WEEK 1 PROBLEMS Problems From Chapter 1
... 1.6 A mutation isolated in the bacterium discussed· in Problem 19 affects one of the enzymes in the pathway shown, but it is not known which step (A, B, or C) is blocked. The final product Z of the pathway is essential for growth. When mutant cells are placed in cultures lacking Z, they cannot grow. ...
... 1.6 A mutation isolated in the bacterium discussed· in Problem 19 affects one of the enzymes in the pathway shown, but it is not known which step (A, B, or C) is blocked. The final product Z of the pathway is essential for growth. When mutant cells are placed in cultures lacking Z, they cannot grow. ...
ppt - eweb.furman.edu
... - histone deacetylases (HDAC’s) remove acetyl groups from lysine amino acids in the histone proteins – this causes the histones to bind DNA more tightly, inhibiting polymerases. - by Inhibiting HDAC’s, histones are relaxed – genes can turn on Queen. - So, although 10-HDA is not a methylation inhib ...
... - histone deacetylases (HDAC’s) remove acetyl groups from lysine amino acids in the histone proteins – this causes the histones to bind DNA more tightly, inhibiting polymerases. - by Inhibiting HDAC’s, histones are relaxed – genes can turn on Queen. - So, although 10-HDA is not a methylation inhib ...
Gene Section AF4p12 (ALL1 fused gene from chromosome 4p12)
... Laboratoire d'Hématologie et de cytogénétique, Hôpital Ed Herriot and INSERM U590, Lyon, France Published in Atlas Database: October 2005 Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Genes/AF4q12ID42970ch4p12.html ...
... Laboratoire d'Hématologie et de cytogénétique, Hôpital Ed Herriot and INSERM U590, Lyon, France Published in Atlas Database: October 2005 Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Genes/AF4q12ID42970ch4p12.html ...
Biology First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... An Austrian monk and botanist who established key principles for the study of genetics; the father of genetics ...
... An Austrian monk and botanist who established key principles for the study of genetics; the father of genetics ...
Slide 1
... In the heterozygous individual there may be some observed difference, e.g. Manx (tailless) cats. Even when dominant the lethal gene may be passed on if it does not have onset until after reproductive age (e.g. Huntington’s). ...
... In the heterozygous individual there may be some observed difference, e.g. Manx (tailless) cats. Even when dominant the lethal gene may be passed on if it does not have onset until after reproductive age (e.g. Huntington’s). ...
Chromosomes, Alleles, Genes, Mutations
... made of DNA and proteins. 4.1.2 Define gene, allele and genome. 4.1.3 Define gene mutation. 4.1.4 Explain the consequences of a base substitution mutation in relation to the processes of transcription and translation, using the example of sickle cell anemia. ...
... made of DNA and proteins. 4.1.2 Define gene, allele and genome. 4.1.3 Define gene mutation. 4.1.4 Explain the consequences of a base substitution mutation in relation to the processes of transcription and translation, using the example of sickle cell anemia. ...
Chapter 16-17 review sheet
... Exam 5 Q2 will cover: Chapter 16: ALL Chapter 17: ALL 1. This is a question – Draw out the process of transcription and translation in a cell and use text where necessary to explain drawings. Make sure every aspect is made clear from gene to folded protein including energy sources. Make sure the fol ...
... Exam 5 Q2 will cover: Chapter 16: ALL Chapter 17: ALL 1. This is a question – Draw out the process of transcription and translation in a cell and use text where necessary to explain drawings. Make sure every aspect is made clear from gene to folded protein including energy sources. Make sure the fol ...
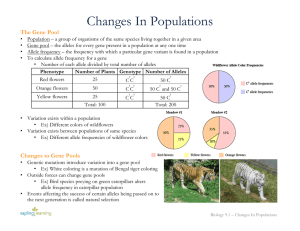
Changes In Populations
... Gene pool – the alleles for every gene present in a population at any one time Allele frequency – the frequency with which a particular gene variant is found in a population To calculate allele frequency for a gene • Number of each allele divided by total number of alleles ...
... Gene pool – the alleles for every gene present in a population at any one time Allele frequency – the frequency with which a particular gene variant is found in a population To calculate allele frequency for a gene • Number of each allele divided by total number of alleles ...
Genetics and Heredity
... • New organisms is produced from the combined DNA of TWO different cells called sex cells. – Male is called sperm & Female is called egg • Fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm unite to form a new organism with half of each parent’s DNA • Plants sexually reproduce from male and female parts of ...
... • New organisms is produced from the combined DNA of TWO different cells called sex cells. – Male is called sperm & Female is called egg • Fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm unite to form a new organism with half of each parent’s DNA • Plants sexually reproduce from male and female parts of ...
Bioinformatics
... • What is the normal function of gene Y? • What mutations have been linked to diseases A and B? • How does the mutation M alter gene function F? • What is the 3D structure of gene Y’s product? • Is gene Y expressed in condition C? • Are there any known variants of gene G? ...
... • What is the normal function of gene Y? • What mutations have been linked to diseases A and B? • How does the mutation M alter gene function F? • What is the 3D structure of gene Y’s product? • Is gene Y expressed in condition C? • Are there any known variants of gene G? ...
