Teacher Guide - Cleveland Museum of Natural History
... deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) - the material found primarily in a cell’s nucleus that carries the instructions for making all the structures and functions of an organism. diploid - cells containing two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent organism. dominant - an allele that expresses its ...
... deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) - the material found primarily in a cell’s nucleus that carries the instructions for making all the structures and functions of an organism. diploid - cells containing two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent organism. dominant - an allele that expresses its ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • Variegation in the color of maize kernels is caused by multiple reversions of an unstable mutation in the C locus, responsible for kernel color • Mutation and its reversion result from Ds (dissociation) element – Transposes into the C gene – Mutates it – Transposes out again, revert to wild type ...
... • Variegation in the color of maize kernels is caused by multiple reversions of an unstable mutation in the C locus, responsible for kernel color • Mutation and its reversion result from Ds (dissociation) element – Transposes into the C gene – Mutates it – Transposes out again, revert to wild type ...
PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE Gene - sequence of DNA that codes
... after the child-bearing years, in forties or so. In this case, the trait is caused by a dominant allele. Expression leads to brain and nerve deterioration and death. An individual only has to have 1 allele for this trait to be expressed. So either a homozygous dominant or a heterozygous individual w ...
... after the child-bearing years, in forties or so. In this case, the trait is caused by a dominant allele. Expression leads to brain and nerve deterioration and death. An individual only has to have 1 allele for this trait to be expressed. So either a homozygous dominant or a heterozygous individual w ...
DNA
... – The point where the DNA strands separate is called the replication fork (Y) – At the replication fork, the enzyme DNA polymerase adds bases according to the basepairing rules. – Two new DNA helixes are formed. ...
... – The point where the DNA strands separate is called the replication fork (Y) – At the replication fork, the enzyme DNA polymerase adds bases according to the basepairing rules. – Two new DNA helixes are formed. ...
X-inactivation
... Histone modification, DNA methylation and chromosome condensation Histone acetylation removes positive charge of histones – thus reduce force of attraction with DNA = open chromatin (active) ...
... Histone modification, DNA methylation and chromosome condensation Histone acetylation removes positive charge of histones – thus reduce force of attraction with DNA = open chromatin (active) ...
Review Questions
... DNA, the recipe for making proteins, never leaves the nucleus (nucleoid region in bacteria). Yet all the protein-making machinery is located out in the cytoplasm. So how does the information get to the cytoplasm? DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA. 2. What is a transcript? A transcript is not a c ...
... DNA, the recipe for making proteins, never leaves the nucleus (nucleoid region in bacteria). Yet all the protein-making machinery is located out in the cytoplasm. So how does the information get to the cytoplasm? DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA. 2. What is a transcript? A transcript is not a c ...
PowerPoint - Oregon State University
... SOD1 gene • However, the toxicity of these mutations is not due to reduced superoxide scavenging ability • Something about these mutations causes them to become toxic to cells ...
... SOD1 gene • However, the toxicity of these mutations is not due to reduced superoxide scavenging ability • Something about these mutations causes them to become toxic to cells ...
Science-Dragon Genetics - Florida Department of Education
... Direct Link: http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/exchange/waldron/dragongenetics1 This is a lab/activity that uses dragons as "research subjects" for genetics research. It highlights independent assortment as well as gene linkage. Students will do the first part of the activity using independent assortment ...
... Direct Link: http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/exchange/waldron/dragongenetics1 This is a lab/activity that uses dragons as "research subjects" for genetics research. It highlights independent assortment as well as gene linkage. Students will do the first part of the activity using independent assortment ...
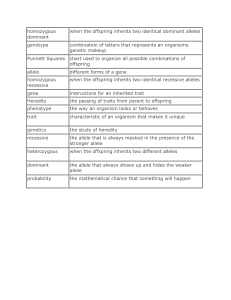
homozygous dominant when the offspring inherits two identical
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
Book 1.indb
... target loci in geographically distant populations First case of Natural genetic engineering: two genes from a wild population fall under the control of a hobo ME with resulting conjoint expression and mutations Multiple unstable insertion alleles differing in transposition rate in the germ and somat ...
... target loci in geographically distant populations First case of Natural genetic engineering: two genes from a wild population fall under the control of a hobo ME with resulting conjoint expression and mutations Multiple unstable insertion alleles differing in transposition rate in the germ and somat ...
Integrated Teaching Area (ITA) Scenarios for Semester One
... forget to discuss formation of chiasmata and crossing over. How can two genes on the same chromosome segregate independently (as described by Mendel’s first law)? Crossing over at meiosis. Two loci close together on one chromosome may segregate together as crossing over is less likely to happen betw ...
... forget to discuss formation of chiasmata and crossing over. How can two genes on the same chromosome segregate independently (as described by Mendel’s first law)? Crossing over at meiosis. Two loci close together on one chromosome may segregate together as crossing over is less likely to happen betw ...
Lecture 3: Mutations
... In 1946 Nobel Prize winner Hermann J. Muller]] (1890-1967) coined the terms amorph, hypomorph, hypermorph, antimorph and neomorph to classify mutations based on their behavior in various genetic situations. Key: In the following sections, alleles are referred to as +=wildtype, m=mutant, Df=gene dele ...
