siRNA therapy delivery etc.pptx
... • Basic research – Determining protein function – Easier than a knockout and may be used for partial knockdowns ...
... • Basic research – Determining protein function – Easier than a knockout and may be used for partial knockdowns ...
DNA & Protein Synthesis
... DNA is too precious and must be kept protected within the nucleus. The Cell makes a working "Photocopy" of itself to do the actual work of making proteins. This copy is called Ribonucleic Acid or RNA. RNA differs from DNA in several important ways. 1. It is much smaller 2. It is single-stranded 3. I ...
... DNA is too precious and must be kept protected within the nucleus. The Cell makes a working "Photocopy" of itself to do the actual work of making proteins. This copy is called Ribonucleic Acid or RNA. RNA differs from DNA in several important ways. 1. It is much smaller 2. It is single-stranded 3. I ...
Course Competency Learning Outcomes
... Discussing the progression of discovery from Classical to Modern Genetics. Defining basic concepts of Classical Genetics. Describing Mendel’s experimental design. Utilizing conventional Mendelian genetic terminology. Explaining Mendel’s principles of segregation, and independent assortment. Solving ...
... Discussing the progression of discovery from Classical to Modern Genetics. Defining basic concepts of Classical Genetics. Describing Mendel’s experimental design. Utilizing conventional Mendelian genetic terminology. Explaining Mendel’s principles of segregation, and independent assortment. Solving ...
The complete mitochondrial genome of the demosponge
... amino acid binding site), resulting in a tRNA that recognizes a different codon and binds the corresponding amino acid. Such a process was reported in the mt-genome of the ...
... amino acid binding site), resulting in a tRNA that recognizes a different codon and binds the corresponding amino acid. Such a process was reported in the mt-genome of the ...
End of chapter 14 questions and answers from the text book
... Pieces of DNA which have a sequence where the same base is repeated many times are called ‘slippery’. When ‘slippery’ DNA is copied during replications, errors may occur in copying. Individual bases may be copied more than once. This may give rise to differences in the protein which is produced by t ...
... Pieces of DNA which have a sequence where the same base is repeated many times are called ‘slippery’. When ‘slippery’ DNA is copied during replications, errors may occur in copying. Individual bases may be copied more than once. This may give rise to differences in the protein which is produced by t ...
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population
... KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. ...
... KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. ...
Baby, don`t stop! - Alexander Mankin Lab
... affecting translational accuracy. It is also not clear if any missense or frameshift mutants could be suppressed, but this remains a possibility. Furthermore, not all nonsense mutations are likely to be countered by this approach. This is because competition between release factors and aminoacyl tRN ...
... affecting translational accuracy. It is also not clear if any missense or frameshift mutants could be suppressed, but this remains a possibility. Furthermore, not all nonsense mutations are likely to be countered by this approach. This is because competition between release factors and aminoacyl tRN ...
genetic engineering
... purebred white four o’clocks, the offspring were pink. When offspring of two homozygous parents ...
... purebred white four o’clocks, the offspring were pink. When offspring of two homozygous parents ...
Figure S1 - G3: Genes | Genomes | Genetics
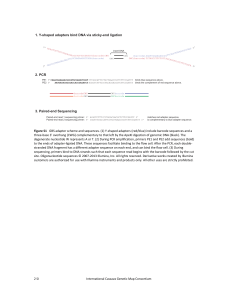
... degenerate nucleotide W represents A or T. (2) During PCR amplification, primers PE1 and PE2 add sequences (bold) to the ends of adapter‐ligated DNA. These sequences facilitate binding to the flow cell. After the PCR, each double‐ stranded DNA fragment has a different adapter sequence on each end, ...
... degenerate nucleotide W represents A or T. (2) During PCR amplification, primers PE1 and PE2 add sequences (bold) to the ends of adapter‐ligated DNA. These sequences facilitate binding to the flow cell. After the PCR, each double‐ stranded DNA fragment has a different adapter sequence on each end, ...
Genetic Testing in Primary Care - Genetics in Primary Care Institute
... • DNA – Chemical structure made up of four bases (A, C, G, and T). o DNA is converted into RNA and then translated into protein. o DNA bases are “read” in groups of three. o Each codon (three bases) is specific for a single amino acid. • Gene – A stretch of DNA sequence needed to make a functional p ...
... • DNA – Chemical structure made up of four bases (A, C, G, and T). o DNA is converted into RNA and then translated into protein. o DNA bases are “read” in groups of three. o Each codon (three bases) is specific for a single amino acid. • Gene – A stretch of DNA sequence needed to make a functional p ...
Chapter 10: Mendel`s Laws of Heredity
... Metaphase II: Sister chromatids line up in the middle of the cell ...
... Metaphase II: Sister chromatids line up in the middle of the cell ...
FEATURE: A structure, characteristic, or behavior of an organism
... Together they constitute a gene. Summary • Nuclei contain chromosomes. • Chromosomes come in almost identical pairs. • Chromosomes have specific active locations called alleles. • The two alleles in identical locations on paired chromosomes constitute a gene ...
... Together they constitute a gene. Summary • Nuclei contain chromosomes. • Chromosomes come in almost identical pairs. • Chromosomes have specific active locations called alleles. • The two alleles in identical locations on paired chromosomes constitute a gene ...
