Synthetic approaches to transcription factor
... transcription factor regulation and function Tim Johnstone BIOL1220 Spring 2010 ...
... transcription factor regulation and function Tim Johnstone BIOL1220 Spring 2010 ...
How Inheritance Works In Swine
... phosphate, sugar, and nitrogenous base) attached end-to-end in a twisting, double-spiral shape. These nucleotides differ only in the type of nitrogenous base they contain. Since five different bases were found, there exist only five different nucleotides. It was later discovered that the expression ...
... phosphate, sugar, and nitrogenous base) attached end-to-end in a twisting, double-spiral shape. These nucleotides differ only in the type of nitrogenous base they contain. Since five different bases were found, there exist only five different nucleotides. It was later discovered that the expression ...
11-2Probability and PunneTt Squares
... Heterozygous- Organisms that have two different alleles for the same trait organisms are hybrid for a particular trait. One allele for black fur and one allele for white fur ...
... Heterozygous- Organisms that have two different alleles for the same trait organisms are hybrid for a particular trait. One allele for black fur and one allele for white fur ...
Construction of the optimal single gene ranking
... to approximately 20 genes per GO group. Based on this, we report subsequent results using only those GO groups containing 20 or more genes. We also excluded GO groups of larger than 1000 genes in order to capture reasonably specific gene properties; however, this criterion had no noticeable effect o ...
... to approximately 20 genes per GO group. Based on this, we report subsequent results using only those GO groups containing 20 or more genes. We also excluded GO groups of larger than 1000 genes in order to capture reasonably specific gene properties; however, this criterion had no noticeable effect o ...
*Exam3 2015 key Revised
... B) E. coli chromosome. C) messenger RNA. D) plasmid. E) yeast “ARS” sequence. Circle the correct answer. 34. [2 points] The PCR reaction mixture does not include: A) oligonucleotide primer(s). B) all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates. C) DNA containing the sequence to be amplified. D) DNA ligase. E ...
... B) E. coli chromosome. C) messenger RNA. D) plasmid. E) yeast “ARS” sequence. Circle the correct answer. 34. [2 points] The PCR reaction mixture does not include: A) oligonucleotide primer(s). B) all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates. C) DNA containing the sequence to be amplified. D) DNA ligase. E ...
Document
... *Animation of gene expression: http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072835125/student_view0/animations.html# ...
... *Animation of gene expression: http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072835125/student_view0/animations.html# ...
Chapter 14 Mendel and the Gene
... They reflect the mechanism by which specific alleles are expressed in phenotype and do not involve the ability of a one allele to subdue another at the level of the DNA They do not determine the relative abundance of alleles in the population Multiple alleles (Fig 14.10) Pleiotropy - the ability of ...
... They reflect the mechanism by which specific alleles are expressed in phenotype and do not involve the ability of a one allele to subdue another at the level of the DNA They do not determine the relative abundance of alleles in the population Multiple alleles (Fig 14.10) Pleiotropy - the ability of ...
An in-silico functional genomics resource: Targeted re
... • 1,846 sequences (RIKEN FL-cDNA and some genes of interest) • MySelect capture array (solution based hybridization) • Designed 120-mer probes (60-bp overlap design) ...
... • 1,846 sequences (RIKEN FL-cDNA and some genes of interest) • MySelect capture array (solution based hybridization) • Designed 120-mer probes (60-bp overlap design) ...
Mendel`s Work
... • Genetics is the study of heredity • Some examples of traits are: eye color, height, nose shape, etc! ...
... • Genetics is the study of heredity • Some examples of traits are: eye color, height, nose shape, etc! ...
7.014 Problem Set 3
... that you studied (M, I and T) back to MIT with you so you can investigate them further. From your initial experiments characterizing how the species obtain energy (Problem Set 1), you noticed that the two autotrophs are capable of surviving in the absence of CO2 if glucose is provided. This suggests ...
... that you studied (M, I and T) back to MIT with you so you can investigate them further. From your initial experiments characterizing how the species obtain energy (Problem Set 1), you noticed that the two autotrophs are capable of surviving in the absence of CO2 if glucose is provided. This suggests ...
Organelle genome evolution
... be added, together with other hypotheses, such as Muller’s ratchet and the high mutagenicity of free radicals1, to selective pressures that, in some but not all lineages, contribute to genetic erosion of organelles. However, their hypothesis is restricted to: (1) uniparentally inherited organelles, ...
... be added, together with other hypotheses, such as Muller’s ratchet and the high mutagenicity of free radicals1, to selective pressures that, in some but not all lineages, contribute to genetic erosion of organelles. However, their hypothesis is restricted to: (1) uniparentally inherited organelles, ...
cognitive measures (set-shifting)
... Treatment outcome will also be investigated in relation to genotypes and phenotypes. Preliminary results concerning Dopamine Receptor D2 (DRD2) gene are presented. ...
... Treatment outcome will also be investigated in relation to genotypes and phenotypes. Preliminary results concerning Dopamine Receptor D2 (DRD2) gene are presented. ...
Transcription
... 2. RNAP II, in nucleoplasm, makes mRNA precursors 3. RNAP III, nucleoplasm, 5S rRNA, tRNA, small RNAs Up to 600kD, up to 12 subunits, 5 of these present in all 3 RNAP types RNAP II has extraordinary C-terminal domain, CTD 52 repeats of PTSPSYS, 50 Ser are phosphorylated Transcription is only initiat ...
... 2. RNAP II, in nucleoplasm, makes mRNA precursors 3. RNAP III, nucleoplasm, 5S rRNA, tRNA, small RNAs Up to 600kD, up to 12 subunits, 5 of these present in all 3 RNAP types RNAP II has extraordinary C-terminal domain, CTD 52 repeats of PTSPSYS, 50 Ser are phosphorylated Transcription is only initiat ...
NAME ______ AVERILL PARK HS THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT
... 8. Record the letters (genes) you have obtained for your baby Reebop in Table 1: Genotype & Phenotype Data. For example, if you have one chromosome with the letter A and another with the letter a, the genotype is Aa. 9. Use the Decoding Key (Table 2) to decide what characteristics (phenotype) your b ...
... 8. Record the letters (genes) you have obtained for your baby Reebop in Table 1: Genotype & Phenotype Data. For example, if you have one chromosome with the letter A and another with the letter a, the genotype is Aa. 9. Use the Decoding Key (Table 2) to decide what characteristics (phenotype) your b ...
Leukaemia Section B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia (B-PLL) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Patients often present with advanced stage disease. B-PLL is characterized by high white blood cell counts and splenomegaly without adenopathy. Bone marrow infiltration pattern is either diffuse or mixed. Blood data: elevated white blood cell counts with prolymphocytes representing more than 55% of ...
... Patients often present with advanced stage disease. B-PLL is characterized by high white blood cell counts and splenomegaly without adenopathy. Bone marrow infiltration pattern is either diffuse or mixed. Blood data: elevated white blood cell counts with prolymphocytes representing more than 55% of ...
Lecture 11 Beyond Mendel
... Gene Interactions and Modified Mendelian Ratios • Phenotypes result from complex interactions of molecules under genetic control. Using genetic analysis one can often detect the patterns of these interactions. For example: • a. In the dihybrid cross AaBb´ x AaBb, nine genotypes will result. If each ...
... Gene Interactions and Modified Mendelian Ratios • Phenotypes result from complex interactions of molecules under genetic control. Using genetic analysis one can often detect the patterns of these interactions. For example: • a. In the dihybrid cross AaBb´ x AaBb, nine genotypes will result. If each ...
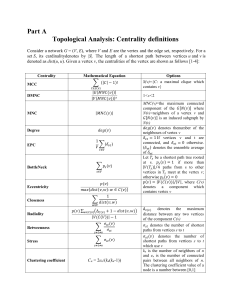
Part B Constraint-based Analysis
... calculating the range of numerical values for every reaction flux in a network. This is carried out byoptimizing for a particular objective, while still satisfying the given constraints set on the system. pFBAis used to label all metabolic genes based on its ability to contribute to the optimal grow ...
... calculating the range of numerical values for every reaction flux in a network. This is carried out byoptimizing for a particular objective, while still satisfying the given constraints set on the system. pFBAis used to label all metabolic genes based on its ability to contribute to the optimal grow ...
Editable PPT - Science Prof Online
... • Images used on this resource, and on the SPO website are, wherever possible, credited and linked to their source. Any words underlined and appearing in blue are links that can be clicked on for more information. PPT files must be viewed in slide show mode to use the hyperlinks directly. • Several ...
... • Images used on this resource, and on the SPO website are, wherever possible, credited and linked to their source. Any words underlined and appearing in blue are links that can be clicked on for more information. PPT files must be viewed in slide show mode to use the hyperlinks directly. • Several ...
Cauliflower mosaic virus: still in the news
... each other for interaction with P6. The interactions between L24/ eIF3 and P6 are crucial for the translational transactivation mechanism, since CaMV is no longer infectious when point mutations in P6 impair these interactions. Park et al. (2001) have demonstrated by pull-down assays that P6 interac ...
... each other for interaction with P6. The interactions between L24/ eIF3 and P6 are crucial for the translational transactivation mechanism, since CaMV is no longer infectious when point mutations in P6 impair these interactions. Park et al. (2001) have demonstrated by pull-down assays that P6 interac ...
Recognition of Human Genes by Stochastic Parsing 1 Introduction
... patterns during the parsing process, but searching the motif patterns after/before finding the coding regions cannot directly affect the parsing process itself. Experimental results have shown that this method reasonably finds and annotates the motifs in the exons in the DNA sequence of human. ...
... patterns during the parsing process, but searching the motif patterns after/before finding the coding regions cannot directly affect the parsing process itself. Experimental results have shown that this method reasonably finds and annotates the motifs in the exons in the DNA sequence of human. ...
Leukaemia Section t(9;12)(q34;p13) ETV6/ABL1 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... The ETV6 gene encodes a transcription factor frequently rearranged in myeloid and lymphoid leukemias. DNA/RNA The ETV6 gene spans a region of less than 250 kb at band 12p13.1 and consists of 8 exons. There are two start codons, one (exon 1a starting at codon 1) located at the beginning of the gene a ...
... The ETV6 gene encodes a transcription factor frequently rearranged in myeloid and lymphoid leukemias. DNA/RNA The ETV6 gene spans a region of less than 250 kb at band 12p13.1 and consists of 8 exons. There are two start codons, one (exon 1a starting at codon 1) located at the beginning of the gene a ...
Document
... from plants that have been grazed alerts surrounding trees to step up their chemical ...
... from plants that have been grazed alerts surrounding trees to step up their chemical ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.