Ascona B-DNA Consortium
... • Stores genetic code as a linear sequence of bases • ≈ 20 Å in diameter ...
... • Stores genetic code as a linear sequence of bases • ≈ 20 Å in diameter ...
Decoding Genetics - Flinn Scientific
... RNA polymerase II “reads” the DNA strand and creates a strand of messenger RNA (mRNA), which then travels out through the nuclear membrane to a ribosome in the cytoplasm of the cell. The ribosome binds to the mRNA strand at the start codon. The start codon is a three base-pair nucleotide sequence—ad ...
... RNA polymerase II “reads” the DNA strand and creates a strand of messenger RNA (mRNA), which then travels out through the nuclear membrane to a ribosome in the cytoplasm of the cell. The ribosome binds to the mRNA strand at the start codon. The start codon is a three base-pair nucleotide sequence—ad ...
View PDF
... It is just the way imposed by the genetic code in the deep inner core of tissue cells in all organisms. A series of defined triplets in the DNA encodes for a precise combination of amino acids at the protein level. ATGGATTGCGTG (DNA or gene) changes to AUGGAUUGCGUG (RNA, single gene product) to enco ...
... It is just the way imposed by the genetic code in the deep inner core of tissue cells in all organisms. A series of defined triplets in the DNA encodes for a precise combination of amino acids at the protein level. ATGGATTGCGTG (DNA or gene) changes to AUGGAUUGCGUG (RNA, single gene product) to enco ...
Inheritance Patterns Simple dominance, incomplete dominance
... Simple Dominance: Using the terms We use capital letters for dominant alleles We use lower case letters for recessive alleles The letters for the alleles should be the same (e.g. F for purple flowers allele, f for white flowers allele) ...
... Simple Dominance: Using the terms We use capital letters for dominant alleles We use lower case letters for recessive alleles The letters for the alleles should be the same (e.g. F for purple flowers allele, f for white flowers allele) ...
Review Relay 1 Cell Reproduction 1. How is mitosis and cell
... _________________________ segment of DNA that codes for a trait _________________________ building block of DNA _________________________ bonds that hold bases together _________________________ bonds that hold backbone together _________________________ guys who discovered the double helix 2. Repli ...
... _________________________ segment of DNA that codes for a trait _________________________ building block of DNA _________________________ bonds that hold bases together _________________________ bonds that hold backbone together _________________________ guys who discovered the double helix 2. Repli ...
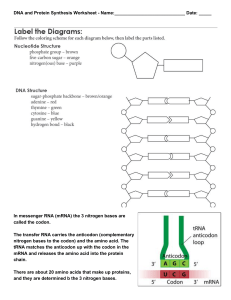
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... and DNA. 1. RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose. 2. RNA is generally single-stranded, instead of ...
... and DNA. 1. RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose. 2. RNA is generally single-stranded, instead of ...
Three subunits of the RNA polymerase II
... The G1G2 and G1G3 genes are identical to SRB10/SSN8 and UME5/SRB11/SSN3, (10-12), which encode cyclin C and a cyclin C-dependent kinase. These two proteins were also recently shown to be subunits of the RNA polymerase II mediator complex (11,13). It should be noted that one of our gig2 complementing ...
... The G1G2 and G1G3 genes are identical to SRB10/SSN8 and UME5/SRB11/SSN3, (10-12), which encode cyclin C and a cyclin C-dependent kinase. These two proteins were also recently shown to be subunits of the RNA polymerase II mediator complex (11,13). It should be noted that one of our gig2 complementing ...
BIOLOGY (Theory)
... In higher plants, seeds and some other vegetative reproductive structures serve as means to tide over periods of stress besides helping in dispersal – they germinate to form new plants under favourable moisture and temperature conditions. They do so by reducing their metabolic activity and going int ...
... In higher plants, seeds and some other vegetative reproductive structures serve as means to tide over periods of stress besides helping in dispersal – they germinate to form new plants under favourable moisture and temperature conditions. They do so by reducing their metabolic activity and going int ...
rabbit - Ensembl Mobile Site
... and the remaining unique set of transcript models were clustered into multitranscript genes where each transcript in a gene has at least one coding exon that overlaps a coding exon from another transcript within the same gene. The final gene set of 19,005 genes included 681 genes with at least one t ...
