Chapter 2- Genetics
... Body cells (_____________________) divide by replicating all the parts and dividing into 2 identical cells (skin, hair, fingernails…). A copy of the DNA must be made before replication; each strand replicates and attaches at a centre point (______________). Original 2 strands of DNA (1 from ea ...
... Body cells (_____________________) divide by replicating all the parts and dividing into 2 identical cells (skin, hair, fingernails…). A copy of the DNA must be made before replication; each strand replicates and attaches at a centre point (______________). Original 2 strands of DNA (1 from ea ...
What is Genetic Engineering?
... DNA of another organism. 4)Once in the new organism, the transferred genes direct the new organism’s cells to make the same protein as the original organism. ...
... DNA of another organism. 4)Once in the new organism, the transferred genes direct the new organism’s cells to make the same protein as the original organism. ...
Lecture # 6 Date
... Punnett square: predicts the results of a genetic cross between individuals of known genotype Homozygous: pair of identical alleles for a character Heterozygous: two different alleles for a gene Phenotype: an organism’s traits Genotype: an organism’s genetic ...
... Punnett square: predicts the results of a genetic cross between individuals of known genotype Homozygous: pair of identical alleles for a character Heterozygous: two different alleles for a gene Phenotype: an organism’s traits Genotype: an organism’s genetic ...
COGENT Visual Aids
... Mutation - Any change in the DNA of a cell. Mutations may be caused by mistakes during cell division, or they may be caused by exposure to DNA-damaging agents in the environment. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or have no effect. If they occur in cells that make eggs or sperm, they can be inhe ...
... Mutation - Any change in the DNA of a cell. Mutations may be caused by mistakes during cell division, or they may be caused by exposure to DNA-damaging agents in the environment. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or have no effect. If they occur in cells that make eggs or sperm, they can be inhe ...
hinv1
... "I don't care other genes (pathways). Any disease welcome, as long as relevant to my gene (pathway)." ...
... "I don't care other genes (pathways). Any disease welcome, as long as relevant to my gene (pathway)." ...
Honors Biology Semester 1 Exam Review 2014
... Tim and Jan both have freckles (a dominant trait), but their son Michael does not. Show with a Punnett square how this is possible. If Tim and Jan have two more children, what is the probability that both of them will have freckles? ...
... Tim and Jan both have freckles (a dominant trait), but their son Michael does not. Show with a Punnett square how this is possible. If Tim and Jan have two more children, what is the probability that both of them will have freckles? ...
Bacteria - The Last Stronghold of Lamarckism?
... bacteria with highly variable shape due to absence of a cell wall. Even genetically identical bacterial cells (clones) may develop different states for a character or group of characters in different environments. We now know that some bacteria adaptively produce a protein (e.g., an inducible enzyme ...
... bacteria with highly variable shape due to absence of a cell wall. Even genetically identical bacterial cells (clones) may develop different states for a character or group of characters in different environments. We now know that some bacteria adaptively produce a protein (e.g., an inducible enzyme ...
3-8-heredity_and_environment
... about 40% of the individual differences that we observe in, say, shyness may in some way be attributable to genetic individual difference. • It does NOT mean that 40% of any person's shyness is due to his/her genes and the other 60% is due to his/her environment. ...
... about 40% of the individual differences that we observe in, say, shyness may in some way be attributable to genetic individual difference. • It does NOT mean that 40% of any person's shyness is due to his/her genes and the other 60% is due to his/her environment. ...
DNA experiments exercise
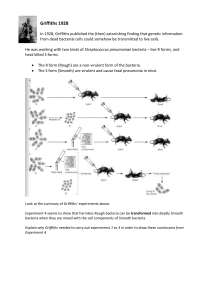
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
Genetics - MrGalusha.org
... about 40% of the individual differences that we observe in, say, shyness may in some way be attributable to genetic individual difference. • It does NOT mean that 40% of any person's shyness is due to his/her genes and the other 60% is due to his/her environment. ...