Improving site-directed RNA editing by screening RNA editing
... deaminases that act on RNA (ADAR). ADARs are an evolutionarily conserved family of enzymes that convert adenosines to inosines within mRNA transcripts. Because inosine is read as guanosine during translation, RNA editing may lead to recoding during translation, resulting in proteins with altered fun ...
... deaminases that act on RNA (ADAR). ADARs are an evolutionarily conserved family of enzymes that convert adenosines to inosines within mRNA transcripts. Because inosine is read as guanosine during translation, RNA editing may lead to recoding during translation, resulting in proteins with altered fun ...
II. The selected examples
... right, up to and including gene 1.3 are early genes. The genes to the right of 1.3 are transcribed after few minutes’ delay – the late genes. 4. Nonsense and temperature-sensitive mutations were used to identify which of the early-gene products is responsible for turning on the late genes. It turns ...
... right, up to and including gene 1.3 are early genes. The genes to the right of 1.3 are transcribed after few minutes’ delay – the late genes. 4. Nonsense and temperature-sensitive mutations were used to identify which of the early-gene products is responsible for turning on the late genes. It turns ...
Spring 2015-Chapter 8
... consuming fish or shellfish that contain high levels of the compound. Ingesting high levels of mercury is associated with permanent brain damage and kidney damage. During pregnancy, the harmful effects of mercury may also be passed to the fetus, causing developmental problems. As such, the Food and ...
... consuming fish or shellfish that contain high levels of the compound. Ingesting high levels of mercury is associated with permanent brain damage and kidney damage. During pregnancy, the harmful effects of mercury may also be passed to the fetus, causing developmental problems. As such, the Food and ...
AP Biology Exam Review T2
... Role of histone modification/DNA methylation on eukaryotic gene expression Explain how enhancers and activator interact with transcription factors to affect gene expression Describe how proteins can be activated, processed and degraded. Describe the proteasomes action and role in gene expression Des ...
... Role of histone modification/DNA methylation on eukaryotic gene expression Explain how enhancers and activator interact with transcription factors to affect gene expression Describe how proteins can be activated, processed and degraded. Describe the proteasomes action and role in gene expression Des ...
Name
... The number and location of bones in many fossil vertebrates is similar to living vertebrates. How would biologist explain this fact? __________________________________________________________________ ...
... The number and location of bones in many fossil vertebrates is similar to living vertebrates. How would biologist explain this fact? __________________________________________________________________ ...
Sex chromosome
... the X and Y •~12 genes on X and Y •regions allow X and Y to pair during meiosis •pseudoautosomal genes are also transcribed from the inactivated X! •both males and females have 2 active copies of these genes ...
... the X and Y •~12 genes on X and Y •regions allow X and Y to pair during meiosis •pseudoautosomal genes are also transcribed from the inactivated X! •both males and females have 2 active copies of these genes ...
“What is that, where is it found and why can it live there
... A fundamental property of living matter is reproduction – the formation of new individuals through the transmission of the genetic information contained within the parent organism’s DNA. The type of reproductive cycle, fertilisation and development of the zygote of any particular species is linked t ...
... A fundamental property of living matter is reproduction – the formation of new individuals through the transmission of the genetic information contained within the parent organism’s DNA. The type of reproductive cycle, fertilisation and development of the zygote of any particular species is linked t ...
FEBS Lett. 586, 2043-2048 - iSSB
... to the aminoacyl-tRNA concentration [44]. As this essay is about genome-scale design, translational bias at the gene and at the codon levels will not be discussed further. These biases alter strand composition and codon choice [46,47]. In turn, both codon and mutational biases shape the ability of t ...
... to the aminoacyl-tRNA concentration [44]. As this essay is about genome-scale design, translational bias at the gene and at the codon levels will not be discussed further. These biases alter strand composition and codon choice [46,47]. In turn, both codon and mutational biases shape the ability of t ...
Heredity
... • The study of how traits are passed from parent to offspring by looking at genes • Genes are small sections of DNA on a chromosomes that has information about a trait • Each chromosome has a gene for the same trait (eye color from mom & eye color from dad) • Traits are determined by alleles on the ...
... • The study of how traits are passed from parent to offspring by looking at genes • Genes are small sections of DNA on a chromosomes that has information about a trait • Each chromosome has a gene for the same trait (eye color from mom & eye color from dad) • Traits are determined by alleles on the ...
Biotechnology: Tools and Techniques of the Trade
... At the end of class today, you will be able to: Explain what a restriction enzyme is and what role they play in the cell Explain how restriction enzymes have been used by biologists as a tool in the manipulation of DNA ...
... At the end of class today, you will be able to: Explain what a restriction enzyme is and what role they play in the cell Explain how restriction enzymes have been used by biologists as a tool in the manipulation of DNA ...
The History of Molecular Genetics
... Won the Nobel prize in medicine in 1962 for their discovery Maurice Wilkins was also included in winning the Nobel prize – Who was excluded??? ...
... Won the Nobel prize in medicine in 1962 for their discovery Maurice Wilkins was also included in winning the Nobel prize – Who was excluded??? ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.