... and the remaining unique set of transcript models were clustered into multitranscript genes where each transcript in a gene has at least one coding exon that overlaps a coding exon from another transcript within the same gene. The final gene set of 19,005 genes included 681 genes with at least one t ...
Bacterial Handout #3 Genetics 200A September 24, 2012 Genetic
... The decision made by λ whether to enter the lytic or lysogenic program is subject to environmental conditions during infection. In particular, low MOI favors lytic growth whereas high MOI favors the lysogenic program. Thus, in the early rounds of infection during plaqe growth, the conditions favo ...
... The decision made by λ whether to enter the lytic or lysogenic program is subject to environmental conditions during infection. In particular, low MOI favors lytic growth whereas high MOI favors the lysogenic program. Thus, in the early rounds of infection during plaqe growth, the conditions favo ...
What is RNA splicing?
... Thus one gene can encode more than one protein. The proteins are similar but not identical and may have distinct properties. This is important in complex organisms ...
... Thus one gene can encode more than one protein. The proteins are similar but not identical and may have distinct properties. This is important in complex organisms ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... Molecular Biology Lecture 15 Chapter 8 Major Shifts in Bacterial Transcription ...
... Molecular Biology Lecture 15 Chapter 8 Major Shifts in Bacterial Transcription ...
Fundamentals of Biotechnology
... that can develop into any type of specialized cell) from embryos ...
... that can develop into any type of specialized cell) from embryos ...
File
... Practical Application of HardyWeinberg Equations • If you know the frequency of the recessive phenotype (aa) you can calculate the percent of the population that are carriers (Aa) and that are AA. ...
... Practical Application of HardyWeinberg Equations • If you know the frequency of the recessive phenotype (aa) you can calculate the percent of the population that are carriers (Aa) and that are AA. ...
Implications of the Human Genome Project for Medical
... as quickly as possible and has identified more than 2 million of these single nucleotide polymorphisms. Of particular interest are those common variants that influence gene function. A powerful set of technologies for studying gene expression is being developed and explored.17 These methodologies, w ...
... as quickly as possible and has identified more than 2 million of these single nucleotide polymorphisms. Of particular interest are those common variants that influence gene function. A powerful set of technologies for studying gene expression is being developed and explored.17 These methodologies, w ...
Translation
... Two major stages involved: • The first stage is called transcription – The 2 strands of the DNA molecule unwind and mRNA copies the genetic code (letters A, C, G and T) from DNA, the master molecule. ...
... Two major stages involved: • The first stage is called transcription – The 2 strands of the DNA molecule unwind and mRNA copies the genetic code (letters A, C, G and T) from DNA, the master molecule. ...
SC435 Genetics Seminar
... • Most traits that vary in the population, including common human diseases with the genetic component, are complex traits • Genetic architecture of a complex trait = specific effects and combined interactions of all genetic and environmental factors ...
... • Most traits that vary in the population, including common human diseases with the genetic component, are complex traits • Genetic architecture of a complex trait = specific effects and combined interactions of all genetic and environmental factors ...
Document
... • In the 20th century, geneticists have extended Mendelian principles not only to diverse organisms, but also to patterns of inheritance more complex than Mendel described. • In fact, Mendel had the good fortune to choose a system that was relatively simple genetically. – Each gene has only two all ...
... • In the 20th century, geneticists have extended Mendelian principles not only to diverse organisms, but also to patterns of inheritance more complex than Mendel described. • In fact, Mendel had the good fortune to choose a system that was relatively simple genetically. – Each gene has only two all ...
solicitud de presupuestos de imprenta
... 5Ht2cr splice variants. PWS-ICdel mice were generally hypolocomotor compared to wild type littermates, but also showed greater motoric skill on the rotarod test. There were no apparent difference in sensory motor gating, nor were there any differences in emotional behaviour in the open field test. C ...
... 5Ht2cr splice variants. PWS-ICdel mice were generally hypolocomotor compared to wild type littermates, but also showed greater motoric skill on the rotarod test. There were no apparent difference in sensory motor gating, nor were there any differences in emotional behaviour in the open field test. C ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.