Key Area 8 Respiration
... On a show me board, in your own words, answer the following: What is respiration? ...
... On a show me board, in your own words, answer the following: What is respiration? ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... Solid nonmetals are dull and brittle, and are also poor conductors of heat and electricity. Most nonmetals are reactive, so they often form compounds. In fact, fluorine (F) is the most reactive element known. Atoms of nonmetals usually gain or share electrons. Only Group 18 of the periodic table con ...
... Solid nonmetals are dull and brittle, and are also poor conductors of heat and electricity. Most nonmetals are reactive, so they often form compounds. In fact, fluorine (F) is the most reactive element known. Atoms of nonmetals usually gain or share electrons. Only Group 18 of the periodic table con ...
Hemoglobin Learning Objective Hemoglobin
... released from Krebs cycle and other cellular processes combines with water to form carbonic acid, which dissociates into protons and bicarbonate ions. Hb which has just released its bound oxygen into the tissues acts as a buffer by binding protons and delivering them to the lungs. In the lungs, the ...
... released from Krebs cycle and other cellular processes combines with water to form carbonic acid, which dissociates into protons and bicarbonate ions. Hb which has just released its bound oxygen into the tissues acts as a buffer by binding protons and delivering them to the lungs. In the lungs, the ...
in the presence of oxygen
... • Muscles only contain enough ATP for a few seconds of intense activity ...
... • Muscles only contain enough ATP for a few seconds of intense activity ...
4.2 Cellular Respiration - Dr Rob's A
... Oxygen is also needed for cellular respiration to go to completion and produced the maximum amount of ATP ...
... Oxygen is also needed for cellular respiration to go to completion and produced the maximum amount of ATP ...
The Atomic Molecular Theory
... came from. These results are examples of a general principle known as the Law of De nite Proportions. ...
... came from. These results are examples of a general principle known as the Law of De nite Proportions. ...
Oxygen Removal in Natural Gas Systems
... water is made at low ppm levels and the after-cooler may not condense any water. There are a number of commercially available catalytic oxidation processes, some of which are described below: ...
... water is made at low ppm levels and the after-cooler may not condense any water. There are a number of commercially available catalytic oxidation processes, some of which are described below: ...
Recombinant Human Myoglobin
... It is a haemoprotein that contributes to intracellular oxygen storage and trans-cellular facilitated diffusion of oxygen. Myoglobin has a single-chain globular structure of 153 amino acids, containing a heme prosthetic group (ironcontaining porphyrin) in the core around which the remaining apoprotei ...
... It is a haemoprotein that contributes to intracellular oxygen storage and trans-cellular facilitated diffusion of oxygen. Myoglobin has a single-chain globular structure of 153 amino acids, containing a heme prosthetic group (ironcontaining porphyrin) in the core around which the remaining apoprotei ...
The Hog-Tie Position and Positional Asphyxia
... It is this author’s opinion that positional asphyxia does occur and is due to an inability of the individual to achieve the work of breathing against an inspiratory load and results in respiratory muscle fatigue and acute respiratory failure. There are many publications in the pulmonary literature ...
... It is this author’s opinion that positional asphyxia does occur and is due to an inability of the individual to achieve the work of breathing against an inspiratory load and results in respiratory muscle fatigue and acute respiratory failure. There are many publications in the pulmonary literature ...
Exercise Metabolism
... 1.Low muscle oxygen (hypoxia) = increased reliance on anaerobic metabolism 2.Accelerated glycolysis – NADH produced faster than it is shuttled into ...
... 1.Low muscle oxygen (hypoxia) = increased reliance on anaerobic metabolism 2.Accelerated glycolysis – NADH produced faster than it is shuttled into ...
reviewTWO
... How many moles of oxygen are needed to react with 0.1 mole of CH4 How many moles of CO2 are produced from 0.1 moles of CH4 How many moles of water are produced from 0.1 moles of CH4 How many moles of carbon dioxide will be produced by 0.1 mole of oxygen gas? How many moles of oxygen gas will react c ...
... How many moles of oxygen are needed to react with 0.1 mole of CH4 How many moles of CO2 are produced from 0.1 moles of CH4 How many moles of water are produced from 0.1 moles of CH4 How many moles of carbon dioxide will be produced by 0.1 mole of oxygen gas? How many moles of oxygen gas will react c ...
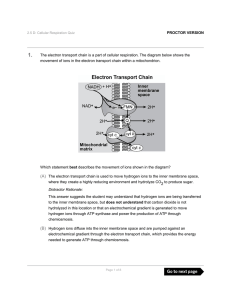
The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
... because there is not enough light available to carry out light reactions. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that the root cutting is consuming oxygen, but does not understand that carbon dioxide (not oxygen) is used during the Calvin cycle to produce sugar and tha ...
... because there is not enough light available to carry out light reactions. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that the root cutting is consuming oxygen, but does not understand that carbon dioxide (not oxygen) is used during the Calvin cycle to produce sugar and tha ...
Unit 6 Chemical Equations and Reactions Balancing Equations
... Balance the following chemical equations using coefficients 1 1Al(OH)3(s) + 3HCl (aq) → 1AlCl3 (aq) + 3H2O (l) 2. 3Fe2O3 (s) + 1CO (g) → 2Fe3O4(s) + 1CO2 (g) 3. 4FeO (s) + 1O2 (g) → 2Fe2O3 (s) 4. 2C6H6 (l) + 15O2 (g) → 12CO2 (g) + 6H2O (g) 5. 3Ca(OH)2 (aq) + 2H3PO4 (aq) → 6H2O (l) + 1Ca3(PO4)2 (s) 6 ...
