Ninth Grade Biology Unit 3 – Growth and Heredity Asexual and
... “Sticky Bars”- Teacher puts multiple choice questions on the board one at a time using Powerpoint or electronic whiteboard. Students write their answers anonymously on sticky notes and the teacher collects them and places them on the board to show the responses in a bar graph format. (Electronic vot ...
... “Sticky Bars”- Teacher puts multiple choice questions on the board one at a time using Powerpoint or electronic whiteboard. Students write their answers anonymously on sticky notes and the teacher collects them and places them on the board to show the responses in a bar graph format. (Electronic vot ...
Document
... • The geometric orientations of the catalytic residues are similar between families, despite different protein folds. • The linear arrangements of the catalytic residues reflect different family relationships. For example the catalytic triad in the chymotrypsin clan (SA) is ordered HDS, but is order ...
... • The geometric orientations of the catalytic residues are similar between families, despite different protein folds. • The linear arrangements of the catalytic residues reflect different family relationships. For example the catalytic triad in the chymotrypsin clan (SA) is ordered HDS, but is order ...
9. Axis Specification in Drosophila
... early in development cell fate depends on interactions among protein gradients specification is flexible; it can alter in response to signals from other cells eventually cells undergo transition from loose commitment to irreversible determination The transition from specification to dete ...
... early in development cell fate depends on interactions among protein gradients specification is flexible; it can alter in response to signals from other cells eventually cells undergo transition from loose commitment to irreversible determination The transition from specification to dete ...
Unusual Pattern Detection in DNA Database Using KMP Algorithm
... DNA is an acronym for the molecule deoxyribonucleic acid. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is called a double helix because it is a double-stranded molecule. DNA contains three components: deoxyribose (a five-carbon sugar), a series of phosphate groups, and four nitrogenous bases, (nitrogen compounds tha ...
... DNA is an acronym for the molecule deoxyribonucleic acid. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is called a double helix because it is a double-stranded molecule. DNA contains three components: deoxyribose (a five-carbon sugar), a series of phosphate groups, and four nitrogenous bases, (nitrogen compounds tha ...
Monohybrid Problems
... In dinosaurs, the “factor” (as Mendel called it) or gene (S) for sharp teeth is dominant over the “factor” or gene (s) for dull teeth. Cross a heterozygous sharp toothed dinosaur with a dulltoothed dinosaur to produce the F1 (first generation) offspring. ...
... In dinosaurs, the “factor” (as Mendel called it) or gene (S) for sharp teeth is dominant over the “factor” or gene (s) for dull teeth. Cross a heterozygous sharp toothed dinosaur with a dulltoothed dinosaur to produce the F1 (first generation) offspring. ...
sex in drosophila
... are sterile, many menstruate regularly and are fertile. The incidence of mental retardation among triple-X females is slightly greater than that in the general population, but most XXX females have normal intelligence. Much rarer are females whose cells contain four or five X chromosomes. These fema ...
... are sterile, many menstruate regularly and are fertile. The incidence of mental retardation among triple-X females is slightly greater than that in the general population, but most XXX females have normal intelligence. Much rarer are females whose cells contain four or five X chromosomes. These fema ...
Build-a-Bug - Wando High School
... Before the synthesis of a protein begins, the corresponding RNA molecule is produced by RNA transcription. One strand of the DNA double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different ...
... Before the synthesis of a protein begins, the corresponding RNA molecule is produced by RNA transcription. One strand of the DNA double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different ...
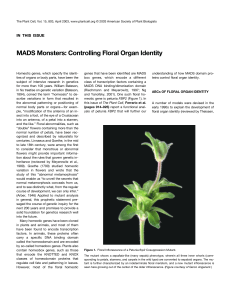
MADS Monsters: Controlling Floral Organ Identity
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
Build-a-Bug - Wando High School
... Before the synthesis of a protein begins, the corresponding RNA molecule is produced by RNA transcription. One strand of the DNA double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different ...
... Before the synthesis of a protein begins, the corresponding RNA molecule is produced by RNA transcription. One strand of the DNA double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different ...
Genetic Mutation
... Aneuploidy leads to a number of syndromes in humans. For example trisomy 21 leads to Down syndrome, characterized by mental retardation and other abnormalities. Aneuploidy involving the sex chromosomes is common. XYY males are normal but XXY males and XXXY males have a syndrome called Klinefelter sy ...
... Aneuploidy leads to a number of syndromes in humans. For example trisomy 21 leads to Down syndrome, characterized by mental retardation and other abnormalities. Aneuploidy involving the sex chromosomes is common. XYY males are normal but XXY males and XXXY males have a syndrome called Klinefelter sy ...
Layman`s Crash Course in Ball Python Genetics
... Most of the time, enough of these genes match up in such a way as to create what we call a “normal” or “wild type” appearance. Even within this “normal” range, there are so many different genes at work, and in so many different combinations, that the appearance of the animals will always have some ...
... Most of the time, enough of these genes match up in such a way as to create what we call a “normal” or “wild type” appearance. Even within this “normal” range, there are so many different genes at work, and in so many different combinations, that the appearance of the animals will always have some ...
7.014 Problem Set 3
... i. Double stranded DNA where both strands are labeled ii. Double stranded DNA where one strand is labeled iii. Double stranded DNA where neither strand is labled Semi-conservative replication was only one of the models of DNA replication proposed after the discovery of DNA structure. One of the ot ...
... i. Double stranded DNA where both strands are labeled ii. Double stranded DNA where one strand is labeled iii. Double stranded DNA where neither strand is labled Semi-conservative replication was only one of the models of DNA replication proposed after the discovery of DNA structure. One of the ot ...
