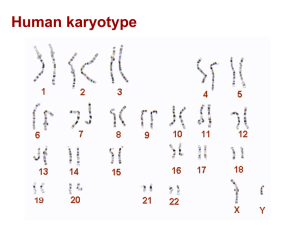
1 Sequence evolution of the disease resistance genes Rcr3 and
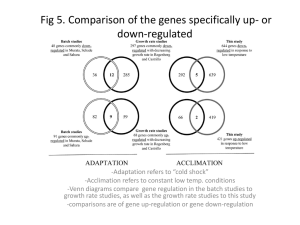
... Rcr3 is tightly integrated in its disease resistance network and therefore has to be highly conserved. Additionally, the specific interaction between Rcr3 and Cf-2 should contribute to purifying selection as well. For the Rin4 gene I reported a very low level of nucleotide diversity as well. Tests o ...
... Rcr3 is tightly integrated in its disease resistance network and therefore has to be highly conserved. Additionally, the specific interaction between Rcr3 and Cf-2 should contribute to purifying selection as well. For the Rin4 gene I reported a very low level of nucleotide diversity as well. Tests o ...
Genetic Disorders
... A group of genetic eye conditions. In the progression of symptoms that generally precedes tunnel vision by years or even decades. Many people with RP do not become legally blind until their 40s or 50s and retain some sight all their life . ...
... A group of genetic eye conditions. In the progression of symptoms that generally precedes tunnel vision by years or even decades. Many people with RP do not become legally blind until their 40s or 50s and retain some sight all their life . ...
MUTATIONS
... Mutations can change the meaning of genes • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA base sequence • Simplest mutation is a point mutation or a change in a single nucleotide that affects one codon • The triplet code has some flexibility because several different codons code for the same aa, so som ...
... Mutations can change the meaning of genes • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA base sequence • Simplest mutation is a point mutation or a change in a single nucleotide that affects one codon • The triplet code has some flexibility because several different codons code for the same aa, so som ...
• Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA base sequence
... Mutations can change the meaning of genes • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA base sequence • Simplest mutation is a point mutation or a change in a single nucleotide that affects one codon • The triplet code has some flexibility because several different codons code for the same aa, so som ...
... Mutations can change the meaning of genes • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA base sequence • Simplest mutation is a point mutation or a change in a single nucleotide that affects one codon • The triplet code has some flexibility because several different codons code for the same aa, so som ...
Detection of different genes heredity
... Sickle-Cell Disease is a genetic disorder that affects the blood. People with sickle-cell disease produce an abnormal form of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Sickle-shaped red blood cells cannot carry as much oxygen as normal-shaped cells. The allele for the sickle-cell ...
... Sickle-Cell Disease is a genetic disorder that affects the blood. People with sickle-cell disease produce an abnormal form of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Sickle-shaped red blood cells cannot carry as much oxygen as normal-shaped cells. The allele for the sickle-cell ...
Final Take-Home Exam
... b. A DNA test for Huntington's disease (HD) indicates the patient has one allele with about 50 triplet repeats and one allele with about 20 triplet repeats. 6. (12 points) A person is simultaneously heterozygous for two autosomal genetic traits. One is a recessive condition for albinism (alleles A a ...
... b. A DNA test for Huntington's disease (HD) indicates the patient has one allele with about 50 triplet repeats and one allele with about 20 triplet repeats. 6. (12 points) A person is simultaneously heterozygous for two autosomal genetic traits. One is a recessive condition for albinism (alleles A a ...
Opposing Effects Of Sodium Function Channel
... ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na ) through a cell's plasma membrane. 10. benign. 11. / the changing of the structure of a gene, resulting in a variant form that may be transmitted to subsequent generations, caused ...
... ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na ) through a cell's plasma membrane. 10. benign. 11. / the changing of the structure of a gene, resulting in a variant form that may be transmitted to subsequent generations, caused ...
Biotechnoloy :Guides for Exam 2
... B. absence of clotting factor IX C. defective protein defective beta globin D. defective muscle protein. 3. Sickle-cell disease is due to a defective beta globin. A. True. B. False. 4. In US any clinical trial for human gene therapy must be approved by A. the RAC committee B. EPA committee C. Biotec ...
... B. absence of clotting factor IX C. defective protein defective beta globin D. defective muscle protein. 3. Sickle-cell disease is due to a defective beta globin. A. True. B. False. 4. In US any clinical trial for human gene therapy must be approved by A. the RAC committee B. EPA committee C. Biotec ...
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
... they inherit it from their parents Some people are born with a characteristic that neither their mother nor their father show The reason the offspring can have this characteristic is because both their parents have heterozygous ...
... they inherit it from their parents Some people are born with a characteristic that neither their mother nor their father show The reason the offspring can have this characteristic is because both their parents have heterozygous ...
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
... 1% of all cases of Alzheimer is inherited Usually occurs over the age of 65 Caused by a mutation in the APP gene There is no cure or treatment to slow down the process of Alzheimer ...
... 1% of all cases of Alzheimer is inherited Usually occurs over the age of 65 Caused by a mutation in the APP gene There is no cure or treatment to slow down the process of Alzheimer ...