... Balance the following chemical equations using coefficients 1 1Al(OH)3(s) + 3HCl (aq) → 1AlCl3 (aq) + 3H2O (l) 2. 3Fe2O3 (s) + 1CO (g) → 2Fe3O4(s) + 1CO2 (g) 3. 4FeO (s) + 1O2 (g) → 2Fe2O3 (s) 4. 2C6H6 (l) + 15O2 (g) → 12CO2 (g) + 6H2O (g) 5. 3Ca(OH)2 (aq) + 2H3PO4 (aq) → 6H2O (l) + 1Ca3(PO4)2 (s) 6 ...
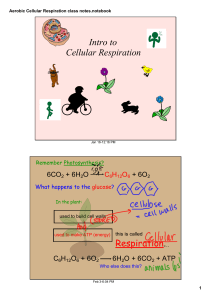
Cellular Respiration
... In the Krebs cycle, the pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA, which is broken down to form CO2, ATP, NADH, and FADH2. One ATP is produced for each pyruvate. CO2 is a byproduct. why we breathe out carbon dioxide! ...
... In the Krebs cycle, the pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA, which is broken down to form CO2, ATP, NADH, and FADH2. One ATP is produced for each pyruvate. CO2 is a byproduct. why we breathe out carbon dioxide! ...
Metabolism without Oxygen
... Fermentation of grape juice into wine produces CO2 as a byproduct. Fermentation tanks have valves so that the pressure inside the tanks created by the carbon dioxide produced can be released. ...
... Fermentation of grape juice into wine produces CO2 as a byproduct. Fermentation tanks have valves so that the pressure inside the tanks created by the carbon dioxide produced can be released. ...
Clinical mathematics review - College of Health Professions
... Metric pressure units (the first two below), based on the Pascal, are a little unfamiliar to most of us. 100 kPa 1000 hPa 1 Bar 1013 mBar 760 torr 760 mm Hg 29.9 in Hg ~1000 cm H2O 14.7 psi ...
... Metric pressure units (the first two below), based on the Pascal, are a little unfamiliar to most of us. 100 kPa 1000 hPa 1 Bar 1013 mBar 760 torr 760 mm Hg 29.9 in Hg ~1000 cm H2O 14.7 psi ...
Consortium for Educational Communication
... The compensation point is the amount of light intensity on the light curve where the rate of photosynthesis exactly matches the rate of respiration. At this point, the uptake of CO2 through photosynthetic pathways is exactly matched to the respiratory release of carbon dioxide, and the uptake of O2 ...
... The compensation point is the amount of light intensity on the light curve where the rate of photosynthesis exactly matches the rate of respiration. At this point, the uptake of CO2 through photosynthetic pathways is exactly matched to the respiratory release of carbon dioxide, and the uptake of O2 ...
Aerobic Cellular Respiration class notes.notebook
... Aerobic Cellular Respiration class notes.notebook ...
... Aerobic Cellular Respiration class notes.notebook ...
Reading 1.3 What Is Matter Composed Of?
... 1700s and early 1800s, scientists began noticing that when certain substances, like hydrogen and oxygen, were combined to produce a new substance, the reactants (hydrogen and oxygen) always reacted in the same proportions by mass. In other words, if gram of hydrogen reacted with grams of oxygen, t ...
... 1700s and early 1800s, scientists began noticing that when certain substances, like hydrogen and oxygen, were combined to produce a new substance, the reactants (hydrogen and oxygen) always reacted in the same proportions by mass. In other words, if gram of hydrogen reacted with grams of oxygen, t ...
CH 9 CQ
... b) They evolved before photosynthesis and used electron acceptors other than oxygen. c) Individual enzymes were present before photosynthesis but served other functions, such as amino acid ...
... b) They evolved before photosynthesis and used electron acceptors other than oxygen. c) Individual enzymes were present before photosynthesis but served other functions, such as amino acid ...
Reading 1.3 What Is Matter Composed Of?
... he used. One common reaction that he studied was the reaction between carbon and oxygen. When carbon and oxygen react, they produce two different substances – we’ll call these substances A and B. It turned out that, given the same amount of carbon, forming B always required exactly twice as much oxy ...
... he used. One common reaction that he studied was the reaction between carbon and oxygen. When carbon and oxygen react, they produce two different substances – we’ll call these substances A and B. It turned out that, given the same amount of carbon, forming B always required exactly twice as much oxy ...
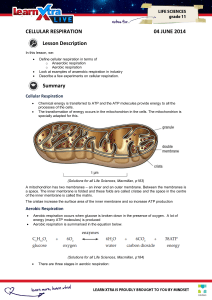
CELLULAR RESPIRATION 04 JUNE 2014 Lesson Description
... carbon dioxide. The hydrogens will be used in oxidative phosphorylation and the carbon dioxide will be breathed out. ...
... carbon dioxide. The hydrogens will be used in oxidative phosphorylation and the carbon dioxide will be breathed out. ...
Cellular Respiration
... One example of respiration in ourselves The lungs absorb oxygen from the air ...
... One example of respiration in ourselves The lungs absorb oxygen from the air ...
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element with symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group on the periodic table and is a highly reactive nonmetallic element and oxidizing agent that readily forms compounds (notably oxides) with most elements. Photosynthesis releases oxygen, and respiration consumes oxygen. Changes in phosphate are related to changes in oxygen concentrations.Oxygen was discovered independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, in Uppsala, in 1773 or earlier, and Joseph Priestley in Wiltshire, in 1774, but Priestley is often given priority because his work was published first. The name oxygen was coined in 1777 by Antoine Lavoisier, whose experiments with oxygen helped to discredit the then-popular phlogiston theory of combustion and corrosion. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς oxys, ""acid"", literally ""sharp"", referring to the sour taste of acids and -γενής -genes, ""producer"", literally ""begetter"", because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition.