Amylase Regulatory interactions during pancreatic development
... How to use this file: 1. Download file to disk. 2. Open File by double clicking. Select “slideshow” option in PowerPoint (PC: press F5). Within the slideshow, point-and-click on arrow, gene, or symbol for exiting to hyperlinked information. Hyperlink information will display when hovering over symbo ...
... How to use this file: 1. Download file to disk. 2. Open File by double clicking. Select “slideshow” option in PowerPoint (PC: press F5). Within the slideshow, point-and-click on arrow, gene, or symbol for exiting to hyperlinked information. Hyperlink information will display when hovering over symbo ...
Multiple Choice Reproduction Review Name: Core: ___ Date
... ___14. An organism's _______ describes its genetic composition. An organism's _______ describes its appearance or observable characteristics. species; heredity phenotype; genotype heredity; species genotype; phenotype ...
... ___14. An organism's _______ describes its genetic composition. An organism's _______ describes its appearance or observable characteristics. species; heredity phenotype; genotype heredity; species genotype; phenotype ...
Mutation
... • Chromosomal mutations affect lots of genes and tend to have a big effect on an organism. • A mutation may break up a gene causing the gene not to work, or it could make a new hybrid gene with a new function (which might turn out to be adaptive – or not). • Translocated genes may also come under th ...
... • Chromosomal mutations affect lots of genes and tend to have a big effect on an organism. • A mutation may break up a gene causing the gene not to work, or it could make a new hybrid gene with a new function (which might turn out to be adaptive – or not). • Translocated genes may also come under th ...
Name - Animo Venice Biology
... – The allele for widow’s peak (W) is dominant over the allele for no widow’s peak (w). ...
... – The allele for widow’s peak (W) is dominant over the allele for no widow’s peak (w). ...
DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA, functioning as the hereditary
... One strand of the exposed DNA, the DNA template, will pair with the free RNA nucleotides, eventually making the mRNA molecule. The opposite exposed strand of DNA does not participate. Free RNA nucleotides in the nucleus pair up with the exposed template strand of the DNA. Remind yourself that in a d ...
... One strand of the exposed DNA, the DNA template, will pair with the free RNA nucleotides, eventually making the mRNA molecule. The opposite exposed strand of DNA does not participate. Free RNA nucleotides in the nucleus pair up with the exposed template strand of the DNA. Remind yourself that in a d ...
Huntington`s disease - patient information
... HD affects the central nervous system. It is caused by a gene expansion on chromosome four. The protein product of the expanded HD gene damages nerve cells in specific areas of the brain that control movements, memory and mood. Genes and chromosomes Our genes can be thought of as a set of instructio ...
... HD affects the central nervous system. It is caused by a gene expansion on chromosome four. The protein product of the expanded HD gene damages nerve cells in specific areas of the brain that control movements, memory and mood. Genes and chromosomes Our genes can be thought of as a set of instructio ...
Slide 1
... genes requires 2phases of study: level of mRNA and analysis of transformants exhibiting interference. ...
... genes requires 2phases of study: level of mRNA and analysis of transformants exhibiting interference. ...
E. coli
... resolution of HJs: CO or no CO gene conversion: one allele turned into the homologous allele (mismatch repair at heteroduplex) ...
... resolution of HJs: CO or no CO gene conversion: one allele turned into the homologous allele (mismatch repair at heteroduplex) ...
Name
... 3. Rubella embryopathy causes infant deafness. This deafness is caused by an infection of the mother during her first trimester. 4. King George III ruled England during the American Revolution. At age 50 he first experienced abdominal pains and constipations, followed by weak limbs, fever, and a fas ...
... 3. Rubella embryopathy causes infant deafness. This deafness is caused by an infection of the mother during her first trimester. 4. King George III ruled England during the American Revolution. At age 50 he first experienced abdominal pains and constipations, followed by weak limbs, fever, and a fas ...
Sex-Linked Inheritance
... Like other genes, sex-linked genes can have dominant and recessive alleles. Recall that females have two X chromosomes, whereas males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. In females, a dominate allele on one X chromosome will mask a recessive allele on the other X chromosome. The situation is ...
... Like other genes, sex-linked genes can have dominant and recessive alleles. Recall that females have two X chromosomes, whereas males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. In females, a dominate allele on one X chromosome will mask a recessive allele on the other X chromosome. The situation is ...
1 - life.illinois.edu
... b. two eggs and two polar bodies. c. three eggs and a polar body. d. four eggs. 30. In animals most inherited simple mutations such as single base changes caused by DNA polymerase errors occur in the a. female germline because their mature eggs are retained from birth till menopause. b. female germl ...
... b. two eggs and two polar bodies. c. three eggs and a polar body. d. four eggs. 30. In animals most inherited simple mutations such as single base changes caused by DNA polymerase errors occur in the a. female germline because their mature eggs are retained from birth till menopause. b. female germl ...
Lect19_TumorSeq
... Mutations in the Tumor Genome • Help us identify important genes for tumorigenesis and cancer progression • Drivers – a.k.a gatekeepers, mutations that cause and accelerate cancers • Passengers – Accidental by-products and thwarted DNA-repair mechanisms • Recurrent mutations on genes or pathways ar ...
