Remarks regarding interstitial solid solutions: •The atomic radius of an interstitial atom must be substantially smaller than that of the host atom. •Metallic materials that have relatively high atomic packing factors crystal structures, the interstitial positions are relatively small. •Normally th ...
Atomic Structure and Crystal Structure File
... • The upper limit of optical microscope ~2000x. • but, some structural elements are too fine/small. • need higher magnification • An image of the structure under investigation is formed using beams of electrons instead of light radiation. • The surface of a specimen to be examined is scanned with an ...
... • The upper limit of optical microscope ~2000x. • but, some structural elements are too fine/small. • need higher magnification • An image of the structure under investigation is formed using beams of electrons instead of light radiation. • The surface of a specimen to be examined is scanned with an ...
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
... The SEM is a very versatile technique that can be used to image at higher resolution and deeper DOF than a light microscope. The SEM has many imaging modes making it useful for many purposes. Electron interaction volume increases with an increase in angle of incidence, accelerating voltage, and a de ...
... The SEM is a very versatile technique that can be used to image at higher resolution and deeper DOF than a light microscope. The SEM has many imaging modes making it useful for many purposes. Electron interaction volume increases with an increase in angle of incidence, accelerating voltage, and a de ...
Faculty Mentor: Dr. Robert Ryan Project Supervisor: Dr. George
... electrical energy into mechanical energy (piezoelectric in ferroelectric materials) and conversion of magnetic energy into mechanical energy (magnetostriction in ferromagnetic materials) to create multiferroic composite materials. In multiferroic composite materials, indirect coupling between electr ...
... electrical energy into mechanical energy (piezoelectric in ferroelectric materials) and conversion of magnetic energy into mechanical energy (magnetostriction in ferromagnetic materials) to create multiferroic composite materials. In multiferroic composite materials, indirect coupling between electr ...
Scott Lascelle Bill Davis Nanomaterials Workshop University of
... smaller units, with the ultimate goal to be able to visualize an individual ...
... smaller units, with the ultimate goal to be able to visualize an individual ...
Periodic Table Test – Study Guide What state of matter are almost all
... Define ionization energy. Amount of energy required to remove an electron Define electronegativity. Ability for an atom to attract electrons in a bond Which one is larger? Na or Li ...
... Define ionization energy. Amount of energy required to remove an electron Define electronegativity. Ability for an atom to attract electrons in a bond Which one is larger? Na or Li ...
LxxB, Overview of Microscopy methods, part b
... Specimens for Electron Backscattered Diffraction (EBSD) analysis or Orientation Imaging Microscopy (OIM) may require special specimen preparation methods. This will be discussed latter. ...
... Specimens for Electron Backscattered Diffraction (EBSD) analysis or Orientation Imaging Microscopy (OIM) may require special specimen preparation methods. This will be discussed latter. ...
AP Chemistry MC Review Questions
... (D) Neutrons and protons in atoms have nearly equal mass. (E) The positive charge of an atom is concentrated in a small region. 23. _____The emission spectrum of hydrogen consists of several series of sharp emission lines in the ultraviolet (Lyman series) in the visible (Balmer series) and in the in ...
... (D) Neutrons and protons in atoms have nearly equal mass. (E) The positive charge of an atom is concentrated in a small region. 23. _____The emission spectrum of hydrogen consists of several series of sharp emission lines in the ultraviolet (Lyman series) in the visible (Balmer series) and in the in ...
Flexbook - Ions and Ion Formation
... The magnesium atom has two electrons in the outermost energy level. When those two are removed, the resulting Mg2+ ion has the same electron configuration as neon does, but it is smaller than neon because the magnesium ion has two more protons in the nucleus. The first two ionization energies for ma ...
... The magnesium atom has two electrons in the outermost energy level. When those two are removed, the resulting Mg2+ ion has the same electron configuration as neon does, but it is smaller than neon because the magnesium ion has two more protons in the nucleus. The first two ionization energies for ma ...
Atom probe

The atom probe was introduced at the 14th International Field Emission Symposium in 1967 by Erwin W. Müller and John Panitz. For the first time an instrument could “... determine the nature of one single atom seen on a metal surface and selected from neighboring atoms at the discretion of the observer”. Erwin Wilhelm Müller, J. A. Panitz, and S. Brooks McLane. The atom probe is closely related to the field ion microscope, the first microscopic instrument capable of atomic resolution, developed in 1951 by Erwin Wilhelm Müller.Atom probes are unlike conventional optical or electron microscopes, in that the magnification effect comes from the magnification provided by a highly curved electric field, rather than by the manipulation of radiation paths. The method is destructive in nature removing ions from a sample surface in order to image and identify them, generating magnifications sufficient to observe individual atoms as they are removed from the sample surface. Through coupling of this magnification method with time of flight mass spectrometry, ions evaporated by application of electric pulses can have their mass-to-charge ratio computed.Through successive evaporation of material, layers of atoms are removed from a specimen, allowing for probing not only of the surface, but also through the material itself. Computer methods are utilised to rebuild a three-dimensional view of the sample, prior to it being evaporated, providing atomic scale information on the structure of a sample, as well as providing the type atomic species information. The instrument allows the three-dimensional reconstruction of up to billions of atoms from a sharp tip (corresponding to specimen volumes of 10,000-10,000,000 nm3).