... In 1946 Nobel Prize winner Hermann J. Muller]] (1890-1967) coined the terms amorph, hypomorph, hypermorph, antimorph and neomorph to classify mutations based on their behavior in various genetic situations. Key: In the following sections, alleles are referred to as +=wildtype, m=mutant, Df=gene dele ...
Gene Switches - Science Take-Out
... food source. However, if glucose is not available and lactose (a disaccharide) is present in the environment, bacteria can survive by switching on the genes that allow them to use lactose as a food source. The structural genes in the lac operon contain the DNA code that produces three proteins. ...
... food source. However, if glucose is not available and lactose (a disaccharide) is present in the environment, bacteria can survive by switching on the genes that allow them to use lactose as a food source. The structural genes in the lac operon contain the DNA code that produces three proteins. ...
Supplementary Methods and Tables Supplementary Methods ChIP
... matrices within a group of sequences and highlight significant enrichments using a random set of sequences as a control. The main limitations of these methods are that they only explore a defined set of matrices and they require previous manipulations of raw data to identify DNA sequences bound by a ...
... matrices within a group of sequences and highlight significant enrichments using a random set of sequences as a control. The main limitations of these methods are that they only explore a defined set of matrices and they require previous manipulations of raw data to identify DNA sequences bound by a ...
Application of Biological Network
... genes to the hub proteins and the interaction of genes with others. • Fig(a) shows us a tendency of all disease genes to form hubs, where we could see the tendency for disease genes to encode proteins with hubs. • Fig(c) shows the same relationship but with only essential disease genes where the ten ...
... genes to the hub proteins and the interaction of genes with others. • Fig(a) shows us a tendency of all disease genes to form hubs, where we could see the tendency for disease genes to encode proteins with hubs. • Fig(c) shows the same relationship but with only essential disease genes where the ten ...
Genetics, evOlutionary psychology
... Heritability is the proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. Heritability may vary based on the range of populations and environments studied Adoption and twin studies have been used by behavior geneticists to determine the heritability of a trait—the extent to which ...
... Heritability is the proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. Heritability may vary based on the range of populations and environments studied Adoption and twin studies have been used by behavior geneticists to determine the heritability of a trait—the extent to which ...
Chapter 4 prenatal ppt
... 280 days from last menstrual cycle Toward end of 40 weeks baby’s weight shifts downward called “Lightening” Baby’s head drops into birth canal Most babies are born with head down If seat down or feet down this is called Breech Presentation Sometimes requires a Caesarian Birth Even thou ...
... 280 days from last menstrual cycle Toward end of 40 weeks baby’s weight shifts downward called “Lightening” Baby’s head drops into birth canal Most babies are born with head down If seat down or feet down this is called Breech Presentation Sometimes requires a Caesarian Birth Even thou ...
chapter 4 prenatal ppt
... 280 days from last menstrual cycle Toward end of 40 weeks baby’s weight shifts downward called “Lightening” Baby’s head drops into birth canal Most babies are born with head down If seat down or feet down this is called Breech Presentation Sometimes requires a Caesarian Birth Even thou ...
... 280 days from last menstrual cycle Toward end of 40 weeks baby’s weight shifts downward called “Lightening” Baby’s head drops into birth canal Most babies are born with head down If seat down or feet down this is called Breech Presentation Sometimes requires a Caesarian Birth Even thou ...
Genetics Review Game
... First group who has the correct answer will receive the point The group with the most points at the end will receive a ...
... First group who has the correct answer will receive the point The group with the most points at the end will receive a ...
Niemann-Pick disease type C
... move cholesterol and lipids within cells. Symptoms of NPC are caused by the accumulation of cholesterol and lipids, primarily in the liver and brain. NPC belongs to a group of diseases called lysosomal storage disorders1. This group includes Niemann-Pick types A and B, which are genetically and clin ...
... move cholesterol and lipids within cells. Symptoms of NPC are caused by the accumulation of cholesterol and lipids, primarily in the liver and brain. NPC belongs to a group of diseases called lysosomal storage disorders1. This group includes Niemann-Pick types A and B, which are genetically and clin ...
Chapter 7: Extending Mendelian Genetics
... genes) X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products (RNA or proteins) as males, which only possess a single copy of the X chromosome. • Abnormal amounts of gene products can be related to oncogenes ...
... genes) X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products (RNA or proteins) as males, which only possess a single copy of the X chromosome. • Abnormal amounts of gene products can be related to oncogenes ...
BB30055: Genes and genomes
... proteins (structural proteins and proteins involved in signal transduction and immune function) However, only 3 cases where a combination of 3 domain types shared by human & yeast proteins. e.g carbomyl-phosphate synthase (involved in the first 3 steps of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis) has 7 domai ...
... proteins (structural proteins and proteins involved in signal transduction and immune function) However, only 3 cases where a combination of 3 domain types shared by human & yeast proteins. e.g carbomyl-phosphate synthase (involved in the first 3 steps of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis) has 7 domai ...