Document
... • controlled with regular infusions of the deficient clotting factor • genetically engineered factor VIII from the genes of Chinese hamster ovary cells – higher purity and safety, – extremely expensive, and – not generally available ...
... • controlled with regular infusions of the deficient clotting factor • genetically engineered factor VIII from the genes of Chinese hamster ovary cells – higher purity and safety, – extremely expensive, and – not generally available ...
12.4 Mutations
... • Changes in the number or structure of chromosomes • Can change locations of genes on chromosomes or number of copies of some genes ...
... • Changes in the number or structure of chromosomes • Can change locations of genes on chromosomes or number of copies of some genes ...
Sickle Cell Part_Natural Selection
... As discussed, Sickle Cell Disease is one of thousands of disorders caused by a single gene. Sickle-cell anemia is an autosomal, recessive human disease. It is caused by a flawed allele for a polypeptide in hemoglobin. As a result, this oxygen carrying protein in the red blood cell causes it to have ...
... As discussed, Sickle Cell Disease is one of thousands of disorders caused by a single gene. Sickle-cell anemia is an autosomal, recessive human disease. It is caused by a flawed allele for a polypeptide in hemoglobin. As a result, this oxygen carrying protein in the red blood cell causes it to have ...
here
... 1. The movie describes the action of what two enzymes? What do the enzymes do and where are they located? Be specific and include a pathway diagram. (A-B) ...
... 1. The movie describes the action of what two enzymes? What do the enzymes do and where are they located? Be specific and include a pathway diagram. (A-B) ...
Genetic disorders - narragansett.k12.ri.us
... the disease strikes people between the ages of 40 and 70, and as many as 30,000 Americans have the disease at any given time This monogenic mutation is believed to make a defective protein that is toxic to motor nerve cells. A common first symptom is a painless weakness in a hand, foot, arm or l ...
... the disease strikes people between the ages of 40 and 70, and as many as 30,000 Americans have the disease at any given time This monogenic mutation is believed to make a defective protein that is toxic to motor nerve cells. A common first symptom is a painless weakness in a hand, foot, arm or l ...
19. Positional cloning
... disease allele can be detected by PCR (Gelehrter Fig. 9-27) 10-30 copies in normal chromosomes 36-121 copies in HD chromosomes correlation between length of repeats and age of onset longer repeats is correlated with earlier age of onset = "anticipation" ethical issues such as chosing to learn ones ...
... disease allele can be detected by PCR (Gelehrter Fig. 9-27) 10-30 copies in normal chromosomes 36-121 copies in HD chromosomes correlation between length of repeats and age of onset longer repeats is correlated with earlier age of onset = "anticipation" ethical issues such as chosing to learn ones ...
Genetics 101
... without ever know it’s there. It just depends on meeting (and deciding to have kids with) someone else who also has one copy of the same mutated gene. Then there's a 1 in 4 chance that both parent will pass on this gene and have an affected child. 4. l have always wondered how an uncommon deletion c ...
... without ever know it’s there. It just depends on meeting (and deciding to have kids with) someone else who also has one copy of the same mutated gene. Then there's a 1 in 4 chance that both parent will pass on this gene and have an affected child. 4. l have always wondered how an uncommon deletion c ...
Test Information Sheet HEXA Gene Analysis in Tay
... (classic TSD) to subacute juvenile and adult onset forms with later onset and slower disease progression. Infants with classic TSD generally appear normal at birth. At 3-6 months of age motor weakness, myoclonic jerks and an exaggerated startle reaction are usually the presenting features followed b ...
... (classic TSD) to subacute juvenile and adult onset forms with later onset and slower disease progression. Infants with classic TSD generally appear normal at birth. At 3-6 months of age motor weakness, myoclonic jerks and an exaggerated startle reaction are usually the presenting features followed b ...
Projecting Human Lifespan
... and make them vulnerable to mutation and death Expanding the length of telomeres with drugs or by gene therapy may be a way of extending lifespan Am J Hum Biol 2011;23:149-67 ...
... and make them vulnerable to mutation and death Expanding the length of telomeres with drugs or by gene therapy may be a way of extending lifespan Am J Hum Biol 2011;23:149-67 ...
The National Enquirer
... both rich and poor countries. The obesity epidemic is at its height in Britain, prompting the Government’s recent decision to restrict healthcare access for the overweight. Massive increases in cancer and heart disease have also occurred in developing countries: blamed on increased tobacco marketing ...
... both rich and poor countries. The obesity epidemic is at its height in Britain, prompting the Government’s recent decision to restrict healthcare access for the overweight. Massive increases in cancer and heart disease have also occurred in developing countries: blamed on increased tobacco marketing ...
uses_lecturenotes.pdf
... 1.) Gene Testing – diagnosis and prediction of disease and disease susceptibility Currently (Summer, 2003), there are more than 900 genetic tests available. As we identify more genes associated with specific disorders, that number will grow. • Carrier screening, which involves identifying unaffected ...
... 1.) Gene Testing – diagnosis and prediction of disease and disease susceptibility Currently (Summer, 2003), there are more than 900 genetic tests available. As we identify more genes associated with specific disorders, that number will grow. • Carrier screening, which involves identifying unaffected ...