... about 40% of the individual differences that we observe in, say, shyness may in some way be attributable to genetic individual difference. • It does NOT mean that 40% of any person's shyness is due to his/her genes and the other 60% is due to his/her environment. ...
You Asked for it….. - Mr. Smith’s Science Page
... In humans, 22 pair of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes ...
... In humans, 22 pair of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes ...
Genetics study guide 2 key
... _Reginald Punnett_ developed a square that is used to visualize all the possible genotypes found in the offspring. combinations of alleles in offspring. 34. There are _23_ chromosomes found in normal sex cells in humans. Humans produce diploid cells through a process called _Mitosis_. 35. There are ...
... _Reginald Punnett_ developed a square that is used to visualize all the possible genotypes found in the offspring. combinations of alleles in offspring. 34. There are _23_ chromosomes found in normal sex cells in humans. Humans produce diploid cells through a process called _Mitosis_. 35. There are ...
Ch. 11.3 Other Patterns of Inheritance
... • Phenotypes of both alleles are completely expressed. Ex. ...
... • Phenotypes of both alleles are completely expressed. Ex. ...
Alzheimer`s Disease: effect of Tau-related genes on the
... Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in the elderly. The predominant sporadic form of AD is a genetically complex disorder probably involving a combination of genetic factors together with environmental influences. To date, the best established genetic risk factor identified ...
... Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in the elderly. The predominant sporadic form of AD is a genetically complex disorder probably involving a combination of genetic factors together with environmental influences. To date, the best established genetic risk factor identified ...
AP Biology
... 33. Is there a direct correlation between size of the genome and the complexity of the organism? ...
... 33. Is there a direct correlation between size of the genome and the complexity of the organism? ...
Aequatus User Guide
... and Core database schema. • Aequatus uses precalculated gene family information and genomic alignments data in the form of CIGAR strings, from Ensembl Compara, and cross-references these sequences to Ensembl Core databases for each species to gather genomic feature information via stable_ids. Aequat ...
... and Core database schema. • Aequatus uses precalculated gene family information and genomic alignments data in the form of CIGAR strings, from Ensembl Compara, and cross-references these sequences to Ensembl Core databases for each species to gather genomic feature information via stable_ids. Aequat ...
2) Inactivation of tumour suppressor genes
... Most frequently mutated gene in cancer (50% mutation rate in most cancers & 90% rate in SCC). It encodes a stress-regulated transcription factor that co-ordinately induces or represses sets of gene products in response to changes in the cellular microenvironment. It is involved in multiple functions ...
... Most frequently mutated gene in cancer (50% mutation rate in most cancers & 90% rate in SCC). It encodes a stress-regulated transcription factor that co-ordinately induces or represses sets of gene products in response to changes in the cellular microenvironment. It is involved in multiple functions ...
43 ppt
... Sam and his wife Maggie are concerned about the inheritance of two disease-‐ causing genes that run in their family. The two genes are 8 map units apart on the same chromosome. They are ...
... Sam and his wife Maggie are concerned about the inheritance of two disease-‐ causing genes that run in their family. The two genes are 8 map units apart on the same chromosome. They are ...
Biology
... in excess of substrate. Which of the following statement is FALSE? A. If the concentration of enzyme is increased in the above reaction mixture, X amount of maltose will be produced in less than 10 minutes. B. If the volume of starch is increased in the above reaction mixture, more than X amount of ...
... in excess of substrate. Which of the following statement is FALSE? A. If the concentration of enzyme is increased in the above reaction mixture, X amount of maltose will be produced in less than 10 minutes. B. If the volume of starch is increased in the above reaction mixture, more than X amount of ...
Set 2 - The Science Spot
... Use your knowledge of genetics to answer each question 1. What term refers to the physical appearance of a trait? Example: Yellow body color 2. What term refers to the gene that is expressed when two different genes for a trait are present in a gene pair? 3. If your grandparents are the parental ge ...
... Use your knowledge of genetics to answer each question 1. What term refers to the physical appearance of a trait? Example: Yellow body color 2. What term refers to the gene that is expressed when two different genes for a trait are present in a gene pair? 3. If your grandparents are the parental ge ...