LECTURE 1 - Berkeley MCB
... F2: 9 purple (A- B-): 7 white (3 A- bb: 3 aa B-: 1 aa bb) RATIO: 9:7 What if a particular allele at one gene masks the effects on another gene determining a particular trait? This is called epistasis, and the masking allele is epistatic to the other and can be recessive or dominant. ---------------- ...
... F2: 9 purple (A- B-): 7 white (3 A- bb: 3 aa B-: 1 aa bb) RATIO: 9:7 What if a particular allele at one gene masks the effects on another gene determining a particular trait? This is called epistasis, and the masking allele is epistatic to the other and can be recessive or dominant. ---------------- ...
DNA Technology and Genomes
... impact, unknown effect on other organisms, loss of flora and fauna biodiversity Access and Intellectual Property: domination of world food production by few companies; increased dependence on industrial nations by developing countries; Ethics: violation of natural organisms’ intrinsic values; tamper ...
... impact, unknown effect on other organisms, loss of flora and fauna biodiversity Access and Intellectual Property: domination of world food production by few companies; increased dependence on industrial nations by developing countries; Ethics: violation of natural organisms’ intrinsic values; tamper ...
Mendelian Genetics
... the F1 generation. The second generation offspring are called the F2 generation. Dominant traits are observed in the organism’s characteristics if present. Recessive traits are traits that are hidden if the dominate trait is present. Recessive traits can only be seen in the organisms if both alleles ...
... the F1 generation. The second generation offspring are called the F2 generation. Dominant traits are observed in the organism’s characteristics if present. Recessive traits are traits that are hidden if the dominate trait is present. Recessive traits can only be seen in the organisms if both alleles ...
Genome editing
... associations with ~200 diseases. • How do these SNPs contribute to disease? • Which genes are contributing to disease? How? ...
... associations with ~200 diseases. • How do these SNPs contribute to disease? • Which genes are contributing to disease? How? ...
Incomplete lineage sorting and other `rogue` data fell the tree of life
... had to take place for this to occur.14 Furthermore, this idea contributes nothing to the evolutionary resolution of the numerous genomic regions across the diverse spectrum of life that show complete mosaics of DNA patterns. A good example of how ILS plagues the evolutionary paradigm can be found in ...
... had to take place for this to occur.14 Furthermore, this idea contributes nothing to the evolutionary resolution of the numerous genomic regions across the diverse spectrum of life that show complete mosaics of DNA patterns. A good example of how ILS plagues the evolutionary paradigm can be found in ...
The HNF-3 Gene Family of Transcription Factors in Mice: Gene
... mouse HNF-3 genes are small and contain only two or 1991, and references therein). The HNF -3 proteins were three (HNF -aß) exons with conserved intron-exon first identified by their ability to bind to important proboundaries. The proximal promoter of tbe mouse HNF- moter elements in the Ql-antitryp ...
... mouse HNF-3 genes are small and contain only two or 1991, and references therein). The HNF -3 proteins were three (HNF -aß) exons with conserved intron-exon first identified by their ability to bind to important proboundaries. The proximal promoter of tbe mouse HNF- moter elements in the Ql-antitryp ...
Biology EOCT Glossary Review by Domain Cells SB1 This category
... ADP This is short for adenosine diphosphate. An organic compound that is composed of adenosine and two phosphate groups. With the addition of another phosphate group, it is converted to ATP for the storage of energy during cell metabolism. It then forms again, from ATP, when a phosphate group is rem ...
... ADP This is short for adenosine diphosphate. An organic compound that is composed of adenosine and two phosphate groups. With the addition of another phosphate group, it is converted to ATP for the storage of energy during cell metabolism. It then forms again, from ATP, when a phosphate group is rem ...
Questions - Kettering Science Academy
... (a) Scientists investigated one aspect of diet on the growth of six people. When the six people were babies, they had different masses of calcium in their diets. The height of each person was recorded when they were 10 and 18 years old. The results are shown in the table. ...
... (a) Scientists investigated one aspect of diet on the growth of six people. When the six people were babies, they had different masses of calcium in their diets. The height of each person was recorded when they were 10 and 18 years old. The results are shown in the table. ...
LINKAGE DATA a, the
... of Emerson a) required both methionine and histidine for normal growth. The histidine requirement resulted from a second mutation located a few units distal to the me-2 locus. It is proposed to designate the me-2 mutant isolation nlnnber P143m and the u P143h. Further information was sought for two ...
... of Emerson a) required both methionine and histidine for normal growth. The histidine requirement resulted from a second mutation located a few units distal to the me-2 locus. It is proposed to designate the me-2 mutant isolation nlnnber P143m and the u P143h. Further information was sought for two ...
Transcription and Translation ppt
... actually attach to the correct protein. The anticodon( tRNA) binds by complimentary base pairing to the nucleotides of the codon. Example: if the codon on a mRNA is UUU, a tRNA with an AAA anticodon will bind to it. The ribosome links adjacent amino acids with a peptide bond, causing the amino a ...
... actually attach to the correct protein. The anticodon( tRNA) binds by complimentary base pairing to the nucleotides of the codon. Example: if the codon on a mRNA is UUU, a tRNA with an AAA anticodon will bind to it. The ribosome links adjacent amino acids with a peptide bond, causing the amino a ...
RNA_and_Protein_Synthesis
... – Messenger RNA = Carry copies of the “instructions” or “messages” to assemble amino acids into proteins ...
... – Messenger RNA = Carry copies of the “instructions” or “messages” to assemble amino acids into proteins ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.