Lektion 12: Bio- og beregningsteknologi
... Methods of gene transfer • Micro injection of DNA in male pronucleus • Embryonic stemcells and homologue recombination • Micro injection or other forms of gene transfer into foetal cells ...
... Methods of gene transfer • Micro injection of DNA in male pronucleus • Embryonic stemcells and homologue recombination • Micro injection or other forms of gene transfer into foetal cells ...
Experience 2 Follow-up 1. Answer the following
... (red) dominant over r (orange). Gene D then determines pigment deposition, and therefore color presence or absence, with D (red or orange color) dominant over d (colorless). A red snake mates with a colorless snake. Their F1 offspring appear in the ratio of 1 red: 1 orange. Determine the genotypes o ...
... (red) dominant over r (orange). Gene D then determines pigment deposition, and therefore color presence or absence, with D (red or orange color) dominant over d (colorless). A red snake mates with a colorless snake. Their F1 offspring appear in the ratio of 1 red: 1 orange. Determine the genotypes o ...
Genetics of AHC - Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood Foundation
... mutation in a specific gene – show symptoms of the disease related to that gene. 100% Penetrance = everyone with a mutation shows symptoms of disease 50% penetrance = half of all indivuals with a muation show symptoms of disease ...
... mutation in a specific gene – show symptoms of the disease related to that gene. 100% Penetrance = everyone with a mutation shows symptoms of disease 50% penetrance = half of all indivuals with a muation show symptoms of disease ...
Genetics Objectives 15
... is transferred and fixed to a nitrocellulose or nylon filter. The filter is then washed by the probe, resulting in a labeled region where the sequence of interest lies. Note: recall that Southern blots are DNA, Northern blots are RNA, and Western blots are proteins ...
... is transferred and fixed to a nitrocellulose or nylon filter. The filter is then washed by the probe, resulting in a labeled region where the sequence of interest lies. Note: recall that Southern blots are DNA, Northern blots are RNA, and Western blots are proteins ...
Slide 1
... belonging to separate spaces of a gene, where we move from DNA to RNA to Protein to Complex Structures. Each one of these spaces has a great wealth of information, but together they allow us to see the bigger picture of how molecules from all gene spaces regulate and interact with each other. ...
... belonging to separate spaces of a gene, where we move from DNA to RNA to Protein to Complex Structures. Each one of these spaces has a great wealth of information, but together they allow us to see the bigger picture of how molecules from all gene spaces regulate and interact with each other. ...
Searching for the key to bone formation
... “Our hypothesis is based on the fact that this protein intervenes from a very early stage of bone differentiation, promoting the formation of cells that will later constitute bones in mammals. Therefore, we propose that the function of this protein is very important in determining if cells will be c ...
... “Our hypothesis is based on the fact that this protein intervenes from a very early stage of bone differentiation, promoting the formation of cells that will later constitute bones in mammals. Therefore, we propose that the function of this protein is very important in determining if cells will be c ...
Assigned exercise
... 1. Start at the NCBI Map Viewer. How many genes in the human genome contain the term "homeo" in their name? To be sure you find them all, search for "*homeo*". The asterisks are wild cards., which means that you are searching for "homeo" preceded or followed by any other characters. Number found: __ ...
... 1. Start at the NCBI Map Viewer. How many genes in the human genome contain the term "homeo" in their name? To be sure you find them all, search for "*homeo*". The asterisks are wild cards., which means that you are searching for "homeo" preceded or followed by any other characters. Number found: __ ...
File
... blood cells from either homozygous sickle-cell patients or healthy heterozygous carriers • Malaria is rarely found among carriers of this mutation • Malaria has served to maintain the otherwise deleterious sickle-cell mutation at high frequency in regions of Africa ...
... blood cells from either homozygous sickle-cell patients or healthy heterozygous carriers • Malaria is rarely found among carriers of this mutation • Malaria has served to maintain the otherwise deleterious sickle-cell mutation at high frequency in regions of Africa ...
Genes and Health
... disorder common among people of sub-Saharan African descent; the disorder protects against malaria, which is endemic in the region). Multiple sclerosis is particularly common among people of Scandinavian descent. Genes have been identified that increase the risk of certain types of breast cancer, pr ...
... disorder common among people of sub-Saharan African descent; the disorder protects against malaria, which is endemic in the region). Multiple sclerosis is particularly common among people of Scandinavian descent. Genes have been identified that increase the risk of certain types of breast cancer, pr ...
Supplementary Figure S3 (ppt 134K)
... The X-linked genes HPRT1 and KDM6A gave twice (read ratio close to 2) the number of standardised reads in female vs male DNA samples. By contrast, the remaining 32 autosomal genes gave similar read numbers from male and female samples. It is noteworthy that the outlying genes CYP2D6 and PTEN (F:M re ...
... The X-linked genes HPRT1 and KDM6A gave twice (read ratio close to 2) the number of standardised reads in female vs male DNA samples. By contrast, the remaining 32 autosomal genes gave similar read numbers from male and female samples. It is noteworthy that the outlying genes CYP2D6 and PTEN (F:M re ...