... Mutations in the Tumor Genome • Help us identify important genes for tumorigenesis and cancer progression • Drivers – a.k.a gatekeepers, mutations that cause and accelerate cancers • Passengers – Accidental by-products and thwarted DNA-repair mechanisms • Recurrent mutations on genes or pathways ar ...
Genome Variant Calling: A sta>s>cal perspec>ve
... smoking induces G-‐>T transversions) so reasonable priors are harder to obtain • the genome is not diploid! • tumor may not be clonal (so this is not a well posed problem) • different DNA repair me ...
... smoking induces G-‐>T transversions) so reasonable priors are harder to obtain • the genome is not diploid! • tumor may not be clonal (so this is not a well posed problem) • different DNA repair me ...
Before you begin this in-class project, you will need the following
... Transcription is a process in which genes, or segments of DNA which encode for mRNA and ultimately a protein, are “turned on.” When this process of gene activation occurs, the segment of double-stranded DNA containing the gene is unwound and “opened.” A protein named RNA Polymerase II begins transcr ...
... Transcription is a process in which genes, or segments of DNA which encode for mRNA and ultimately a protein, are “turned on.” When this process of gene activation occurs, the segment of double-stranded DNA containing the gene is unwound and “opened.” A protein named RNA Polymerase II begins transcr ...
Genomics Post-ENCODE
... • Hunting for genetic variants that influence gene expression Linking genetic variants to changes in gene expression – regulatory variants or “expression quantitative trait loci” (eQTL) These will be different between tissues ...
... • Hunting for genetic variants that influence gene expression Linking genetic variants to changes in gene expression – regulatory variants or “expression quantitative trait loci” (eQTL) These will be different between tissues ...
DNA Strand 2
... DNA gene sequence code. The nucleotides of the DNA and the mRNA molecules are arranged in a nucleotide code called a codon. Each time a gene is copied onto mRNA it is codon after codon after codon until that segment of code stops. Every time you see three nucleotides together it is called a codon an ...
... DNA gene sequence code. The nucleotides of the DNA and the mRNA molecules are arranged in a nucleotide code called a codon. Each time a gene is copied onto mRNA it is codon after codon after codon until that segment of code stops. Every time you see three nucleotides together it is called a codon an ...
NONRANDOM GENE DISTRIBUTION ON HUMAN CHROMOSOMES
... Human chromosomes are heterogeneous in structure and function. This is the reason for specific banding patterns produced by various chromosome staining techniques. The human genome is a mosaic of isochors and can be partitioned into five families, L1, L2, H1, H2 and H3, characterized by increasing G ...
... Human chromosomes are heterogeneous in structure and function. This is the reason for specific banding patterns produced by various chromosome staining techniques. The human genome is a mosaic of isochors and can be partitioned into five families, L1, L2, H1, H2 and H3, characterized by increasing G ...
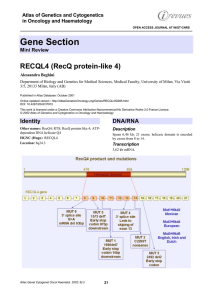
Gene Section RECQL4 (RecQ protein-like 4) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... helicases and contains from aa 476 to 824 an helicase domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
... helicases and contains from aa 476 to 824 an helicase domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
Transcriptome Profiling in Human Congenital Heart Disease
... • The 1000 Genomes project found 38 million SNPs, 1.4 million short insertions or deletions, and more than 14 thousand larger deletions • The NHLBI Exome Sequencing Project targeted 22MBases across 2,440 individuals and found 563,700 variants, 82% of which were novel. They averaged 200 novel, coding ...
... • The 1000 Genomes project found 38 million SNPs, 1.4 million short insertions or deletions, and more than 14 thousand larger deletions • The NHLBI Exome Sequencing Project targeted 22MBases across 2,440 individuals and found 563,700 variants, 82% of which were novel. They averaged 200 novel, coding ...
msb145487-sup-0021-Legends
... performed on the known SFARI ASD genes from different releases. The newly added genes were those from Sep. 2012 to Jul. 2013, representing the growth of our knowledge. Fig. S8. Absolute expression of genes in the 2 groups across 295 brain sections. The median of each group in each brain section (in ...
... performed on the known SFARI ASD genes from different releases. The newly added genes were those from Sep. 2012 to Jul. 2013, representing the growth of our knowledge. Fig. S8. Absolute expression of genes in the 2 groups across 295 brain sections. The median of each group in each brain section (in ...
2016 Final Exam Answer Key
... beads. Describe each enzymatic step needed to measure the mRNA/pre-mRNA ratio in this sample by rtPCR. Describe the following: DNaseI treatment to remove genomic DNA; cDNA synthesis with reverse transcriptase, PCR steps with the oligos outlined above to amplify both mRNA and pre-mRNA B) (2 pts) Use ...
... beads. Describe each enzymatic step needed to measure the mRNA/pre-mRNA ratio in this sample by rtPCR. Describe the following: DNaseI treatment to remove genomic DNA; cDNA synthesis with reverse transcriptase, PCR steps with the oligos outlined above to amplify both mRNA and pre-mRNA B) (2 pts) Use ...
Genetic Disorders Mendelian Disorders
... Growth is often accelerated during mid-childhood, so adults with this syndrome are often very tall. Severe acne may develop in puberty, leading to a pock-marked ...
... Growth is often accelerated during mid-childhood, so adults with this syndrome are often very tall. Severe acne may develop in puberty, leading to a pock-marked ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.